A recloser automatically restores power after temporary faults by interrupting and re-energizing the line, while a sectionalizer detects permanent faults and isolates faulty sections without interrupting the main circuit. Your choice depends on the need for automatic fault recovery versus precise fault isolation to enhance grid reliability and reduce outage times.
Table of Comparison
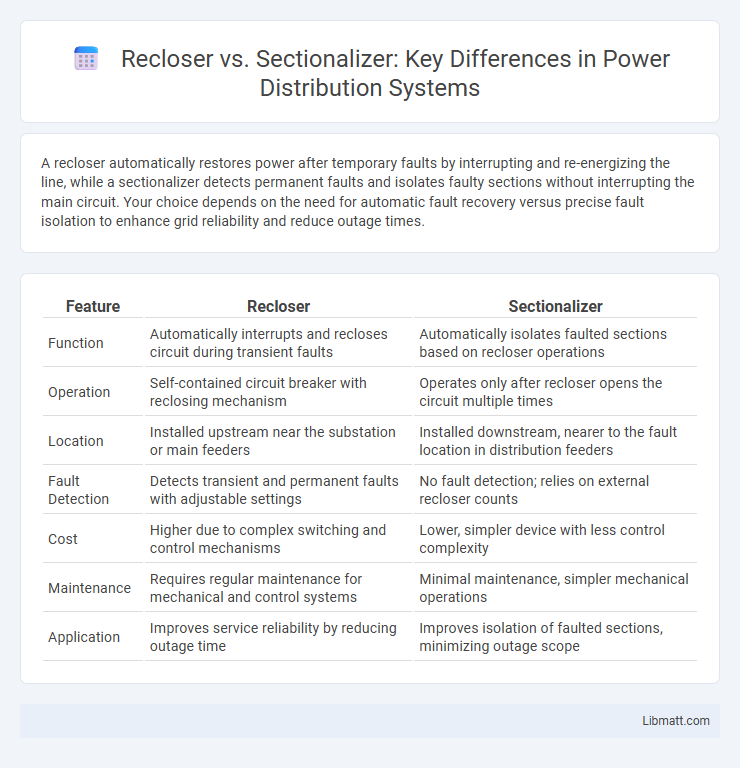
| Feature | Recloser | Sectionalizer |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Automatically interrupts and recloses circuit during transient faults | Automatically isolates faulted sections based on recloser operations |
| Operation | Self-contained circuit breaker with reclosing mechanism | Operates only after recloser opens the circuit multiple times |
| Location | Installed upstream near the substation or main feeders | Installed downstream, nearer to the fault location in distribution feeders |
| Fault Detection | Detects transient and permanent faults with adjustable settings | No fault detection; relies on external recloser counts |
| Cost | Higher due to complex switching and control mechanisms | Lower, simpler device with less control complexity |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance for mechanical and control systems | Minimal maintenance, simpler mechanical operations |
| Application | Improves service reliability by reducing outage time | Improves isolation of faulted sections, minimizing outage scope |
Introduction to Reclosers and Sectionalizers
Reclosers and sectionalizers are essential devices in distribution networks designed to enhance system reliability and quickly isolate faults. Reclosers automatically interrupt fault currents and attempt to restore power, while sectionalizers identify faulted sections and open after a predetermined number of operations by the recloser. Understanding the distinct functionality of each device can help you optimize grid protection and minimize outage durations.
Key Definitions: What is a Recloser?
A recloser is an automated electrical device designed to detect and interrupt temporary faults in power distribution lines by opening and reclosing the circuit rapidly to restore service without manual intervention. It helps improve system reliability by minimizing outage durations caused by transient disturbances such as lightning or momentary contact with vegetation. Unlike sectionalizers, reclosers have the capability to interrupt fault current directly, making them critical components in grid protection and automation systems.
Key Definitions: What is a Sectionalizer?
A sectionalizer is an automatic electric device designed to isolate faulty sections of a power distribution network by opening the circuit after a predetermined number of fault current interruptions. Unlike reclosers, sectionalizers do not interrupt fault current but operate in coordination with upstream protective devices, enabling selective isolation and minimizing outage areas. This function enhances grid reliability and efficiency in fault management within electrical distribution systems.
Working Principles: Recloser vs Sectionalizer
Reclosers and sectionalizers operate differently to enhance power distribution reliability; a recloser automatically interrupts and restores power after detecting temporary faults by opening and reclosing its switch, while a sectionalizer detects the number of fault current interruptions caused by upstream devices and opens only after they have cleared the fault, isolating the affected section. Your power system benefits from reclosers' ability to quickly restore service after transient faults, and sectionalizers' precise sectional isolation minimizes outages by collaborating with upstream reclosers. Understanding these distinct working principles helps optimize fault management and improves overall grid stability.
Applications in Power Distribution Networks
Reclosers are primarily used in power distribution networks to automatically interrupt and restore power during transient faults, improving system reliability and reducing outage duration. Sectionalizers complement reclosers by isolating faulted sections after multiple recloser operations, preventing unnecessary outages in unaffected areas. Your distribution system benefits from integrating both devices to optimize fault management and enhance overall network stability.
Advantages of Reclosers
Reclosers offer rapid automatic restoration of power after temporary faults, significantly reducing outage duration for consumers. They enable multiple reclosing attempts, improving system reliability and minimizing manual intervention compared to sectionalizers. Equipped with advanced fault detection and communication features, reclosers enhance grid automation and fault isolation efficiency.
Advantages of Sectionalizers
Sectionalizers offer precise fault isolation by automatically opening only the faulted section of a distribution line, minimizing service interruptions for your entire network. Their ability to operate without power during fault conditions enhances reliability and reduces maintenance costs compared to reclosers. Sectionalizers improve grid stability by coordinating with upstream reclosers to clear faults efficiently, ensuring faster restoration of unaffected sections.
Key Differences Between Reclosers and Sectionalizers
Reclosers are automated circuit breakers designed to detect and interrupt transient faults by momentarily opening and reclosing the circuit, minimizing downtime. Sectionalizers, on the other hand, are protective devices that isolate faulted segments by counting interruptions from upstream reclosers and opening only after those reclosers have operated multiple times. Understanding these key differences helps you optimize fault management and improve the reliability of your distribution network.
Choosing the Right Device: Factors to Consider
Selecting the right device between a recloser and a sectionalizer depends on factors such as the type of fault, system automation requirements, and maintenance capabilities. Reclosers are ideal for temporary fault isolation and automatic reclosing, while sectionalizers excel in permanently isolating faulted sections without reclosing functionality. Consider system design, fault frequency, and cost-effectiveness to determine the optimal device for reliable distribution network protection.
Future Trends in Distribution Automation
Future trends in distribution automation emphasize the integration of advanced Reclosers and Sectionalizers with IoT technology and AI-driven analytics to enhance grid reliability and fault detection speed. Reclosers increasingly incorporate adaptive protection schemes and remote monitoring capabilities, while Sectionalizers evolve with precise fault location awareness and automated sectionalizing functions. The convergence of these smart devices supports predictive maintenance, grid resilience, and seamless integration with renewable energy sources.
Recloser vs Sectionalizer Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com