Boiler efficiency measures how effectively a boiler converts fuel into heat for water or steam, while furnace efficiency focuses on converting fuel into heat for air in a heating system. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right equipment for optimal energy savings and comfort in your home.
Table of Comparison
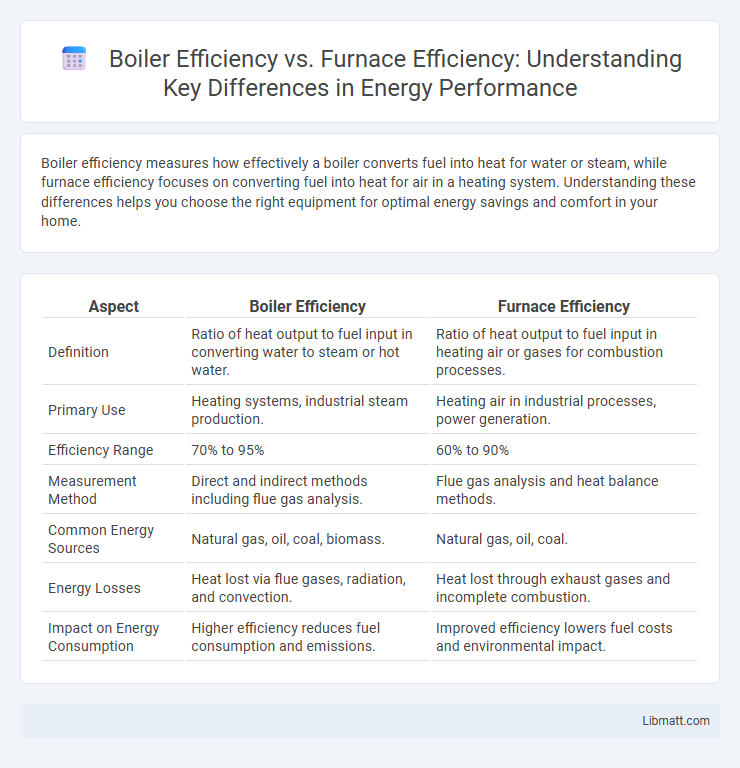
| Aspect | Boiler Efficiency | Furnace Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ratio of heat output to fuel input in converting water to steam or hot water. | Ratio of heat output to fuel input in heating air or gases for combustion processes. |
| Primary Use | Heating systems, industrial steam production. | Heating air in industrial processes, power generation. |
| Efficiency Range | 70% to 95% | 60% to 90% |
| Measurement Method | Direct and indirect methods including flue gas analysis. | Flue gas analysis and heat balance methods. |
| Common Energy Sources | Natural gas, oil, coal, biomass. | Natural gas, oil, coal. |
| Energy Losses | Heat lost via flue gases, radiation, and convection. | Heat lost through exhaust gases and incomplete combustion. |
| Impact on Energy Consumption | Higher efficiency reduces fuel consumption and emissions. | Improved efficiency lowers fuel costs and environmental impact. |
Understanding Boiler Efficiency
Boiler efficiency measures the effectiveness of converting fuel energy into steam or hot water, typically ranging between 80% and 90%. It is calculated using the ratio of heat output to energy input, factoring in losses due to flue gases and incomplete combustion. Understanding boiler efficiency is crucial for optimizing fuel consumption, reducing operational costs, and minimizing environmental impact in heating systems.
Defining Furnace Efficiency
Furnace efficiency measures how well a furnace converts fuel into usable heat, typically expressed as Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) percentage. It evaluates the amount of heat delivered to your home compared to the energy content of the fuel consumed, highlighting energy losses through exhaust gases and system components. Understanding furnace efficiency helps you choose a heating system that maximizes energy savings and reduces utility costs.
Key Differences Between Boilers and Furnaces
Boiler efficiency measures how well a boiler converts fuel into heat for water or steam, providing consistent radiant heat throughout a property, while furnace efficiency assesses how effectively a furnace converts fuel into warm air distributed via ducts. Boilers typically offer higher energy efficiency and quieter operation compared to furnaces, which heat spaces more quickly but may experience heat loss through ductwork. Understanding these differences ensures you select the right heating system that optimizes your home's energy use and comfort.
How Efficiency is Measured in Boilers
Boiler efficiency is measured by comparing the heat output to the fuel energy input, expressed as a percentage, with common methods including direct and indirect tests. The direct method calculates efficiency by dividing the energy delivered to the working fluid by the energy supplied through fuel, while the indirect method estimates losses such as flue gas temperature and unburned fuel to determine efficiency. Understanding these measurements helps you optimize your boiler's performance and reduce energy consumption compared to furnace efficiency metrics.
Furnace Efficiency Rating Systems
Furnace efficiency rating systems primarily use the Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) metric, which measures the percentage of fuel converted to heat over a typical year, with modern furnaces achieving AFUE ratings between 80% and 98%. Unlike boilers that often use combustion efficiency and thermal efficiency metrics, furnace AFUE accounts for seasonal variations and standby losses, providing a more comprehensive efficiency assessment. High AFUE-rated furnaces significantly reduce energy consumption and emissions, offering cost savings and environmental benefits compared to lower-rated systems.
Factors Influencing Boiler Efficiency
Boiler efficiency is primarily influenced by combustion quality, heat transfer effectiveness, and proper maintenance, ensuring optimal fuel utilization and minimal energy loss. Factors such as flue gas temperature, excess air levels, and fouling of heat exchanger surfaces directly impact boiler performance, often requiring regular monitoring to maintain efficiency. Your system's efficiency can be maximized by adjusting burner settings, preventing scale buildup, and improving insulation to reduce heat loss.
Variables Affecting Furnace Efficiency
Furnace efficiency is primarily influenced by factors such as combustion air supply, fuel type, heat exchanger condition, and flue gas temperature. Proper adjustment of air-to-fuel ratio ensures complete combustion, reducing heat loss and increasing efficiency. Additionally, maintaining clean heat exchangers and minimizing excess air help optimize furnace performance and energy utilization.
Typical Efficiency Ranges: Boilers vs Furnaces
Boiler efficiency typically ranges from 70% to 90%, with high-efficiency models exceeding 95%, while furnace efficiency generally falls between 78% and 98%, depending on the type and age of the unit. Condensing boilers and furnaces achieve higher efficiency by recovering latent heat through advanced heat exchanger technology. Understanding these efficiency ranges is critical for selecting heating systems that optimize energy consumption and reduce utility costs.
Energy Cost Implications of Boiler and Furnace Choice
Boiler efficiency directly impacts energy costs by determining how effectively fuel is converted into heat, with modern high-efficiency boilers reaching up to 98% efficiency, leading to significant fuel savings. Furnace efficiency, while also critical, typically ranges between 80% and 98%, affecting energy consumption primarily in heating air rather than water or steam. Choosing a high-efficiency boiler or furnace reduces overall energy expenses and carbon footprint, with boilers being more cost-effective for whole-house heating due to their superior heat transfer and lower fuel use.
Choosing the Right System for Maximum Efficiency
Boiler efficiency measures how effectively a boiler converts fuel into heat, focusing on water heating, while furnace efficiency pertains to heating air for distribution throughout a home or building. Understanding your heating needs and system type is crucial for choosing between a boiler or furnace since boilers excel in providing consistent, radiant heat in colder climates, whereas furnaces deliver rapid, warm airflow ideal for variable temperatures. By selecting the right system based on these efficiency metrics, you can maximize energy savings and ensure your home stays comfortably warm year-round.
Boiler Efficiency vs Furnace Efficiency Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com