Cold chain ensures the uninterrupted refrigeration of temperature-sensitive products like vaccines and perishable foods during storage and transportation, preserving their efficacy and safety. Warm chain, in contrast, maintains products such as certain fruits and vegetables within a specific warm temperature range to prevent chilling injuries, optimizing freshness without the risks associated with cold exposure.
Table of Comparison
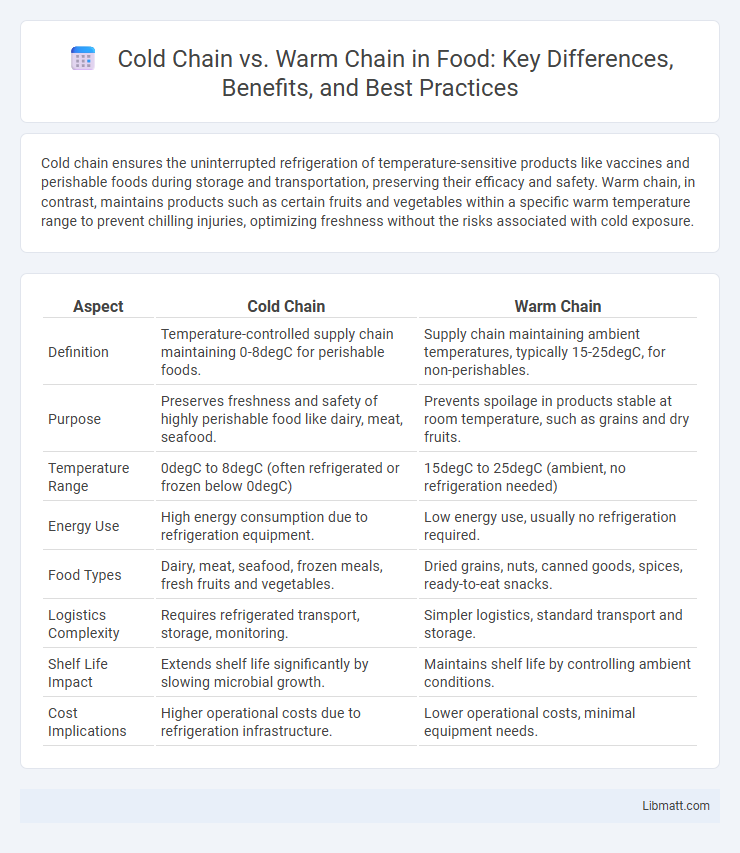
| Aspect | Cold Chain | Warm Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temperature-controlled supply chain maintaining 0-8degC for perishable foods. | Supply chain maintaining ambient temperatures, typically 15-25degC, for non-perishables. |
| Purpose | Preserves freshness and safety of highly perishable food like dairy, meat, seafood. | Prevents spoilage in products stable at room temperature, such as grains and dry fruits. |
| Temperature Range | 0degC to 8degC (often refrigerated or frozen below 0degC) | 15degC to 25degC (ambient, no refrigeration needed) |
| Energy Use | High energy consumption due to refrigeration equipment. | Low energy use, usually no refrigeration required. |
| Food Types | Dairy, meat, seafood, frozen meals, fresh fruits and vegetables. | Dried grains, nuts, canned goods, spices, ready-to-eat snacks. |
| Logistics Complexity | Requires refrigerated transport, storage, monitoring. | Simpler logistics, standard transport and storage. |
| Shelf Life Impact | Extends shelf life significantly by slowing microbial growth. | Maintains shelf life by controlling ambient conditions. |
| Cost Implications | Higher operational costs due to refrigeration infrastructure. | Lower operational costs, minimal equipment needs. |
Introduction to Cold Chain and Warm Chain
Cold Chain and Warm Chain are specialized logistics systems designed to maintain temperature-sensitive products throughout storage and transportation. The Cold Chain actively preserves items like vaccines and perishable foods at low temperatures, typically between 2degC and 8degC, ensuring product efficacy and safety. Warm Chain complements this by sustaining products that require a stable ambient temperature range, generally between 20degC and 25degC, crucial for goods like certain pharmaceuticals and fresh produce to remain viable.
Definitions: What is Cold Chain?
