A HACCP plan focuses on identifying and controlling physical, chemical, and biological hazards in food production through preventive measures, while a HARPC plan emphasizes hazard analysis and risk-based preventive controls for all potential hazards throughout the food supply chain. You can choose between them based on whether your priority is traditional food safety protocols (HACCP) or a broader risk-based approach required by the FDA under FSMA for preventive controls.
Table of Comparison
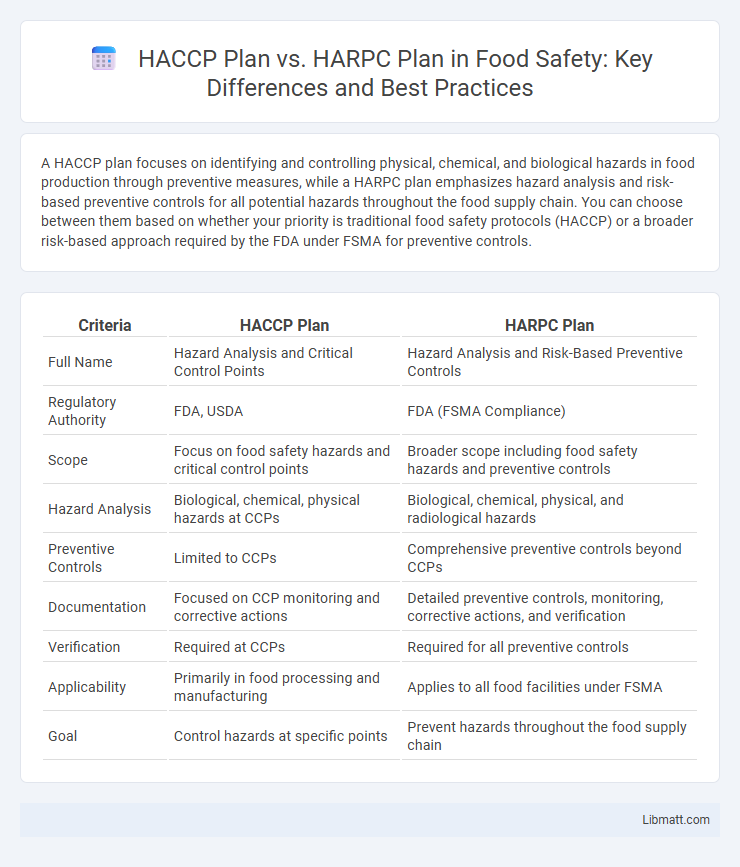
| Criteria | HACCP Plan | HARPC Plan |
|---|---|---|
| Full Name | Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points | Hazard Analysis and Risk-Based Preventive Controls |
| Regulatory Authority | FDA, USDA | FDA (FSMA Compliance) |
| Scope | Focus on food safety hazards and critical control points | Broader scope including food safety hazards and preventive controls |
| Hazard Analysis | Biological, chemical, physical hazards at CCPs | Biological, chemical, physical, and radiological hazards |
| Preventive Controls | Limited to CCPs | Comprehensive preventive controls beyond CCPs |
| Documentation | Focused on CCP monitoring and corrective actions | Detailed preventive controls, monitoring, corrective actions, and verification |
| Verification | Required at CCPs | Required for all preventive controls |
| Applicability | Primarily in food processing and manufacturing | Applies to all food facilities under FSMA |
| Goal | Control hazards at specific points | Prevent hazards throughout the food supply chain |
Understanding HACCP: Definition and Core Principles
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) is a systematic approach to food safety that identifies, evaluates, and controls hazards throughout the food production process. Its core principles include conducting hazard analysis, determining critical control points, establishing critical limits, monitoring procedures, corrective actions, verification, and record-keeping. Your HACCP plan ensures proactive risk management to prevent contamination and protect consumer health.
What is HARPC? Overview and Key Requirements
HARPC (Hazard Analysis and Risk-Based Preventive Controls) is a food safety plan mandated by the FDA under the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) requiring facilities to identify and evaluate known or reasonably foreseeable hazards in their production processes. Key requirements of HARPC include conducting a thorough hazard analysis, implementing preventive controls to mitigate identified risks, monitoring the effectiveness of these controls, and maintaining detailed records to ensure food safety compliance. Your HARPC plan must be tailored to address chemical, biological, and physical hazards throughout every stage of your food production to effectively prevent contamination and protect consumer health.
