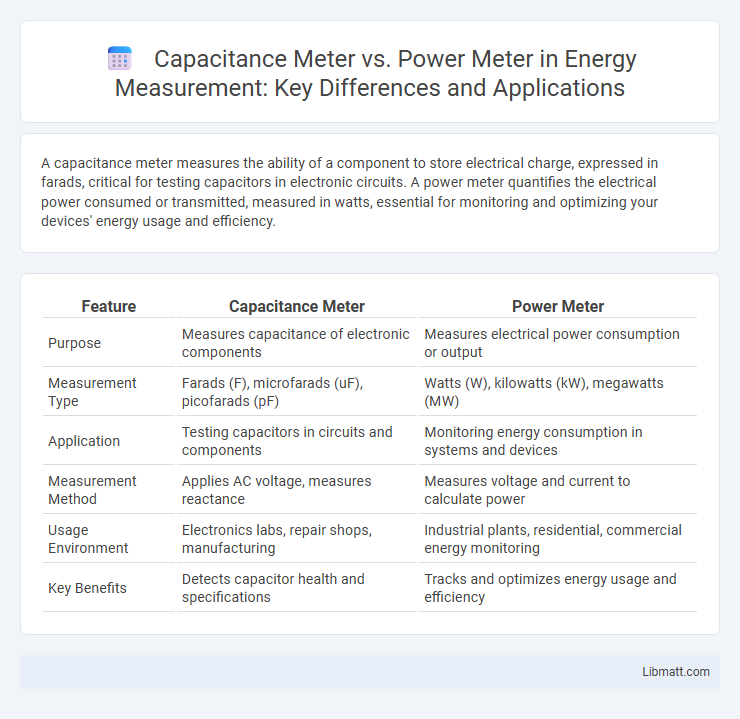
A capacitance meter measures the ability of a component to store electrical charge, expressed in farads, critical for testing capacitors in electronic circuits. A power meter quantifies the electrical power consumed or transmitted, measured in watts, essential for monitoring and optimizing your devices' energy usage and efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Capacitance Meter | Power Meter |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Measures capacitance of electronic components | Measures electrical power consumption or output |
| Measurement Type | Farads (F), microfarads (uF), picofarads (pF) | Watts (W), kilowatts (kW), megawatts (MW) |
| Application | Testing capacitors in circuits and components | Monitoring energy consumption in systems and devices |
| Measurement Method | Applies AC voltage, measures reactance | Measures voltage and current to calculate power |
| Usage Environment | Electronics labs, repair shops, manufacturing | Industrial plants, residential, commercial energy monitoring |
| Key Benefits | Detects capacitor health and specifications | Tracks and optimizes energy usage and efficiency |
Introduction to Capacitance and Power Meters
Capacitance meters accurately measure the capacitance of electronic components, essential for evaluating capacitor performance and quality. Power meters quantify electrical power consumption or output in circuits, crucial for energy efficiency and system diagnostics. Understanding the distinct functions of these instruments helps optimize your electronic testing and maintenance processes.
Basic Principle of Capacitance Meter
A capacitance meter measures the ability of a component to store electrical charge by applying an alternating current (AC) signal and detecting the resulting voltage phase shift, which is directly related to the capacitance value. It operates based on the principle that a capacitor's reactance varies inversely with frequency and capacitance, allowing accurate quantification of capacitance in picofarads to microfarads. Unlike power meters that measure real power consumption in watts, capacitance meters focus exclusively on the capacitance characteristic critical in circuit design and component testing.
Core Functionality of Power Meter
A power meter primarily measures electrical power in watts, providing insights into real-time energy consumption and efficiency within electrical circuits or devices. Unlike a capacitance meter, which assesses capacitance values of capacitors, a power meter evaluates voltage, current, and power factor to calculate actual power usage. Understanding your power meter's core functionality helps optimize energy management and ensure electrical system performance.
Key Differences Between Capacitance Meters and Power Meters
Capacitance meters measure the ability of a component to store electrical charge, focusing primarily on capacitors and their dielectric properties, while power meters quantify the electrical power consumed or delivered in a circuit, often expressed in watts. Capacitance meters provide critical data on capacitance values, loss factors, and equivalent series resistance, essential for component characterization and quality control. Power meters, on the other hand, are vital for assessing energy efficiency, power consumption, and load performance in electrical systems and devices.
Applications of Capacitance Meters
Capacitance meters are essential for measuring the capacitance value of electronic components, making them ideal for testing capacitors in circuit design, troubleshooting, and quality control. These devices help you verify the integrity and specifications of capacitors in applications such as HVAC systems, automotive electronics, and consumer appliances. Unlike power meters, which measure electrical power consumption and efficiency, capacitance meters focus solely on the accurate assessment of capacitance to ensure proper circuit functionality.
Common Uses for Power Meters
Power meters are essential for accurately measuring electrical power in circuits, making them indispensable in applications like testing power supplies, monitoring energy consumption, and analyzing the efficiency of electrical devices. They are commonly used in industrial environments to ensure machinery operates within safe power limits and in renewable energy systems to track solar panel output. Your ability to assess power performance with a power meter supports optimizing system reliability and energy management.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Meter
Capacitance meters offer precise measurement of capacitance values, essential for testing capacitors and dielectric materials, with advantages including ease of use and high accuracy in low-frequency measurements; however, they are limited by their inability to measure power-related parameters and may be less effective at high frequencies. Power meters excel in measuring electrical power, including real, reactive, and apparent power, beneficial for monitoring system efficiency and energy consumption, yet they often have complex interfaces and can be expensive for casual or hobbyist users. Understanding your specific measurement needs helps determine whether a capacitance meter for component testing or a power meter for system analysis is most suitable.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Capacitance and Power Meters
Choosing between a capacitance meter and a power meter depends on the specific measurement needs, such as whether the focus is on electrical component properties or overall energy consumption. Capacitance meters are essential for accurately measuring the capacitance value of capacitors, useful in applications like circuit design and troubleshooting, while power meters measure electrical power usage, important for energy efficiency and load monitoring. Accuracy requirements, frequency range, and the type of electrical parameter to monitor--capacitance or power--are critical factors influencing the selection.
Latest Innovations in Electrical Measurement Tools
Latest innovations in electrical measurement tools have led to advanced capacitance meters featuring higher accuracy, miniaturization, and integration with digital interfaces for seamless data logging and analysis. Power meters now incorporate real-time power quality monitoring, wireless connectivity, and enhanced diagnostics for both AC and DC systems, providing comprehensive insights into energy consumption and efficiency. Your choice between a capacitance meter and a power meter depends on whether you need precise measurement of stored electric charge or detailed power parameters for system optimization.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Meter for Your Needs
Choosing between a capacitance meter and a power meter depends on your specific diagnostic requirements; capacitance meters accurately measure the capacity of electrical components, essential for testing capacitors in circuits. Power meters focus on measuring electrical power consumption and efficiency, crucial for monitoring energy usage in appliances and industrial equipment. Your selection should align with whether your priority is evaluating component functionality or assessing overall energy performance.
Capacitance Meter vs Power Meter Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com