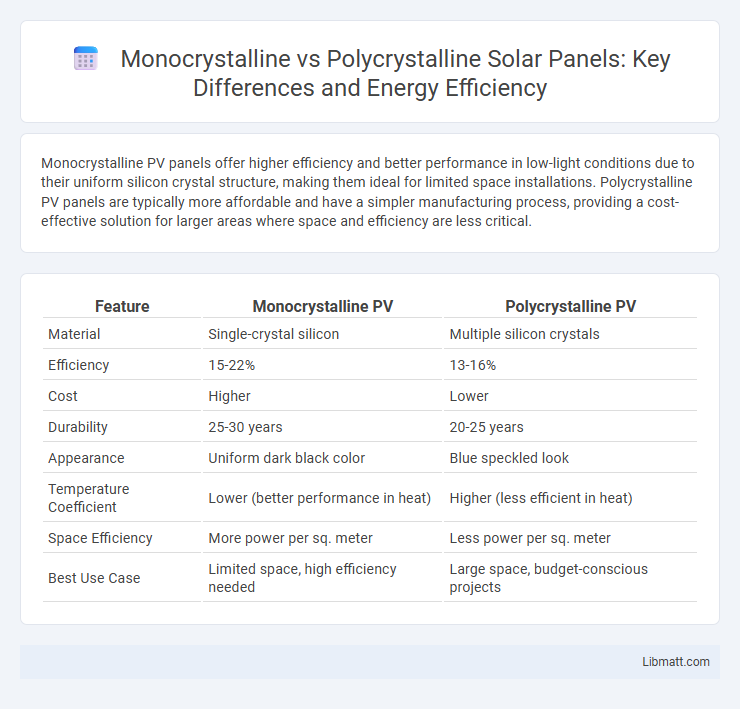
Monocrystalline PV panels offer higher efficiency and better performance in low-light conditions due to their uniform silicon crystal structure, making them ideal for limited space installations. Polycrystalline PV panels are typically more affordable and have a simpler manufacturing process, providing a cost-effective solution for larger areas where space and efficiency are less critical.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Monocrystalline PV | Polycrystalline PV |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Single-crystal silicon | Multiple silicon crystals |
| Efficiency | 15-22% | 13-16% |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Durability | 25-30 years | 20-25 years |
| Appearance | Uniform dark black color | Blue speckled look |
| Temperature Coefficient | Lower (better performance in heat) | Higher (less efficient in heat) |
| Space Efficiency | More power per sq. meter | Less power per sq. meter |
| Best Use Case | Limited space, high efficiency needed | Large space, budget-conscious projects |
Introduction to Monocrystalline and Polycrystalline PV
Monocrystalline PV panels consist of single-crystal silicon, offering higher efficiency and better performance in low-light conditions compared to polycrystalline panels, which are made from multiple silicon crystals. Polycrystalline PV panels are more cost-effective due to simpler manufacturing processes but generally have lower efficiency and a shorter lifespan. Understanding the fundamental differences in material structure helps you choose the right solar technology based on energy needs and budget.
What Are Monocrystalline Solar Panels?
Monocrystalline solar panels consist of single-crystal silicon cells known for their high efficiency and sleek black appearance. These panels deliver superior energy output per square meter due to the purity and uniformity of the silicon wafer, making them ideal for limited roof spaces. Their longevity and performance under low-light conditions contribute to their premium status in the photovoltaic industry.
What Are Polycrystalline Solar Panels?
Polycrystalline solar panels consist of multiple silicon crystals melted together, creating a distinctive blue, speckled appearance. They generally offer lower efficiency compared to monocrystalline panels due to grain boundaries that reduce electron flow. Polycrystalline panels remain a cost-effective solution for residential and commercial solar installations with moderate space requirements.
Key Differences: Structure and Materials
Monocrystalline PV panels consist of single-crystal silicon, providing higher efficiency and a uniform black appearance due to the pure silicon structure. Polycrystalline PV panels are made from multiple silicon crystals melted together, resulting in a blue, speckled look and slightly lower efficiency. Understanding these structural and material differences can help you choose the best solar panel type for your energy needs and installation environment.
Efficiency Comparison: Monocrystalline vs Polycrystalline
Monocrystalline photovoltaic (PV) panels typically achieve higher efficiency rates of around 15-20% due to their uniform silicon crystal structure, which enhances electron flow. Polycrystalline panels generally exhibit lower efficiency, averaging 13-16%, because their multiple crystal fragments create boundaries that interrupt electron movement. The higher efficiency of monocrystalline panels makes them more suitable for limited space installations where maximum power output is essential.
Cost and Affordability Analysis
Monocrystalline PV panels generally exhibit higher efficiency but come at a premium cost due to more energy-intensive manufacturing processes and higher purity silicon usage. Polycrystalline panels offer a more affordable alternative with slightly lower efficiency, making them a cost-effective choice for budget-conscious solar installations. The decision between the two often balances upfront cost and long-term energy yield, with polycrystalline favored in cost-sensitive projects and monocrystalline preferred where space efficiency and maximum output per panel are critical.
Lifespan and Durability Factors
Monocrystalline PV panels typically offer a longer lifespan, often exceeding 25 years, due to their uniform silicon crystal structure, which provides enhanced durability and resistance to environmental stressors. Polycrystalline panels may have a slightly shorter lifespan, generally around 20-25 years, as their multiple crystal structures can create minor vulnerabilities to temperature fluctuations and physical wear. Your choice between these types impacts long-term performance and maintenance costs, with monocrystalline usually delivering greater reliability over time.
Performance in Different Climates
Monocrystalline PV panels excel in performance under varied climatic conditions, maintaining higher efficiency in low-light and high-temperature environments. Polycrystalline PV modules typically perform better in cooler climates but may experience reduced efficiency during peak heat due to their crystalline structure. Your choice between monocrystalline and polycrystalline should consider local climate factors to optimize energy production.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Monocrystalline PV panels offer higher efficiency and longer lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing environmental waste. Polycrystalline panels require less energy to manufacture, lowering their carbon footprint during production, but their slightly lower efficiency may lead to higher overall land use. Both technologies contribute to sustainable energy solutions by reducing dependence on fossil fuels, with monocrystalline systems providing optimal long-term environmental benefits due to better performance.
Choosing the Right PV Technology for Your Needs
Monocrystalline photovoltaic (PV) panels offer higher efficiency and better performance in limited space, making them ideal for maximizing energy output on smaller rooftops. Polycrystalline PV panels generally cost less and perform well in moderate climates, providing a budget-friendly option for larger installations. Choosing the right PV technology depends on your available space, budget, and energy goals to ensure optimal solar power generation.
Monocrystalline vs Polycrystalline PV Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com