Critical Peak Pricing charges significantly higher rates during short periods of extreme demand to incentivize drastic usage reductions, while Time-of-Use Pricing sets variable rates based on predictable daily or seasonal demand patterns. Your choice between these models affects how you manage energy consumption and optimize costs during peak and off-peak hours.
Table of Comparison
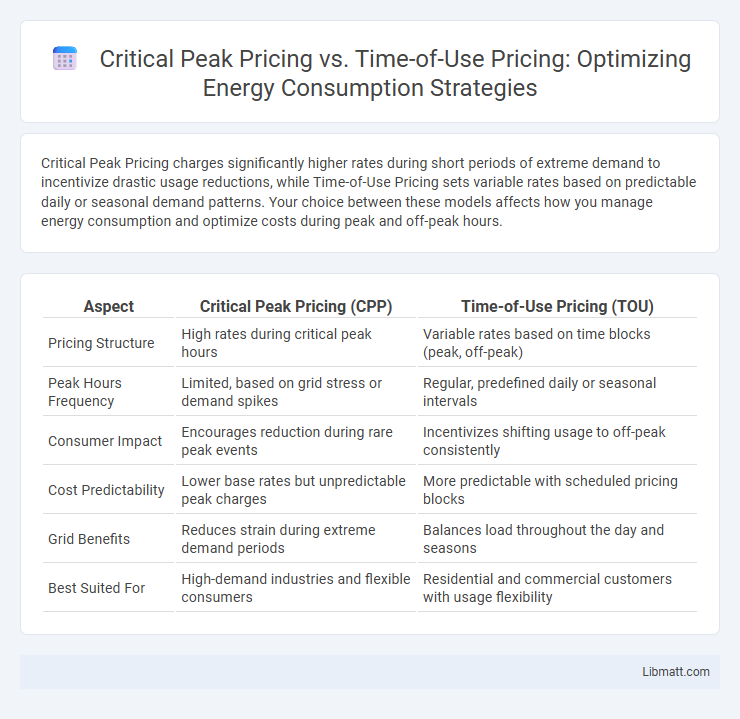
| Aspect | Critical Peak Pricing (CPP) | Time-of-Use Pricing (TOU) |
|---|---|---|
| Pricing Structure | High rates during critical peak hours | Variable rates based on time blocks (peak, off-peak) |
| Peak Hours Frequency | Limited, based on grid stress or demand spikes | Regular, predefined daily or seasonal intervals |
| Consumer Impact | Encourages reduction during rare peak events | Incentivizes shifting usage to off-peak consistently |
| Cost Predictability | Lower base rates but unpredictable peak charges | More predictable with scheduled pricing blocks |
| Grid Benefits | Reduces strain during extreme demand periods | Balances load throughout the day and seasons |
| Best Suited For | High-demand industries and flexible consumers | Residential and commercial customers with usage flexibility |
Introduction to Electricity Pricing Models
Critical Peak Pricing (CPP) and Time-of-Use (TOU) Pricing are two electricity pricing models designed to influence consumer energy usage patterns. CPP imposes significantly higher rates during brief peak demand periods to encourage reduced consumption when the grid is most stressed, while TOU Pricing establishes different rates for predefined time blocks throughout the day reflecting typical demand variations. Your choice between these models can impact both your energy costs and consumption behavior based on how you shift or reduce electricity use during peak times.
What is Critical Peak Pricing (CPP)?
Critical Peak Pricing (CPP) is an electricity tariff structure that charges significantly higher rates during short, designated peak demand periods to encourage reduced consumption when the grid is most stressed. This pricing model typically activates a few times per year during extreme demand events, signaling consumers to cut back usage and help prevent outages or the need for expensive peaker plants. CPP is designed to provide utilities with a demand reduction tool that balances grid reliability while offering consumers a financial incentive to alter their energy behavior during critical peak hours.
