Direct steam injection heats your product rapidly by injecting steam directly into the material, ensuring fast temperature rise and uniform distribution, ideal for liquid processing. Jacketed vessel heating uses steam circulated through the vessel's jacket, providing gentle, controlled heating suitable for sensitive or viscous products without direct steam contact.
Table of Comparison
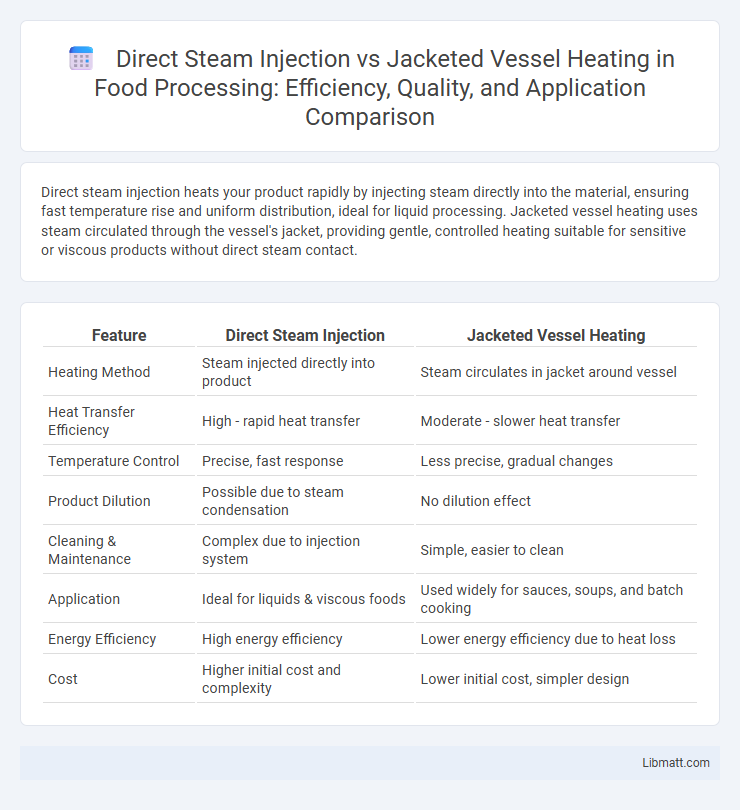
| Feature | Direct Steam Injection | Jacketed Vessel Heating |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Steam injected directly into product | Steam circulates in jacket around vessel |
| Heat Transfer Efficiency | High - rapid heat transfer | Moderate - slower heat transfer |
| Temperature Control | Precise, fast response | Less precise, gradual changes |
| Product Dilution | Possible due to steam condensation | No dilution effect |
| Cleaning & Maintenance | Complex due to injection system | Simple, easier to clean |
| Application | Ideal for liquids & viscous foods | Used widely for sauces, soups, and batch cooking |
| Energy Efficiency | High energy efficiency | Lower energy efficiency due to heat loss |
| Cost | Higher initial cost and complexity | Lower initial cost, simpler design |
Introduction to Industrial Heating Methods
Direct steam injection offers rapid and uniform heating by injecting steam directly into the product, ensuring precise temperature control and energy efficiency in industrial processes. Jacketed vessel heating relies on steam or hot water circulating around the vessel's exterior, providing gentle and consistent heat distribution suitable for temperature-sensitive materials. Selecting the optimal heating method depends on your process requirements, product sensitivity, and energy considerations.
Overview of Direct Steam Injection
Direct steam injection (DSI) heats liquids by injecting live steam directly into the product, ensuring rapid and uniform temperature increase. This method offers precise temperature control, high energy efficiency, and minimizes product loss due to its fast heat transfer capabilities. Your processing speed and product consistency improve significantly compared to jacketed vessel heating, which relies on indirect conduction through vessel walls.
Understanding Jacketed Vessel Heating
Jacketed vessel heating involves circulating hot fluids such as steam, hot water, or thermal oil through a double-walled vessel to evenly transfer heat to the product inside, ensuring precise temperature control and minimizing the risk of localized overheating. This method provides gentle, consistent heating ideal for temperature-sensitive materials and maintains product integrity during processing. Compared to direct steam injection, jacketed vessels offer cleaner heating without direct contact between steam and product, reducing contamination risks and facilitating easier maintenance.
Key Differences Between DSI and Jacketed Heating
Direct steam injection (DSI) heats products by injecting live steam directly into the liquid, allowing rapid temperature rise and precise control, while jacketed vessels use steam or hot water circulated through an external jacket, providing indirect and uniform heating. DSI offers faster heat transfer and reduces thermal degradation risks due to shorter heating times, whereas jacketed vessels provide more gentle, even heating suitable for heat-sensitive products. Energy efficiency in DSI is higher because steam is utilized directly in the product, contrasting with jacketed vessels where heat loss can occur through the vessel walls.
Efficiency Comparison: DSI vs Jacketed Vessels
Direct steam injection (DSI) offers superior heating efficiency compared to jacketed vessels by delivering steam directly into the liquid, enabling rapid and uniform heat transfer with minimal energy loss. Jacketed vessels rely on conduction through the vessel walls, creating slower heating rates and increased energy consumption due to heat dissipation. Your choice of DSI can result in faster processing times and reduced operational costs, optimizing overall thermal efficiency in industrial applications.
Energy Consumption and Cost Analysis
Direct steam injection (DSI) offers superior energy efficiency compared to jacketed vessel heating by delivering steam directly into the product, minimizing heat loss and reducing overall energy consumption by up to 30%. Jacketed vessels often experience heat transfer inefficiencies due to conduction and convection limits, leading to higher operational costs and longer heating cycles. Cost analysis reveals DSI systems have lower utility expenses and faster processing times, resulting in significant savings on energy bills and increased production throughput.
Impact on Product Quality and Consistency
Direct steam injection provides rapid and uniform heating, minimizing thermal gradients that can degrade sensitive product attributes, thus enhancing product quality and consistency. Jacketed vessel heating often results in slower heat transfer and uneven temperature distribution, potentially causing localized overheating or underheating that affects texture and flavor uniformity. Choosing direct steam injection is optimal for processes requiring precise temperature control and consistent product characteristics.
Safety Considerations for Both Methods
Direct steam injection offers rapid and uniform heating but requires stringent safety measures to prevent steam burns and contamination, as steam directly contacts the product. Jacketed vessel heating minimizes direct contact risks by containing steam within the vessel walls, reducing the chance of product contamination and improving operator safety. Both methods necessitate proper pressure controls, regular maintenance, and compliance with industry safety standards to ensure safe operation.
Maintenance and Operational Requirements
Direct steam injection systems require frequent maintenance due to steam trap monitoring and potential scaling, demanding regular cleaning to prevent blockages and maintain efficiency. Jacketed vessel heating generally involves simpler maintenance, focusing on inspecting seals and ensuring proper insulation, resulting in lower operational downtime. Operationally, direct steam injection offers rapid heating but necessitates robust control systems for steam flow, while jacketed vessels provide more uniform heating with less frequent adjustments.
Choosing the Right Heating Solution for Your Process
Direct steam injection heats fluids rapidly by injecting steam directly into the product, offering precise temperature control and high energy efficiency for processes requiring fast heating or temperature spikes. Jacketed vessel heating surrounds the container with steam or hot fluid, providing uniform, gentle heating ideal for sensitive products or processes needing consistent temperature maintenance. Selecting between these methods depends on product sensitivity, heating speed, process control requirements, and energy costs to optimize operational efficiency and product quality.
direct steam injection vs jacketed vessel heating Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com