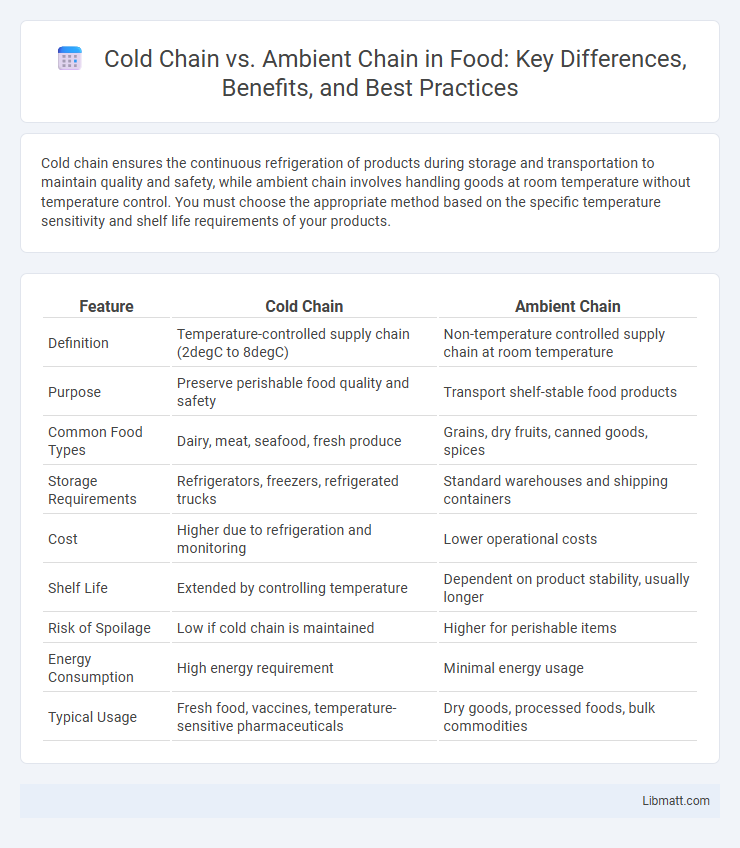
Cold chain ensures the continuous refrigeration of products during storage and transportation to maintain quality and safety, while ambient chain involves handling goods at room temperature without temperature control. You must choose the appropriate method based on the specific temperature sensitivity and shelf life requirements of your products.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cold Chain | Ambient Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temperature-controlled supply chain (2degC to 8degC) | Non-temperature controlled supply chain at room temperature |
| Purpose | Preserve perishable food quality and safety | Transport shelf-stable food products |
| Common Food Types | Dairy, meat, seafood, fresh produce | Grains, dry fruits, canned goods, spices |
| Storage Requirements | Refrigerators, freezers, refrigerated trucks | Standard warehouses and shipping containers |
| Cost | Higher due to refrigeration and monitoring | Lower operational costs |
| Shelf Life | Extended by controlling temperature | Dependent on product stability, usually longer |
| Risk of Spoilage | Low if cold chain is maintained | Higher for perishable items |
| Energy Consumption | High energy requirement | Minimal energy usage |
| Typical Usage | Fresh food, vaccines, temperature-sensitive pharmaceuticals | Dry goods, processed foods, bulk commodities |
Introduction to Cold Chain and Ambient Chain
Cold chain logistics involves the transportation and storage of temperature-sensitive products such as pharmaceuticals, perishable foods, and vaccines, maintaining a controlled environment typically between 2degC and 8degC to ensure product integrity and safety. Ambient chain logistics, by contrast, manages goods that are stable at room temperature, eliminating the need for refrigeration but requiring careful handling to prevent exposure to extreme heat, humidity, or contamination. Both chains are critical components of supply chain management, with cold chain emphasizing temperature control and ambient chain focusing on protecting products under standard environmental conditions.
