Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the root zone, minimizing wastage and enhancing water efficiency for your plants, while sprinkler irrigation covers a broader area by spraying water over the soil surface, suitable for lawns and crops requiring uniform moisture. Choosing the right system depends on factors like water availability, crop type, and field size to optimize irrigation effectiveness and conserve resources.
Table of Comparison
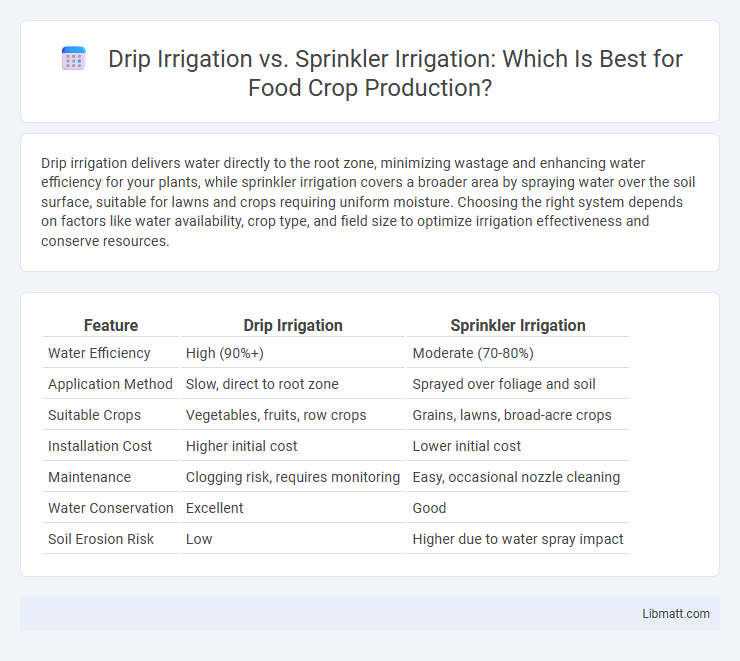
| Feature | Drip Irrigation | Sprinkler Irrigation |
|---|---|---|
| Water Efficiency | High (90%+) | Moderate (70-80%) |
| Application Method | Slow, direct to root zone | Sprayed over foliage and soil |
| Suitable Crops | Vegetables, fruits, row crops | Grains, lawns, broad-acre crops |
| Installation Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Maintenance | Clogging risk, requires monitoring | Easy, occasional nozzle cleaning |
| Water Conservation | Excellent | Good |
| Soil Erosion Risk | Low | Higher due to water spray impact |
Introduction to Irrigation Systems
Drip irrigation conserves water by delivering moisture directly to plant roots through a network of tubes and emitters, enhancing efficiency and reducing evaporation. Sprinkler irrigation mimics natural rainfall by distributing water over the soil surface via overhead nozzles, making it suitable for a wide range of crops and terrains. Understanding these irrigation systems helps you select the best method tailored to your agricultural needs and water availability.
Overview of Drip Irrigation
Drip irrigation is a water-efficient agricultural technique that delivers water directly to the root zone of plants through a network of valves, pipes, tubing, and emitters. This system minimizes evaporation and runoff by providing slow, precise irrigation tailored to the specific water needs of crops. Widely used in arid regions and high-value crop production, drip irrigation enhances plant health and conserves water resources compared to traditional sprinkler systems.
Overview of Sprinkler Irrigation
Sprinkler irrigation uses a system of pipes and spray heads to distribute water over crops, mimicking natural rainfall. It is highly effective for various land types and crop patterns, providing uniform water coverage and reducing labor costs. Your choice of sprinkler irrigation can enhance water efficiency and improve crop yields by targeting large areas with controlled water application.
Water Efficiency Comparison
Drip irrigation offers superior water efficiency by delivering water directly to the root zone, reducing evaporation and runoff significantly compared to sprinkler irrigation, which disperses water over a larger area and often results in higher water loss. Studies show drip systems can save up to 50% more water than sprinklers, making them ideal for arid regions and conserving water resources. Sprinkler irrigation, although less efficient, is better suited for uniform coverage of large fields but typically consumes 20-30% more water due to evaporation and wind drift.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Drip irrigation systems demand precise installation involving tubing, emitters, and pressure regulators to ensure water reaches plant roots efficiently, while sprinkler irrigation setups require positioning sprinkler heads and connecting pipes for broad water coverage. Maintenance for drip systems includes regular emitter cleaning to prevent clogging and occasional tube inspections, whereas sprinkler systems need routine checks for nozzle clogs, alignment, and potential leaks. Understanding these installation and upkeep differences helps you choose the irrigation method best suited to your agricultural or landscaping needs, optimizing water use and system longevity.
Cost Analysis: Drip vs Sprinkler
Drip irrigation systems typically have higher initial installation costs due to extensive tubing and emitter requirements but offer lower long-term water and energy expenses by delivering water directly to plant roots. Sprinkler irrigation involves moderate setup costs with greater water loss from evaporation and runoff, potentially increasing operational costs over time. Analyzing total cost of ownership reveals drip irrigation's efficiency often leads to better return on investment in water-scarce regions compared to sprinkler systems.
Suitability for Different Crops
Drip irrigation is highly suitable for row crops, fruit trees, and vegetables that require precise water delivery directly to the root zone, minimizing water wastage and promoting healthier plant growth. Sprinkler irrigation works best for field crops, lawns, and cereals where uniform water distribution over a large area is necessary. Your choice between drip and sprinkler irrigation depends on the crop type, soil conditions, and water efficiency needs.
Impact on Soil Health
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the plant roots, minimizing soil erosion and reducing nutrient runoff, which enhances soil structure and microbial activity. Sprinkler irrigation, while efficient for broad coverage, can cause surface runoff and soil compaction, potentially leading to decreased soil aeration and increased erosion risk. Maintaining optimal soil health is crucial for sustainable agriculture, and drip irrigation offers significant advantages in preserving soil integrity and moisture balance.
Environmental Considerations
Drip irrigation conserves water by delivering moisture directly to plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff, which significantly reduces water wastage compared to sprinkler irrigation. Sprinkler systems often cause higher water loss through evaporation and wind drift, making them less efficient in arid environments. Your choice between these methods impacts water sustainability and soil health, with drip irrigation offering superior environmental benefits for conserving resources.
Choosing the Right Irrigation System
Choosing the right irrigation system depends on factors like crop type, soil characteristics, and water availability; drip irrigation offers targeted water delivery, minimizing evaporation and runoff, which suits row crops and orchards. Sprinkler irrigation provides broader coverage, ideal for lawns, gardens, and varied terrain, but may result in higher water loss through evaporation and wind drift. Evaluating water efficiency, installation costs, and maintenance needs ensures optimal irrigation system selection for sustainable water management.
Drip Irrigation vs Sprinkler Irrigation Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com