Switchgear encompasses a range of electrical devices, including circuit breakers, designed to control, protect, and isolate electrical equipment, ensuring safe power distribution. A circuit breaker specifically functions to automatically interrupt current flow during overloads or short circuits, protecting your electrical system from damage.
Table of Comparison
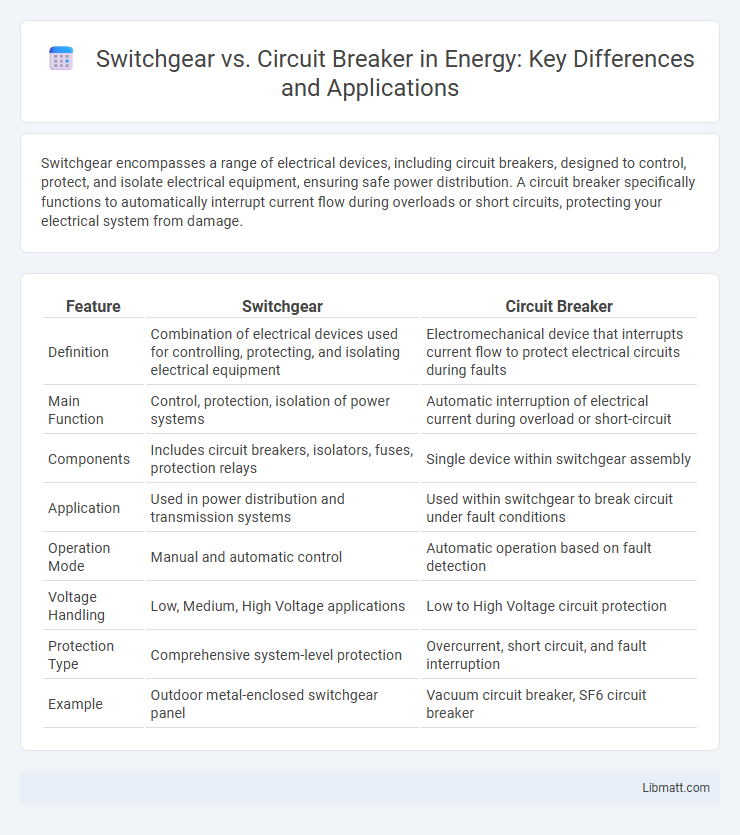
| Feature | Switchgear | Circuit Breaker |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combination of electrical devices used for controlling, protecting, and isolating electrical equipment | Electromechanical device that interrupts current flow to protect electrical circuits during faults |
| Main Function | Control, protection, isolation of power systems | Automatic interruption of electrical current during overload or short-circuit |
| Components | Includes circuit breakers, isolators, fuses, protection relays | Single device within switchgear assembly |
| Application | Used in power distribution and transmission systems | Used within switchgear to break circuit under fault conditions |
| Operation Mode | Manual and automatic control | Automatic operation based on fault detection |
| Voltage Handling | Low, Medium, High Voltage applications | Low to High Voltage circuit protection |
| Protection Type | Comprehensive system-level protection | Overcurrent, short circuit, and fault interruption |
| Example | Outdoor metal-enclosed switchgear panel | Vacuum circuit breaker, SF6 circuit breaker |
Understanding Switchgear: Definition and Functions
Switchgear refers to an integrated assembly of electrical components designed to control, protect, and isolate electrical equipment in power systems. It includes devices such as circuit breakers, switches, fuses, and relays, all working together to ensure safe and reliable operation of electrical circuits. Switchgear functions to interrupt fault currents, regulate power flow, and maintain system stability by enabling quick disconnection and isolation of electrical equipment during abnormal conditions.
Circuit Breakers Explained: Key Roles and Types
Circuit breakers are critical components in electrical systems designed to interrupt current flow and protect circuits from damage caused by overloads or short circuits. Key types include miniature circuit breakers (MCBs) for residential use, molded case circuit breakers (MCCBs) for industrial applications, and air, oil, vacuum, or SF6 circuit breakers for high-voltage systems. Understanding the specific roles of various circuit breakers ensures your electrical installations remain safe and reliable under different operating conditions.
Core Differences Between Switchgear and Circuit Breakers
Switchgear is an umbrella term encompassing a wide range of electrical devices such as fuses, relays, and circuit breakers that control, protect, and isolate electrical equipment. Circuit breakers are specific components within switchgear designed to automatically interrupt current flow during faults to protect electrical circuits from damage. The core difference lies in switchgear's broader functionality and composition, while circuit breakers focus primarily on interrupting current to ensure circuit safety.
Components and Construction: Switchgear vs Circuit Breaker
Switchgear consists of multiple components including switches, fuses, relays, and circuit breakers, designed to control, protect, and isolate electrical equipment. Circuit breakers are specific devices within switchgear with a primary function to interrupt current flow during faults, featuring components like contacts, arc quenching mechanisms, and operating mechanisms. Your choice depends on whether you need a complete control system (switchgear) or a single protective device (circuit breaker).
Applications of Switchgear in Electrical Systems
Switchgear plays a crucial role in electrical systems by controlling, protecting, and isolating electrical equipment to ensure reliable power supply and system safety. It is widely used in power generation plants, transmission and distribution networks, and industrial facilities to manage electrical faults and maintain operational continuity. The applications of switchgear include voltage regulation, fault detection, and load switching, providing essential protection for transformers, motors, and generators.
Typical Uses of Circuit Breakers in Power Distribution
Circuit breakers serve critical roles in power distribution by protecting electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits, ensuring system safety and reliability. They are typically installed at various points such as residential panels, commercial buildings, and industrial facilities to interrupt current flow during faults. Unlike switchgear, which encompasses a broader range of devices for controlling and isolating electrical equipment, circuit breakers specifically provide automatic protection and enable quick fault isolation in power networks.
Advantages and Limitations of Switchgear
Switchgear offers enhanced control and protection for electrical systems by isolating faults and enabling maintenance without disrupting the entire network, making it ideal for complex power distribution. Its advantages include improved reliability, safety, and the ability to handle high voltages, but limitations involve higher initial costs and the need for regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Your choice of switchgear should balance these benefits against budget constraints and operational requirements.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers provide reliable protection by automatically interrupting electrical flow during overloads or short circuits, enhancing safety and preventing equipment damage. They offer easy reset capabilities, allowing quick restoration of power without replacing components, which reduces downtime and maintenance costs. However, circuit breakers can be more expensive than simple fuses and may require periodic testing to ensure proper operation, which could add to maintenance efforts in your electrical system.
Safety Features: Switchgear Compared to Circuit Breakers
Switchgear offers enhanced safety features by integrating multiple protective devices, including circuit breakers, fuses, and disconnect switches, to isolate electrical equipment during faults or maintenance. Compared to individual circuit breakers, switchgear provides comprehensive fault detection, automatic isolation, and arc flash protection, reducing risks of electrical hazards and equipment damage. Your electrical system's safety is significantly improved with switchgear's coordinated protection and remote operation capabilities.
Selecting Between Switchgear and Circuit Breakers: Key Considerations
Selecting between switchgear and circuit breakers hinges on factors such as system voltage level, interrupting capacity, and application type. Switchgear provides comprehensive control, protection, and isolation for electrical equipment, making it suitable for complex power distribution systems. Circuit breakers offer focused protection by interrupting fault currents and are typically chosen for specific circuit safeguarding within the switchgear assembly or standalone installations.
Switchgear vs Circuit Breaker Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com