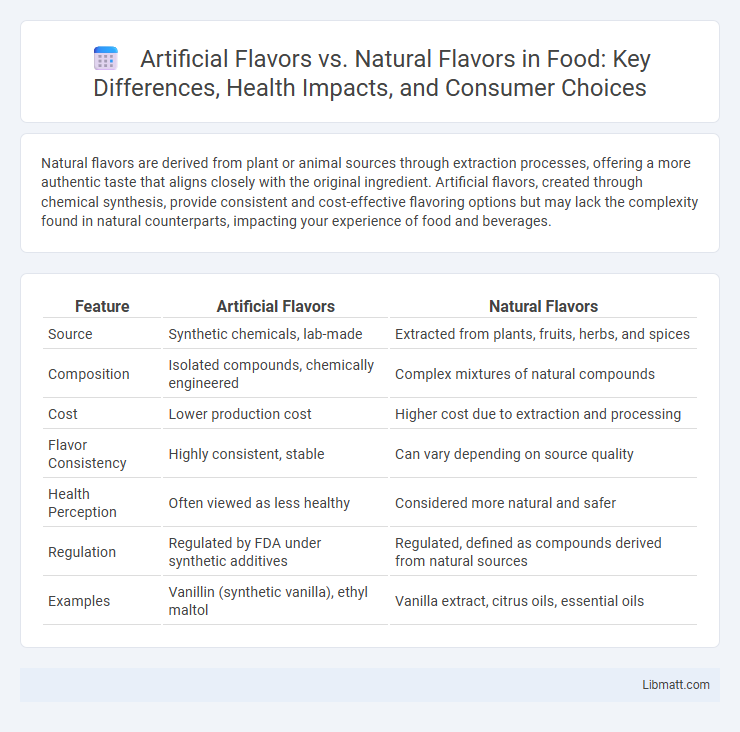
Natural flavors are derived from plant or animal sources through extraction processes, offering a more authentic taste that aligns closely with the original ingredient. Artificial flavors, created through chemical synthesis, provide consistent and cost-effective flavoring options but may lack the complexity found in natural counterparts, impacting your experience of food and beverages.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Artificial Flavors | Natural Flavors |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Synthetic chemicals, lab-made | Extracted from plants, fruits, herbs, and spices |
| Composition | Isolated compounds, chemically engineered | Complex mixtures of natural compounds |
| Cost | Lower production cost | Higher cost due to extraction and processing |
| Flavor Consistency | Highly consistent, stable | Can vary depending on source quality |
| Health Perception | Often viewed as less healthy | Considered more natural and safer |
| Regulation | Regulated by FDA under synthetic additives | Regulated, defined as compounds derived from natural sources |
| Examples | Vanillin (synthetic vanilla), ethyl maltol | Vanilla extract, citrus oils, essential oils |
Introduction to Artificial and Natural Flavors
Artificial flavors are chemically synthesized compounds designed to mimic the taste of natural ingredients, often providing a consistent and cost-effective alternative in food production. Natural flavors are derived from plant or animal sources through extraction, distillation, or other physical processes, preserving the original flavor profile of the source. Both types impact product labeling, consumer perception, and regulatory standards within the food industry.
Defining Artificial Flavors
Artificial flavors are chemically synthesized compounds designed to replicate the taste of natural ingredients by targeting specific flavor molecules. These flavors are created in laboratories using various chemical processes to mimic the sensory experience of natural foods, often allowing more consistent and intense taste profiles. Understanding the distinction between artificial and natural flavors can help you make informed choices based on ingredient transparency and dietary preferences.
What Are Natural Flavors?
Natural flavors are derived from plant or animal sources through physical processes such as distillation or extraction, preserving the original taste without chemical synthesis. These flavors are regulated by the FDA and must originate from natural ingredients like spices, fruits, or herbs, ensuring authenticity in your food products. Choosing natural flavors supports a more transparent and potentially healthier ingredient profile compared to artificial alternatives.
How Artificial Flavors Are Made
Artificial flavors are synthesized through chemical processes that replicate the molecular composition of natural flavor compounds, often using petrochemicals or fermentation byproducts as base materials. These lab-created substances are designed to mimic specific taste profiles by combining various flavoring agents like esters, aldehydes, and ketones. The production of artificial flavors allows for consistent quality, cost efficiency, and a broader range of flavor possibilities compared to natural extracts.
The Production Process of Natural Flavors
Natural flavors are extracted from plant or animal sources through methods such as distillation, solvent extraction, and fermentation to capture their authentic taste profiles. These processes preserve the original chemical compounds responsible for flavor, ensuring the essence remains true to the source. Unlike artificial flavors synthesized from chemical ingredients, natural flavor production emphasizes maintaining the integrity and complexity of native flavor molecules.
Health Implications: Artificial vs Natural Flavors
Artificial flavors often contain synthetic chemical compounds that may pose health risks such as allergic reactions, hyperactivity in children, or potential carcinogenic effects when consumed in large amounts. Natural flavors, derived from plant or animal sources, generally provide a safer alternative, although they can also trigger allergies or sensitivities in some individuals. Research highlights that minimizing exposure to artificial additives and opting for natural flavorings can contribute to better overall health outcomes and reduced risk of negative reactions.
Flavor Intensity and Consistency
Artificial flavors offer higher flavor intensity and greater consistency due to their synthetic origin, allowing precise replication of desired taste profiles in food products. Natural flavors, derived from plant or animal sources, can exhibit variability in intensity and subtle flavor nuances depending on seasonal and source differences. Manufacturers often choose artificial flavors to ensure uniform taste and stronger flavor impact across production batches, while natural flavors appeal to consumers seeking authentic ingredient sources despite potential variability.
Regulatory Guidelines and Labeling
Regulatory guidelines for artificial flavors and natural flavors differ significantly, with agencies like the FDA requiring clear labeling to distinguish these ingredients on food packaging. Natural flavors are derived from plant or animal sources and must be identified as such, whereas artificial flavors are synthesized chemicals mimicking natural taste profiles. Understanding these labeling requirements helps you make informed choices about the flavor additives in your food products.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Consumer preferences increasingly favor natural flavors due to growing awareness of health and ingredient transparency, driving a significant shift in the food and beverage industry. Market trends indicate a rising demand for clean-label products, with natural flavors capturing a larger share compared to artificial flavors, which face scrutiny over potential health concerns. This shift influences product formulations, marketing strategies, and regulatory standards emphasizing natural ingredients to meet evolving consumer expectations.
Future of Food: Innovations in Flavor Science
Innovations in flavor science are driving a shift towards more sustainable, natural, and lab-grown flavor compounds, drastically reducing reliance on artificial additives. Advances in biotechnology enable the creation of natural flavors using microbial fermentation, offering safer, more consistent, and environmentally friendly alternatives. Your food choices will increasingly benefit from these breakthroughs, blending science and nature to enhance taste while supporting health and ecological balance.
Artificial Flavors vs Natural Flavors Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com