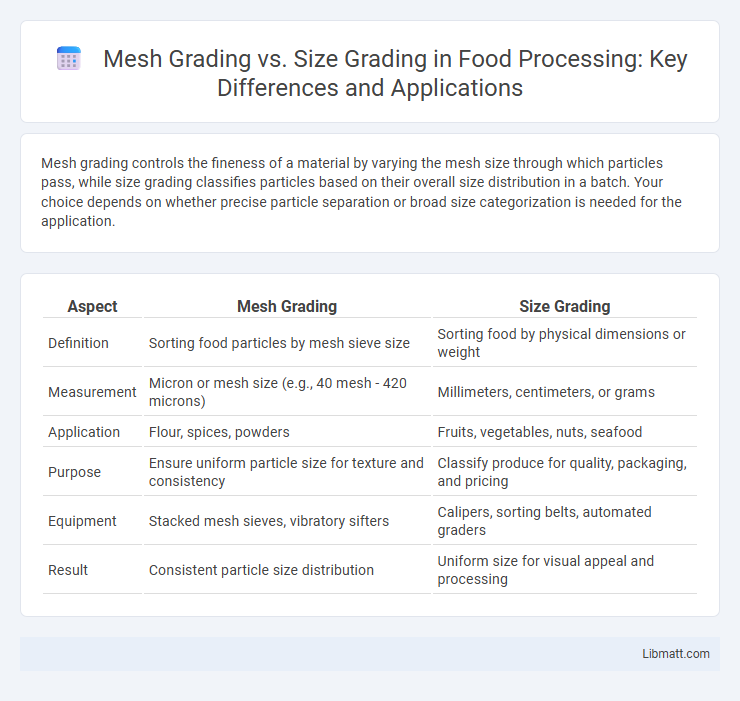
Mesh grading controls the fineness of a material by varying the mesh size through which particles pass, while size grading classifies particles based on their overall size distribution in a batch. Your choice depends on whether precise particle separation or broad size categorization is needed for the application.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Mesh Grading | Size Grading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sorting food particles by mesh sieve size | Sorting food by physical dimensions or weight |
| Measurement | Micron or mesh size (e.g., 40 mesh - 420 microns) | Millimeters, centimeters, or grams |
| Application | Flour, spices, powders | Fruits, vegetables, nuts, seafood |
| Purpose | Ensure uniform particle size for texture and consistency | Classify produce for quality, packaging, and pricing |
| Equipment | Stacked mesh sieves, vibratory sifters | Calipers, sorting belts, automated graders |
| Result | Consistent particle size distribution | Uniform size for visual appeal and processing |
Introduction to Mesh Grading and Size Grading
Mesh grading segments a 3D model into smaller uniform cells or polygons, enabling precise manipulation of geometric detail for computer graphics and finite element analysis. Size grading alters the dimensions of mesh elements progressively, optimizing computational resources by refining areas requiring higher accuracy and coarsening less critical regions. Both techniques enhance model efficiency, balancing visual fidelity and processing performance.
Definition of Mesh Grading
Mesh grading refers to the categorization of materials based on the number of openings per linear inch in a mesh screen, which determines particle size distribution and filtration effectiveness. Size grading, by contrast, classifies particles or materials according to their physical dimensions or diameter without considering the mesh screen specifications. Mesh grading is crucial for industries like construction and mining, where precise control over particle size separation impacts product quality and process efficiency.
What is Size Grading?
Size grading is the process of adjusting patterns or molds to create a range of sizes for a product, ensuring a consistent fit across different dimensions. It involves systematically increasing or decreasing specific measurements, such as length, width, and circumference, based on a base size. Your product benefits from accurate size grading by achieving a balanced fit that meets diverse customer body shapes and sizing standards.
Key Differences Between Mesh Grading and Size Grading
Mesh grading involves adjusting the dimensions of a pattern using a grid of intersecting lines, allowing precise control over the shape and contour changes, while size grading scales the entire pattern up or down uniformly to create different sizes. Mesh grading is ideal for complex designs requiring variable adjustments at specific points, enhancing fit and style, whereas size grading is simpler and more suited for standard size increments. The key difference lies in the level of control and customization mesh grading offers compared to the proportionate resizing approach of size grading.
Applications of Mesh Grading in Industry
Mesh grading is widely applied in industries such as filtration, aerospace, and electronics, where variable particle size separation and controlled porosity are crucial. Its ability to provide gradual changes in mesh size enhances efficiency in sorting, sieving, and material separation processes compared to uniform size grading. You benefit from improved product quality and process optimization by using mesh grading tailored to specific industrial applications.
Common Uses of Size Grading
Size grading is largely used in the apparel and footwear industries to create consistent product variations across different dimensions such as length, width, and height, ensuring each size meets specific body measurement standards. This method helps manufacturers efficiently scale designs while maintaining proportion and fit for diverse consumer groups. Your product development process benefits from size grading by enabling accurate replication of base patterns into multiple sizes, reducing material waste and production time.
Advantages of Mesh Grading
Mesh grading offers superior control over particle distribution, enhancing uniformity and reducing segregation in concrete mixes. This method improves packing density, which leads to higher strength and durability of the final product. Mesh grading also optimizes material usage by facilitating better blending of aggregates based on size ranges, minimizing voids and maximizing the performance characteristics of the mix.
Benefits of Size Grading
Size grading enhances garment fit by accommodating various body shapes through incremental adjustments in pattern dimensions, leading to improved comfort and appearance. This method reduces production waste and inventory costs by standardizing sizes while maintaining design integrity. Size grading also simplifies manufacturing processes, allowing for efficient scaling of clothing lines across multiple size ranges without compromising quality.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Mesh and Size Grading
When choosing between mesh grading and size grading, factors such as the product's weight variation, packaging requirements, and target market preferences play crucial roles. Mesh grading offers uniformity by sorting particles through standardized sieve sizes, ideal for granular materials requiring precise grading, while size grading focuses on categorizing items based on dimensional attributes, suitable for products like apparel or manufactured parts. Consider production efficiency, cost implications, and the desired accuracy of grading to determine the most effective method for specific industry applications.
Conclusion: Mesh Grading vs Size Grading
Mesh grading offers precise control over the distribution of particle sizes, enhancing material separation efficiency, while size grading focuses on categorizing particles into uniform size ranges for consistent downstream processing. Your choice between mesh grading and size grading depends on specific application needs, such as desired particle uniformity or separation accuracy. Understanding the fundamental differences helps optimize process outcomes in industries like mining, pharmaceuticals, and construction.
mesh grading vs size grading Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com