Understanding Time-of-Use (TOU) Pricing
Time-of-Use (TOU) pricing charges electricity rates based on predetermined time blocks, reflecting varying demand levels throughout the day, encouraging consumers to shift usage to off-peak hours. This pricing mechanism helps balance grid load by reducing consumption during peak periods and lowering overall energy costs. Utilities often implement TOU rates with distinct peak, off-peak, and shoulder periods to promote energy efficiency and demand response.
Key Differences: CPP vs TOU
Critical Peak Pricing (CPP) charges significantly higher rates during a few extreme demand periods to encourage rapid reduction in electricity use, while Time-of-Use (TOU) Pricing offers varying rates throughout the day based on predictable demand patterns. CPP targets short, critical peak events typically lasting a few hours, whereas TOU provides consistent price signals across multiple time blocks to influence daily consumption habits. Understanding these key differences helps you optimize energy costs by adjusting usage either during critical peaks or throughout different times of the day.
Benefits of Critical Peak Pricing
Critical Peak Pricing (CPP) offers significant cost savings during extreme demand periods by charging higher rates only when the grid is under significant stress, encouraging you to reduce usage precisely when it matters most. This targeted approach helps alleviate grid congestion, lowers peak demand costs, and supports overall system reliability more effectively than Time-of-Use (TOU) Pricing, which applies variable rates based on set time blocks regardless of actual grid conditions. CPP's flexibility aligns consumer behavior with real-time grid needs, maximizing both economic and environmental benefits.
Advantages of Time-of-Use Pricing
Time-of-Use Pricing offers the advantage of predictable electricity rates based on predetermined peak and off-peak hours, enabling you to plan your energy consumption efficiently. This pricing model encourages energy usage during off-peak periods, reducing strain on the grid and lowering your overall electricity costs. Utilities benefit from smoother demand patterns, improving grid reliability and supporting sustainable energy management.
Challenges and Limitations of CPP
Critical Peak Pricing (CPP) faces challenges such as consumer difficulty in predicting peak event days, leading to limited responsiveness and potential bill volatility. The effectiveness of CPP depends heavily on accurate and timely communication, which can be hindered by technological and behavioral constraints. Moreover, CPP programs may disproportionately impact vulnerable populations who cannot easily shift or reduce their electricity usage during critical periods.
Drawbacks of TOU Pricing
Time-of-Use (TOU) Pricing can result in higher energy costs during off-peak periods if your consumption does not align with prescribed time blocks. The fixed price intervals may not accurately reflect real-time supply and demand fluctuations, limiting flexibility and potential savings. This structure can lead to unintended peak shifting rather than overall peak reduction, undermining grid efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Choosing the Right Pricing Model for Consumers
Critical Peak Pricing targets specific high-demand periods with significantly higher rates to incentivize consumers to reduce usage during peak events, while Time-of-Use Pricing spreads different rates across predefined time blocks throughout the day. Your choice depends on your energy consumption patterns and flexibility; if you can shift usage away from rare, critical peaks, Critical Peak Pricing may offer savings, whereas consistent adjustment to varying hourly rates suits Time-of-Use Pricing better. Evaluating your daily energy needs and responsiveness to price signals helps determine the optimal pricing model for cost efficiency.
Future Trends in Electricity Pricing
Critical Peak Pricing (CPP) and Time-of-Use (TOU) Pricing are evolving as key mechanisms in dynamic electricity markets, with future trends emphasizing increased integration of real-time data and smart grid technologies to enhance demand response and grid stability. CPP targets a limited number of high-demand periods with higher rates, encouraging users to reduce consumption during peak stress times, while TOU pricing offers variable rates based on predefined time blocks to promote overall load shifting. The advancement of AI-driven analytics and IoT-enabled smart meters is expected to optimize these pricing models further, enabling more granular, personalized, and flexible electricity rates that align with renewable energy variability and consumer behavior patterns.
Critical Peak Pricing vs Time-of-Use Pricing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com