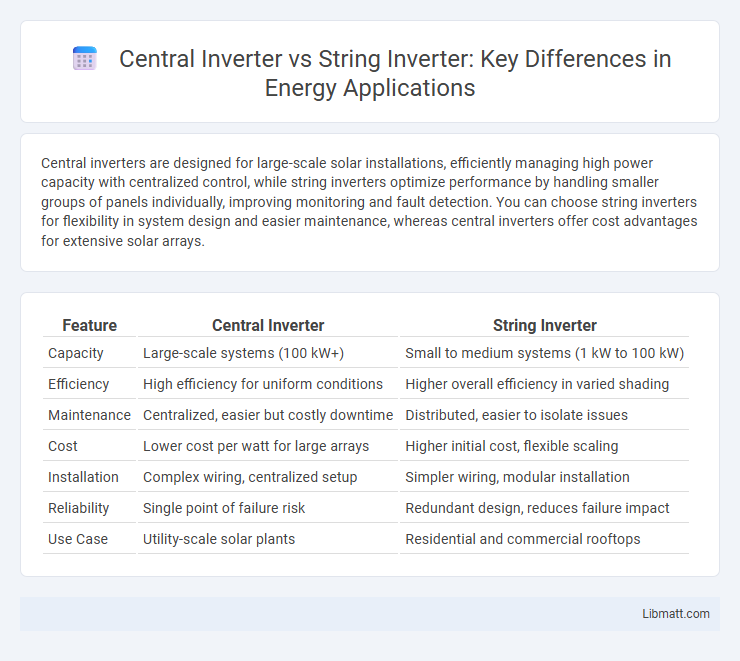
Central inverters are designed for large-scale solar installations, efficiently managing high power capacity with centralized control, while string inverters optimize performance by handling smaller groups of panels individually, improving monitoring and fault detection. You can choose string inverters for flexibility in system design and easier maintenance, whereas central inverters offer cost advantages for extensive solar arrays.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Central Inverter | String Inverter |
|---|---|---|
| Capacity | Large-scale systems (100 kW+) | Small to medium systems (1 kW to 100 kW) |
| Efficiency | High efficiency for uniform conditions | Higher overall efficiency in varied shading |
| Maintenance | Centralized, easier but costly downtime | Distributed, easier to isolate issues |
| Cost | Lower cost per watt for large arrays | Higher initial cost, flexible scaling |
| Installation | Complex wiring, centralized setup | Simpler wiring, modular installation |
| Reliability | Single point of failure risk | Redundant design, reduces failure impact |
| Use Case | Utility-scale solar plants | Residential and commercial rooftops |
Introduction to Central and String Inverters
Central inverters are large-scale devices designed to convert direct current (DC) power from multiple solar strings into alternating current (AC) for utility-scale solar installations. String inverters convert DC power from individual solar panel strings, offering modularity and easier maintenance for residential or commercial systems. Your choice depends on system size and maintenance preferences, with central inverters suited for large arrays and string inverters ideal for smaller, segmented setups.
How Central Inverters Work
Central inverters convert direct current (DC) generated by multiple solar panels into alternating current (AC) at a single, centralized point, optimizing energy conversion for large-scale solar systems. Your solar array's combined DC power flows into the central inverter, which then synchronizes and converts it efficiently for grid use or on-site consumption. This centralized approach simplifies system design but may reduce overall efficiency if shading or panel mismatch occurs.
How String Inverters Operate
String inverters convert the direct current (DC) generated by a series of solar panels, known as a string, into alternating current (AC) usable by your home or the grid. Each string inverter monitors and optimizes the performance of its connected panels, enabling better control and quicker detection of issues compared to a central inverter that handles multiple strings simultaneously. Your solar energy system benefits from this modular approach by improving efficiency and simplifying maintenance.
Key Differences Between Central and String Inverters
Central inverters handle large-scale solar power conversion for utility-scale projects by aggregating energy from multiple strings into a single, high-capacity unit, whereas string inverters convert DC to AC power at a smaller scale, managing individual strings of solar panels for residential or commercial systems. Central inverters offer higher efficiency in large installations but lack flexibility and are more vulnerable to single points of failure, while string inverters provide modularity, easier maintenance, and improved performance monitoring at the panel level. Cost-effectiveness and scalability also differ, with central inverters being more economical for extensive arrays and string inverters preferred for systems requiring adaptability and incremental expansion.
Efficiency Comparison: Central vs String Inverter
Central inverters typically offer higher efficiency rates, often exceeding 98%, due to their ability to manage large-scale solar arrays with centralized control and optimized power conversion. String inverters generally have efficiency ratings around 95-97%, as they handle smaller, segmented portions of the solar system, which can result in slight energy losses from shading and mismatch between panels. Efficiency differences impact overall energy yield, making central inverters more suitable for large commercial installations, while string inverters provide flexibility and reliable performance in smaller or residential solar setups.
Installation and Scalability Considerations
Central inverters require a more complex installation process involving centralized equipment and extensive wiring, making them less flexible for gradual system expansion. String inverters offer straightforward installation with modular string connections, allowing easier scalability by adding additional strings without major reconfiguration. For projects anticipating phased growth or diverse system sizes, string inverters provide superior adaptability and reduced installation complexity.
Maintenance and Reliability
Central inverters typically require less frequent maintenance due to their centralized location and robust design, but a failure can impact the entire system, increasing downtime risk. String inverters offer higher reliability through decentralized operation, allowing individual strings to continue functioning if one inverter fails, which simplifies maintenance and reduces overall system downtime. Choosing between the two depends on your system size and maintenance preferences to optimize reliability and operational continuity.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Long-Term Value
Central inverters typically require a higher initial investment due to their capacity to handle large-scale solar arrays efficiently, offering cost savings in installation and maintenance for utility-sized projects. String inverters, with lower upfront costs and modular design, provide flexibility and easier scalability, making them suitable for smaller systems or residential use. Your choice between central and string inverters should consider both the scale of your solar installation and long-term value, including potential savings from improved energy yield and reduced downtime.
Ideal Applications for Central and String Inverters
Central inverters are ideal for large-scale solar installations such as utility-scale power plants and commercial rooftops due to their high capacity and centralized design. String inverters are better suited for residential or small commercial systems where modularity and ease of maintenance are important, allowing flexibility in panel layout and shading conditions. Your choice between central and string inverters depends on the system size, site complexity, and budget considerations.
Choosing the Right Inverter for Your Solar Project
Central inverters, designed for large-scale solar projects, consolidate multiple strings of solar panels into one large, high-capacity unit, offering efficiency and simpler maintenance for commercial installations. String inverters, ideal for residential or smaller commercial systems, optimize individual panel strings, enhancing system adaptability and minimizing energy losses from shading or panel mismatch. Choosing the right inverter depends on your project size, budget, and desired system performance to maximize energy harvest and reliability.
Central inverter vs String inverter Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com