Controlled thawing ensures a consistent and safe temperature environment that minimizes microbial growth and preserves food quality, while ambient thawing exposes food to fluctuating temperatures, increasing the risk of bacterial contamination and spoilage. Your choice between these methods significantly impacts food safety and texture retention during the thawing process.
Table of Comparison
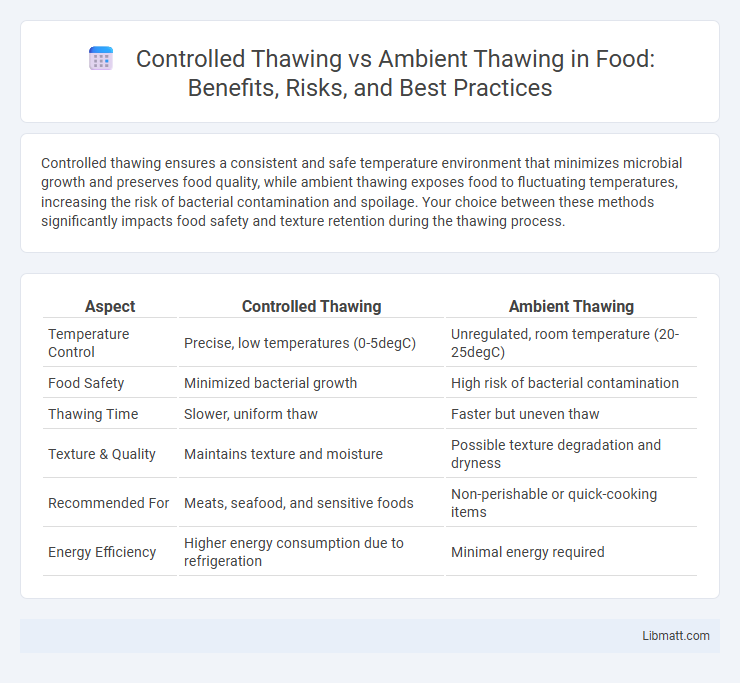
| Aspect | Controlled Thawing | Ambient Thawing |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Precise, low temperatures (0-5degC) | Unregulated, room temperature (20-25degC) |
| Food Safety | Minimized bacterial growth | High risk of bacterial contamination |
| Thawing Time | Slower, uniform thaw | Faster but uneven thaw |
| Texture & Quality | Maintains texture and moisture | Possible texture degradation and dryness |
| Recommended For | Meats, seafood, and sensitive foods | Non-perishable or quick-cooking items |
| Energy Efficiency | Higher energy consumption due to refrigeration | Minimal energy required |
Introduction to Thawing Methods
Controlled thawing maintains precise temperature settings to ensure safe and uniform thawing of frozen products, reducing the risk of bacterial growth and preserving quality. Ambient thawing occurs at room temperature, which can lead to uneven thawing and increased microbial activity, potentially compromising food safety. Understanding these thawing methods helps you select the optimal process for maintaining product integrity and safety.
What is Controlled Thawing?
Controlled thawing is a precise method of defrosting food by maintaining consistent, safe temperatures, typically between 33degF and 40degF (0.5degC to 4.4degC), to prevent bacterial growth and preserve quality. This technique often involves using specialized equipment like refrigerated chambers or water thawing systems with regulated temperature control. Controlled thawing reduces the risk of foodborne pathogens compared to ambient thawing, which occurs at room temperature and can allow harmful bacteria to multiply rapidly.
Understanding Ambient Thawing
Ambient thawing involves defrosting food at room temperature, which can lead to uneven thawing and increased risk of bacterial growth. Controlled thawing uses precise temperature regulation to ensure food thaws evenly, preserving quality and safety. Understanding ambient thawing helps you make safer, more informed decisions about food handling and preparation.
Key Differences Between Controlled and Ambient Thawing
Controlled thawing regulates temperature and environment to ensure consistent and safe defrosting, minimizing microbial growth and preserving food quality. Ambient thawing relies on room temperature, which can cause uneven thawing and increase the risk of bacterial contamination. Choosing controlled thawing helps maintain product safety and quality, especially for perishable items.
Impact on Product Quality
Controlled thawing minimizes microbial growth and preserves texture by maintaining consistent temperatures, which significantly reduces the risk of spoilage and enhances product safety. Ambient thawing accelerates deterioration through uneven temperature exposure, causing drip loss, texture degradation, and potential spoilage. Your choice of thawing method directly affects the integrity and shelf life of food products, making controlled thawing essential for maintaining optimum quality.
Food Safety Considerations
Controlled thawing maintains consistent low temperatures, minimizing bacterial growth and preserving food safety by reducing time spent in the temperature danger zone (40degF to 140degF). Ambient thawing exposes food to fluctuating temperatures, increasing the risk of pathogen proliferation and potential foodborne illnesses. Proper thawing methods, such as refrigeration or controlled thawing equipment, are critical to ensuring safe consumption and preventing contamination.
Thawing Efficiency and Speed
Controlled thawing significantly improves thawing efficiency and speed by maintaining consistent temperatures that minimize cellular damage and reduce thawing time. Ambient thawing relies on room temperature conditions, which can lead to uneven warming and prolong the overall thawing process. Optimizing your thawing method with controlled environments ensures faster, safer results for sensitive items like frozen food or biological samples.
Energy Consumption and Costs
Controlled thawing uses precise temperature regulation to minimize energy consumption compared to ambient thawing, which often relies on fluctuating room temperatures and can lead to higher energy waste. Your facility can reduce operational costs by investing in controlled thawing systems that optimize energy use while maintaining consistent thawing conditions. Energy-efficient thawing methods lower utility bills and decrease environmental impact, providing long-term cost savings in food processing or storage environments.
Best Practices for Thawing Methods
Controlled thawing ensures food safety by maintaining temperatures between 1degC and 4degC, preventing bacterial growth during the thawing process. Ambient thawing at room temperature (above 4degC) increases the risk of microbial contamination and uneven thawing, compromising food quality and safety. Best practices prioritize controlled thawing methods such as refrigeration, cold water immersion, or microwave thawing to minimize pathogen development and preserve texture and flavor.
Choosing the Right Thawing Method for Your Needs
Controlled thawing uses precise temperature settings to maintain food safety and quality, minimizing bacterial growth and preserving texture, especially important for meats and seafood. Ambient thawing, typically done at room temperature, is faster but increases the risk of uneven thawing and microbial contamination, making it less suitable for prolonged durations or sensitive items. Selecting the appropriate thawing method depends on factors like food type, time constraints, and safety requirements, with controlled thawing favored in professional kitchens and ambient thawing reserved for immediate use scenarios.
controlled thawing vs ambient thawing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com