Regulatory Background: HACCP vs HARPC
HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point) is a regulatory framework established by the FDA and USDA primarily for food safety, focusing on identifying and controlling biological, chemical, and physical hazards in the food production process. HARPC (Hazard Analysis Risk-Based Preventive Controls), mandated by the FDA under the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) of 2011, expands on HACCP principles by requiring comprehensive risk-based preventive controls across the entire food supply chain, emphasizing proactive measures over reactive corrections. Unlike HACCP's process-specific control points, HARPC mandates written plans with detailed preventive controls, monitoring, corrective actions, and verification procedures to enhance compliance with modern food safety regulations.
Industries and Applications: Who Uses Each Plan?
HACCP plans are predominantly utilized in food manufacturing, processing, and service industries to identify and control critical points in food safety. HARPC plans are mandated for all food facilities under the FDA, including food ingredient suppliers, packaging manufacturers, and storage facilities, emphasizing hazard prevention across broader supply chains. Both plans target compliance and risk management but serve distinct regulatory scopes and operational focuses within the food industry.
Key Components: HACCP Plan Structure
HACCP Plan structure consists of seven key components: hazard analysis, critical control points identification, establishing critical limits, monitoring procedures, corrective actions, verification processes, and record-keeping. These components systematically ensure food safety by preventing, eliminating, or reducing hazards to acceptable levels. Your HACCP Plan provides a thorough framework for identifying risks and maintaining consistent control throughout the food production process.
Essential Elements: HARPC Plan Framework
HARPC Plan framework centers on identifying and evaluating all potential hazards across food production by conducting thorough hazard analysis, which includes biological, chemical, physical, and radiological risks. It requires the implementation of risk-based preventive controls, encompassing process controls, supply chain controls, and sanitation controls to mitigate identified hazards effectively. Documentation and verification are critical elements, ensuring continuous monitoring, corrective action procedures, and validation of control measures to maintain food safety compliance under the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA).
Main Differences Between HACCP and HARPC
HACCP Plan focuses primarily on identifying and controlling physical, chemical, and biological hazards in food production through a preventive approach, while HARPC Plan, mandated by the FSMA, broadens the scope to include all potential hazards and requires a comprehensive risk-based preventive control system. HACCP emphasizes critical control points and monitoring procedures, whereas HARPC demands thorough hazard analysis, preventive controls, supply chain programs, and corrective actions. Your choice between HACCP and HARPC depends on regulatory requirements, with HARPC typically applying to facilities involved in food manufacturing under FDA jurisdiction.
Compliance and Documentation Requirements
The HACCP plan requires systematic identification and control of food safety hazards with detailed documentation of monitoring, corrective actions, and verification processes to ensure compliance with FDA and USDA guidelines. In contrast, the HARPC plan, mandated by the FDA under the FSMA, emphasizes a more comprehensive risk-based approach, requiring documented hazard analysis, risk management, performance standards, and verification procedures focused on preventing contamination throughout the supply chain. Both plans necessitate rigorous record-keeping, with HACCP focusing on critical control points and HARPC demanding broader preventive controls documentation to meet regulatory inspections and audits.
Benefits of Implementing HACCP and HARPC
Implementing a HACCP plan enhances food safety by systematically identifying and controlling biological, chemical, and physical hazards through critical control points, reducing contamination risks and ensuring regulatory compliance. HARPC plans expand on this by incorporating comprehensive risk-based preventive controls, fostering early detection and mitigation of potential hazards in the entire supply chain, and aligning with FDA requirements for proactive food safety management. Both frameworks improve consumer confidence, minimize product recalls, and streamline operational efficiencies in food manufacturing facilities.
Choosing the Right Food Safety Plan for Your Business
Choosing the right food safety plan for your business depends on the specific regulatory requirements and risk factors involved. HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point) focuses on identifying and controlling physical, chemical, and biological hazards in food production, ideal for traditional food processors. HARPC (Hazard Analysis and Risk-Based Preventive Controls) expands on HACCP by incorporating preventive controls for risks including allergens and sanitation, making it essential for facilities subject to the FDA Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA).
HACCP Plan vs HARPC Plan Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com