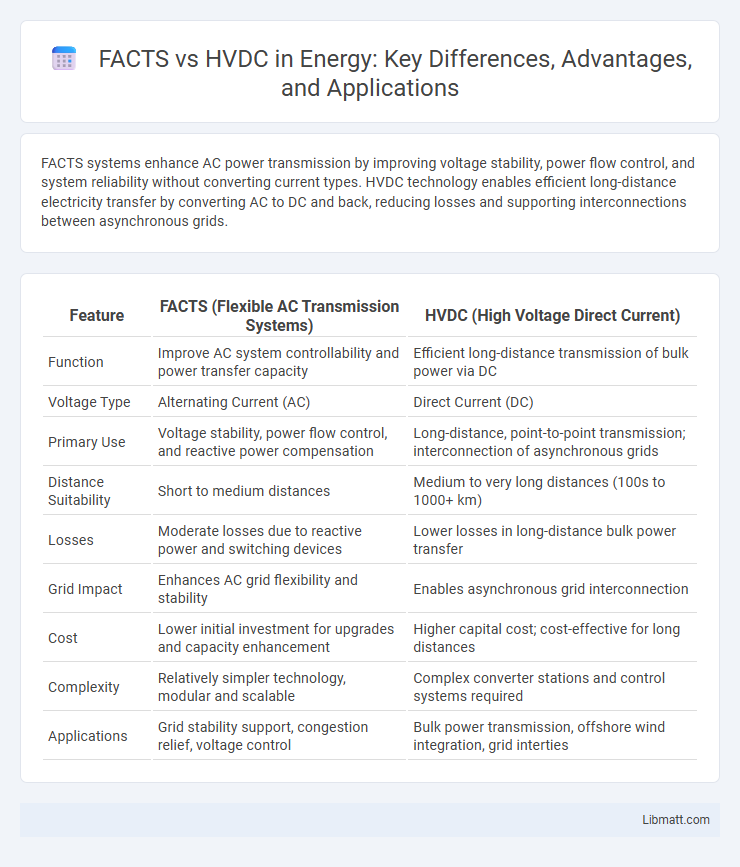
FACTS systems enhance AC power transmission by improving voltage stability, power flow control, and system reliability without converting current types. HVDC technology enables efficient long-distance electricity transfer by converting AC to DC and back, reducing losses and supporting interconnections between asynchronous grids.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | FACTS (Flexible AC Transmission Systems) | HVDC (High Voltage Direct Current) |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Improve AC system controllability and power transfer capacity | Efficient long-distance transmission of bulk power via DC |
| Voltage Type | Alternating Current (AC) | Direct Current (DC) |
| Primary Use | Voltage stability, power flow control, and reactive power compensation | Long-distance, point-to-point transmission; interconnection of asynchronous grids |
| Distance Suitability | Short to medium distances | Medium to very long distances (100s to 1000+ km) |
| Losses | Moderate losses due to reactive power and switching devices | Lower losses in long-distance bulk power transfer |
| Grid Impact | Enhances AC grid flexibility and stability | Enables asynchronous grid interconnection |
| Cost | Lower initial investment for upgrades and capacity enhancement | Higher capital cost; cost-effective for long distances |
| Complexity | Relatively simpler technology, modular and scalable | Complex converter stations and control systems required |
| Applications | Grid stability support, congestion relief, voltage control | Bulk power transmission, offshore wind integration, grid interties |
Introduction to FACTS and HVDC
Flexible AC Transmission Systems (FACTS) enhance the controllability and increase the power transfer capability of AC transmission networks through power electronic devices, improving system stability and power quality. High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) technology enables efficient long-distance bulk power transmission by converting AC to DC and back, reducing losses and allowing asynchronous interconnection between different grid frequencies. Both technologies are essential for modern grid optimization, with FACTS primarily improving AC system dynamics and HVDC facilitating high-capacity, resilient power transfer.