The Cold Chain is a temperature-controlled supply chain designed to preserve and extend the shelf life of perishable products such as pharmaceuticals, food, and chemicals by maintaining specific low-temperature ranges throughout storage, transportation, and distribution. It involves specialized equipment like refrigerated trucks, cold storage warehouses, and temperature monitoring systems to ensure product integrity and prevent spoilage. Maintaining a consistent cold chain reduces the risk of microbial growth and chemical degradation, ensuring safety and efficacy of temperature-sensitive goods.
Definitions: What is Warm Chain?
Warm Chain refers to a supply chain process designed to maintain products, especially perishable goods or pharmaceuticals, within a controlled temperature range above freezing but below room temperature, typically between 2degC and 8degC. Unlike the Cold Chain, which requires continuous refrigeration at near-freezing temperatures, the Warm Chain ensures product quality and safety through moderate temperature control to prevent spoilage or degradation. This system is crucial for items such as certain vaccines, fresh produce, and dairy products that are sensitive to both freezing and excessive heat.
Key Differences Between Cold Chain and Warm Chain
Cold chain involves temperature-controlled supply chains typically maintained between 2degC and 8degC to preserve perishable items like vaccines and seafood, whereas warm chain operates at ambient or slightly elevated temperatures for products such as fresh produce and pharmaceuticals sensitive to freezing. The primary difference lies in the required temperature range and handling protocols, with cold chain emphasizing refrigeration and warm chain focusing on protection from heat and humidity. Your choice between cold and warm chain logistics depends on the specific temperature sensitivity and stability of the goods being transported.
Importance in Pharmaceutical Logistics
Cold chain logistics ensures the integrity of temperature-sensitive pharmaceuticals by maintaining a controlled environment from production to delivery, preventing degradation and preserving efficacy. Warm chain logistics supports drugs that require stable, non-refrigerated conditions, essential for products like certain vaccines and oral medications. Effective management of both cold and warm chains is critical to safeguarding drug quality, regulatory compliance, and patient safety in pharmaceutical supply chains.
Role in Food Supply and Safety
Cold Chain and Warm Chain systems play crucial roles in maintaining food supply and safety by controlling temperature-sensitive environments during storage and transportation. The Cold Chain preserves perishable items like dairy, meat, and seafood at low temperatures to prevent microbial growth and spoilage, while the Warm Chain manages products such as fruits, vegetables, and certain pharmaceuticals that require ambient temperature conditions to maintain quality. Ensuring the correct chain is followed minimizes foodborne illness risks and reduces waste, safeguarding Your supply from farm to table.
Temperature Control Requirements
Cold Chain systems require strict temperature control typically ranging from 2degC to 8degC to preserve perishable goods like vaccines, pharmaceuticals, and fresh food during transportation and storage. Warm Chain logistics allow for higher temperature ranges, often between 8degC and 25degC, suitable for products that can withstand mild temperature variations without spoilage. Understanding your product's specific temperature control requirements ensures effective preservation and compliance with regulatory standards.
Cost Implications and Efficiency
Cold chain logistics require significant investment in refrigeration equipment and energy consumption, driving higher operational costs compared to warm chain systems. Warm chain solutions often reduce expenses by maintaining moderate temperature ranges, lowering energy use and simplifying storage requirements. Your choice between cold chain and warm chain directly impacts overall efficiency, with cold chain ensuring product integrity for temperature-sensitive goods but at increased cost, while warm chain offers cost-effective handling for less sensitive items.
Technological Innovations in Cold and Warm Chains
Technological innovations in cold chain systems include IoT-based temperature sensors, real-time monitoring, and AI-driven predictive analytics that ensure optimal conditions for perishable goods. Warm chain advancements feature smart packaging, phase change materials, and automated tracking to maintain temperature-sensitive products without strict refrigeration. Your supply chain can benefit significantly from integrating these technologies, enhancing product quality and reducing spoilage.
Future Trends and Challenges
Future trends in cold chain logistics include increased adoption of IoT sensors for real-time temperature monitoring and AI-driven predictive analytics to enhance supply chain efficiency. Challenges involve managing energy consumption and environmental impact while ensuring compliance with stringent regulatory standards for temperature-sensitive pharmaceuticals and perishables. Growth in warm chain technology focuses on maintaining optimal conditions for products like fresh produce and vaccines, addressing shelf-life extension and minimizing waste.
Cold Chain vs Warm Chain Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com