Key Differences Between Cold Chain and Ambient Chain
Cold chain logistics involve maintaining products at specific low temperatures, typically between 2degC and 8degC, to preserve the quality and safety of perishable goods like pharmaceuticals and food. Ambient chain refers to the storage and transportation of goods at room temperature, usually between 15degC and 25degC, suitable for non-perishable products. Your choice between cold chain and ambient chain depends on the temperature sensitivity of the product and the required shelf life.
Importance of Temperature Control in Logistics
Temperature control in logistics is critical for preserving product quality and safety, especially for pharmaceuticals, perishable foods, and sensitive chemicals. Cold chain systems maintain a consistent temperature range, typically between 2degC and 8degC, to prevent spoilage, microbial growth, and degradation. In contrast, ambient chain logistics handle products stable at room temperature, reducing costs but requiring careful monitoring to avoid temperature excursions that could compromise integrity.
Industries Relying on Cold Chain Solutions
Pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and food industries heavily rely on cold chain solutions to maintain product integrity and prevent spoilage. Vaccines, biologics, frozen foods, and perishable goods require stringent temperature control throughout transportation and storage. Cold chain logistics ensure regulatory compliance, reduce waste, and preserve efficacy across healthcare and food supply sectors.
Applications of Ambient Chain Logistics
Ambient chain logistics specializes in the storage and transportation of non-perishable goods such as canned foods, dry goods, and household products that do not require temperature control. This method supports efficient supply chains by reducing energy costs and simplifying handling procedures compared to cold chain logistics. Your business can benefit from ambient chain logistics by ensuring product integrity while optimizing operational expenditures in sectors like retail, pharmaceuticals, and consumer packaged goods.
Cost Comparison: Cold Chain vs Ambient Chain
Cold Chain logistics incur higher costs due to specialized refrigeration equipment, temperature monitoring, and energy consumption essential for maintaining controlled environments. Ambient Chain systems significantly reduce expenses by eliminating the need for cooling infrastructure, resulting in lower operational and transportation costs. However, product sensitivity and shelf-life requirements typically justify the premium investment in Cold Chain for temperature-sensitive goods.
Challenges in Cold Chain Management
Cold chain management involves maintaining products at specific low temperatures to ensure quality and safety, presenting challenges such as high energy costs, risk of temperature fluctuations, and complex logistics coordination. Ambient chain management, by contrast, deals with products stable at room temperature, requiring less stringent controls but still demanding careful handling to prevent contamination or spoilage. You must rely on robust monitoring systems and contingency plans to overcome cold chain vulnerabilities and ensure product integrity throughout transportation and storage.
Advancements in Ambient Chain Technology
Recent advancements in ambient chain technology have revolutionized supply chain logistics by enabling temperature-sensitive products to be stored and transported without refrigeration, reducing costs and environmental impact. Innovative materials such as temperature-stabilizing packaging and phase-change insulation enhance product integrity across diverse conditions. Your business can now leverage these technologies to achieve more efficient, sustainable distribution while maintaining safety and quality standards.
Regulatory Compliance for Both Chains
Cold chain regulatory compliance requires strict adherence to temperature-controlled storage and transportation standards established by agencies such as the FDA, WHO, and EMA to ensure product efficacy and safety. Ambient chain compliance focuses on maintaining consistent environmental conditions as specified by product labels and relevant guidelines, with oversight from organizations including the ICH and ISO. Both chains demand comprehensive documentation, monitoring systems, and validation protocols to meet international pharmaceutical and food safety regulations.
Future Trends in Temperature-Controlled Logistics
Future trends in temperature-controlled logistics emphasize advanced IoT sensors and blockchain technology to enhance real-time monitoring and data transparency in both cold chain and ambient chain systems. Innovations in sustainable packaging and energy-efficient refrigeration units aim to reduce carbon footprints while maintaining precise temperature controls from production to delivery. Increased integration of AI-driven predictive analytics optimizes route planning and inventory management, minimizing spoilage and ensuring compliance with stringent regulatory standards.
Cold Chain vs Ambient Chain Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com