Fundamental Concepts: FACTS vs HVDC
Flexible AC Transmission Systems (FACTS) enhance the controllability and increase the power transfer capability of AC networks by using power electronics to regulate voltage, impedance, and phase angle. High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) systems transmit electricity over long distances using direct current, minimizing losses and enabling asynchronous grid interconnections. While FACTS devices improve AC system stability and flexibility, HVDC provides efficient bulk power transfer and grid interconnectivity across regions.
Historical Development and Evolution
FACTS (Flexible AC Transmission Systems) technology emerged in the late 20th century, driven by the need to enhance power system stability and control in alternating current networks. HVDC (High Voltage Direct Current) systems date back to the early 20th century but gained significant advancements with the development of thyristor valves in the 1970s, enabling long-distance and efficient DC power transmission. Both technologies have evolved with innovations in power electronics, improving grid reliability, integration of renewable energy, and reduction of transmission losses.
Key Technologies and Components
FACTS (Flexible AC Transmission Systems) utilize power electronic devices like thyristors and gate turn-off thyristors (GTOs) to control AC power flow and enhance grid stability by adjusting voltage, impedance, and phase angle. HVDC (High Voltage Direct Current) systems rely on converters, such as line-commutated converters (LCC) or voltage source converters (VSC), to convert AC to DC and back, enabling efficient long-distance power transmission with reduced losses. Your choice between FACTS and HVDC depends on the need for dynamic AC grid control or bulk power transfer over vast distances.
Applications in Modern Power Systems
FACTS devices enhance voltage stability, improve power quality, and increase transmission capacity in AC systems, making them ideal for real-time load balancing and fault control. HVDC technology excels in long-distance and underwater power transmission, enabling efficient interconnection between asynchronous grids and integration of renewable energy sources. Your choice depends on system requirements; FACTS suits dynamic AC network control, while HVDC supports high-capacity, long-haul, and cross-border power flows.
Advantages and Limitations
FACTS (Flexible AC Transmission Systems) improve grid stability and control by enhancing power quality, voltage regulation, and reducing transmission losses, making them ideal for AC networks. HVDC (High Voltage Direct Current) offers long-distance, high-capacity power transmission with lower losses and better controllability over asynchronous grids, but requires costly converter stations. Your choice between FACTS and HVDC depends on system requirements, considering FACTS' ease of integration versus HVDC's efficiency for bulk power transfer across extensive distances.
System Integration and Compatibility
Flexible AC Transmission Systems (FACTS) enhance system integration by improving voltage stability and reactive power control within existing AC grids, allowing seamless compatibility with traditional infrastructure. High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) systems enable efficient long-distance power transmission and facilitate asynchronous interconnections between different AC networks, supporting grid expansion and cross-border power exchange. Both technologies complement grid modernization efforts by addressing distinct challenges in system integration and compatibility, with FACTS optimizing AC performance and HVDC ensuring reliable high-capacity transmission.
Economic Considerations and Cost Analysis
Flexible AC Transmission Systems (FACTS) generally involve lower initial investment costs compared to High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) systems, making them more economical for short to medium transmission distances. HVDC is cost-effective for long-distance, high-capacity power transfer due to reduced transmission losses and lower conductor requirements over extended routes. Comprehensive cost analysis must account for installation, maintenance, and operational expenses, where HVDC's higher upfront costs can be offset by lower long-term transmission costs and enhanced grid stability benefits.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
FACTS (Flexible AC Transmission Systems) and HVDC (High Voltage Direct Current) technologies offer different environmental benefits that impact sustainability. FACTS devices improve the efficiency and stability of existing AC grids, reducing energy losses and minimizing the need for new infrastructure, which helps lower the environmental footprint. HVDC systems enable long-distance power transmission with significantly lower line losses and support the integration of renewable energy sources, making your power grid more sustainable and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Future Trends and Innovations
Future trends in FACTS technology emphasize integrating advanced control algorithms and AI-driven predictive maintenance to enhance grid stability and efficiency. Innovations in HVDC focus on ultra-high voltage applications and modular multi-level converters, promoting long-distance, low-loss power transmission with improved scalability. Both technologies are converging towards smart grid integration, supporting renewable energy and decentralized power systems.
FACTS vs HVDC Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com