Baking uses indirect, consistent heat to cook foods evenly and is ideal for bread, cakes, and casseroles, while roasting employs higher temperatures to create a browned, flavorful crust on meats and vegetables. Understanding these methods enhances your ability to achieve desired textures and flavors in various dishes.
Table of Comparison
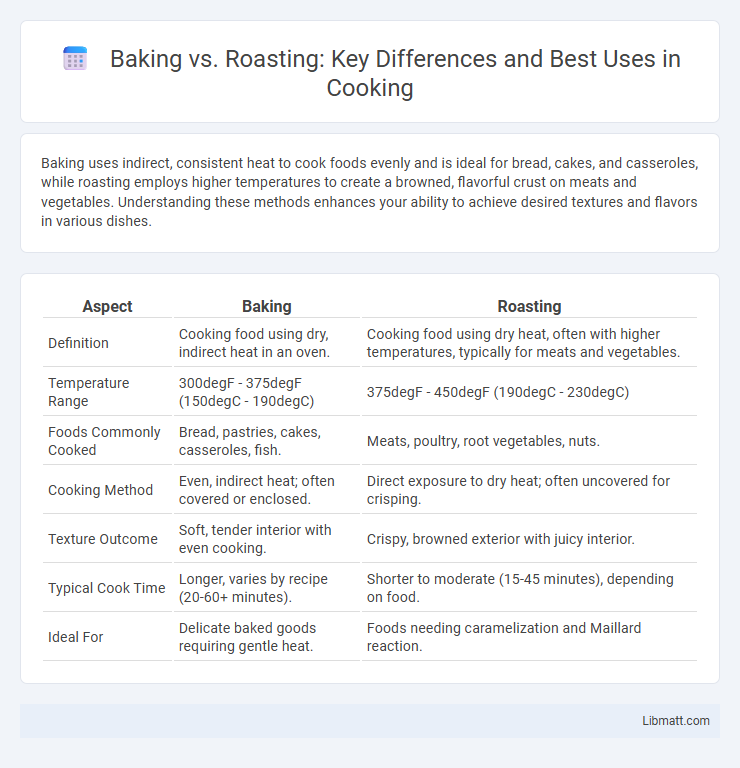
| Aspect | Baking | Roasting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cooking food using dry, indirect heat in an oven. | Cooking food using dry heat, often with higher temperatures, typically for meats and vegetables. |
| Temperature Range | 300degF - 375degF (150degC - 190degC) | 375degF - 450degF (190degC - 230degC) |
| Foods Commonly Cooked | Bread, pastries, cakes, casseroles, fish. | Meats, poultry, root vegetables, nuts. |
| Cooking Method | Even, indirect heat; often covered or enclosed. | Direct exposure to dry heat; often uncovered for crisping. |
| Texture Outcome | Soft, tender interior with even cooking. | Crispy, browned exterior with juicy interior. |
| Typical Cook Time | Longer, varies by recipe (20-60+ minutes). | Shorter to moderate (15-45 minutes), depending on food. |
| Ideal For | Delicate baked goods requiring gentle heat. | Foods needing caramelization and Maillard reaction. |
Baking vs Roasting: Key Differences Explained
Baking involves cooking food evenly using dry heat in an enclosed space, typically for bread, pastries, and casseroles, whereas roasting applies higher heat to tenderize and caramelize meats and vegetables, creating a crispy exterior. The temperature for baking generally ranges from 300degF to 375degF, while roasting uses higher temperatures, often 375degF to 450degF, to achieve browning and Maillard reactions. Understanding these key differences helps you select the best method to enhance texture and flavor in your dishes.
The Science Behind Baking and Roasting
Baking and roasting rely on dry heat cooking methods, but their scientific difference lies in temperature and food composition; baking typically uses moderate heat (300-375degF) to transform batters and dough through starch gelatinization and protein coagulation. Roasting involves higher temperatures (above 400degF) that promote Maillard reactions and caramelization, enhancing flavor and browning, especially in meats and vegetables. Both processes rely on heat transfer through air or conduction, affecting the texture, moisture content, and chemical changes within the food matrix.
Temperature and Time: What Sets Baking Apart from Roasting?
Baking usually occurs at lower temperatures ranging from 325degF to 375degF and requires longer cooking times to ensure even heat penetration, ideal for delicate items like bread and cakes. Roasting uses higher temperatures, typically between 400degF and 450degF, to achieve a browned, flavorful exterior on meats and vegetables while preserving juiciness inside. Understanding the temperature and time difference helps you choose the right method to enhance your dish's texture and flavor.
Best Foods for Baking vs Roasting
Baking is ideal for foods like bread, cakes, pastries, and casseroles, where even, moderate heat creates a soft or fluffy texture. Roasting suits vegetables, meats, and poultry, as the higher temperatures caramelize the exterior, adding a rich flavor and crispy texture. Understanding these distinctions allows you to select the best cooking method for your ingredients, enhancing flavor and texture.
Techniques: How to Bake and Roast Like a Pro
Master baking by maintaining consistent oven temperature between 325degF and 375degF, using dry, indirect heat ideal for breads, cakes, and pastries that require even rising and browning. Roasting demands higher heat, typically between 400degF and 450degF, to caramelize the surface of meats and vegetables, enhancing flavor through Maillard reactions. You can perfect these techniques by using accurate oven thermometers, proper rack placement, and monitoring internal food temperatures with a reliable meat thermometer for optimal doneness.
Texture and Flavor: What to Expect from Each Method
Baking produces a tender, evenly cooked texture by surrounding food with indirect, consistent heat, often resulting in moist interiors and soft crusts ideal for breads and cakes. Roasting uses higher temperatures and direct dry heat, creating a caramelized, crispy exterior with intensified, deeper flavors suitable for meats and vegetables. Expect baking to preserve moisture and subtle flavors, while roasting enhances Maillard reactions, generating richer, browned surfaces and complex taste profiles.
Nutritional Impact: Baking vs Roasting
Baking preserves more nutrients in vegetables compared to roasting, as it typically uses lower temperatures and less direct heat exposure. Roasting can enhance flavor through caramelization but may cause slight nutrient loss, especially in heat-sensitive vitamins like vitamin C. You can optimize your nutrient intake by choosing baking when prioritizing nutritional value and roasting when aiming for richer taste and texture.
Equipment Essentials for Baking and Roasting
Oven temperature control and proper cookware are essential for both baking and roasting, with baking requiring consistent low to moderate heat and roasting needing higher temperatures. Baking typically uses flat, rimmed baking sheets or cake pans designed for even heat distribution, while roasting demands sturdy roasting pans or racks that allow air circulation around meats and vegetables. Reliable oven thermometers and heat-resistant gloves are crucial tools to ensure precision and safety in both cooking methods.
Common Mistakes When Baking and Roasting
Common mistakes when baking and roasting include incorrect temperature settings and improper timing, which can lead to undercooked or burnt dishes. You might also overlook the importance of preheating the oven or using the wrong cookware, both critical for even heat distribution. Ensuring accurate measurements and monitoring the cooking process closely can dramatically improve your results.
Expert Tips: Choosing Between Baking and Roasting
Expert tips for choosing between baking and roasting emphasize temperature and food type: baking uses lower, consistent heat ideal for delicate items like cakes and breads, while roasting applies higher heat to develop caramelization and crispiness in vegetables and meats. Consider the desired texture and moisture retention, as baking maintains softness whereas roasting enhances flavor through browning. Equipment choice also matters; baking typically requires an oven set to around 325-375degF, and roasting benefits from 400degF or higher for optimal results.
Baking vs Roasting Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com