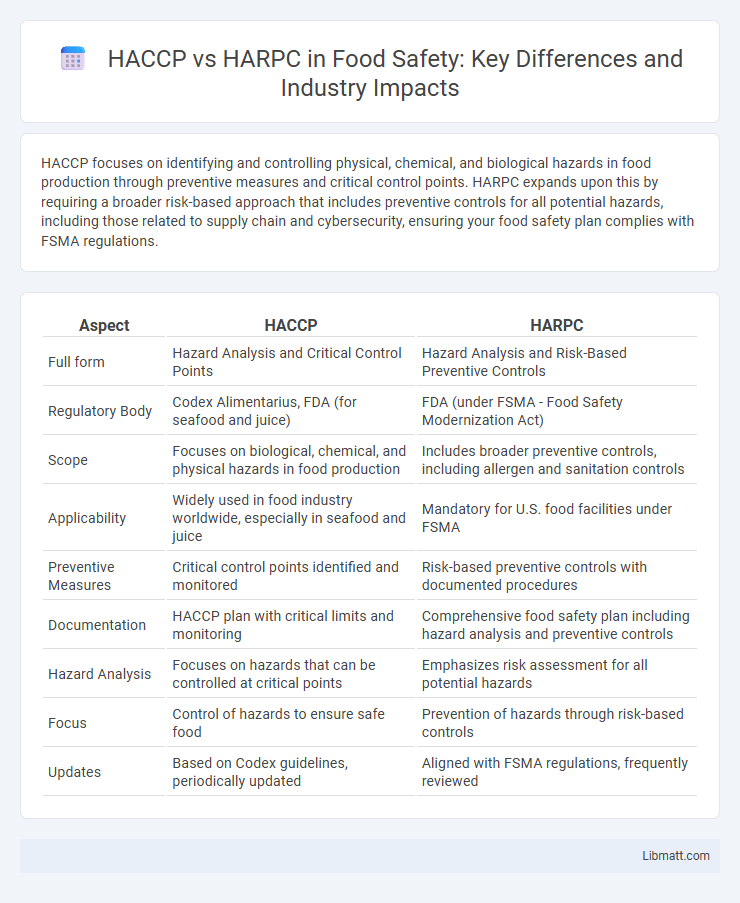
HACCP focuses on identifying and controlling physical, chemical, and biological hazards in food production through preventive measures and critical control points. HARPC expands upon this by requiring a broader risk-based approach that includes preventive controls for all potential hazards, including those related to supply chain and cybersecurity, ensuring your food safety plan complies with FSMA regulations.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | HACCP | HARPC |
|---|---|---|
| Full form | Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points | Hazard Analysis and Risk-Based Preventive Controls |
| Regulatory Body | Codex Alimentarius, FDA (for seafood and juice) | FDA (under FSMA - Food Safety Modernization Act) |
| Scope | Focuses on biological, chemical, and physical hazards in food production | Includes broader preventive controls, including allergen and sanitation controls |
| Applicability | Widely used in food industry worldwide, especially in seafood and juice | Mandatory for U.S. food facilities under FSMA |
| Preventive Measures | Critical control points identified and monitored | Risk-based preventive controls with documented procedures |
| Documentation | HACCP plan with critical limits and monitoring | Comprehensive food safety plan including hazard analysis and preventive controls |
| Hazard Analysis | Focuses on hazards that can be controlled at critical points | Emphasizes risk assessment for all potential hazards |
| Focus | Control of hazards to ensure safe food | Prevention of hazards through risk-based controls |
| Updates | Based on Codex guidelines, periodically updated | Aligned with FSMA regulations, frequently reviewed |
Introduction to HACCP and HARPC
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) is a preventive food safety management system designed to identify and control biological, chemical, and physical hazards throughout food production processes. HARPC (Hazard Analysis and Risk-Based Preventive Controls) is a regulatory framework mandated by the FDA under the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA), emphasizing a risk-based approach to prevent food safety hazards in all U.S. food facilities. Both systems focus on hazard identification and mitigation but differ in scope, regulatory requirements, and implementation methods.
Defining HACCP: Principles and Purpose
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) is a systematic preventive approach to food safety that identifies, evaluates, and controls physical, chemical, and biological hazards throughout the food production process. Its seven core principles include conducting hazard analysis, determining critical control points, establishing critical limits, monitoring procedures, corrective actions, verification processes, and record-keeping. The primary purpose of HACCP is to ensure food safety by proactively preventing contamination and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards in food manufacturing and handling.
Understanding HARPC: Key Components
HARPC (Hazard Analysis and Risk-Based Preventive Controls) emphasizes comprehensive risk assessment and implementation of preventive controls in food safety management. Key components include identifying potential hazards, developing and applying preventive measures, monitoring controls, verifying effectiveness, and maintaining proper documentation. Unlike HACCP, HARPC expands its scope to include allergen hazards, sanitation controls, and supplier verification programs, aligning with FSMA requirements.
Regulatory Background: FDA and FSMA
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) is a preventive food safety system mandated internationally and recognized by the FDA, primarily focusing on identifying and controlling biological, chemical, and physical hazards in the production process. HARPC (Hazard Analysis and Risk-Based Preventive Controls) emerged from the FDA's Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA), emphasizing a broader, risk-based approach with mandatory preventive controls that apply to nearly all FDA-regulated food facilities. Your food safety plan under FSMA aligns with HARPC requirements, ensuring compliance through documented hazard analysis and implementation of preventive controls to reduce risks.
Core Differences Between HACCP and HARPC
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) centers on identifying and controlling physical, chemical, and biological hazards at specific points in the food production process. HARPC (Hazard Analysis and Risk-Based Preventive Controls) expands this approach by requiring a comprehensive risk-based preventive control plan, including supplier verification and food defense measures. You must understand that HARPC, mandated by the FDA under the FSMA, places broader emphasis on prevention and supply chain oversight compared to HACCP's traditional focus on critical control points.
Implementation Requirements for Food Facilities
HACCP requires food facilities to conduct hazard analysis, establish critical control points, set critical limits, monitor controls, take corrective actions, verify system effectiveness, and maintain documentation. HARPC mandates food facilities to implement a comprehensive risk-based preventative controls plan, encompassing hazard identification, risk evaluation, preventive controls, monitoring procedures, corrective actions, verification, and supply chain controls under the FSMA regulatory framework. Both systems emphasize documentation and verification but HARPC expands upon HACCP by incorporating broader risk management and compliance with FDA Food Safety Modernization Act standards.
Risk Assessment Approaches: HACCP vs HARPC
HACCP employs a proactive, preventive risk assessment targeting specific biological, chemical, and physical hazards at critical control points in the food production process to ensure safety. HARPC expands upon HACCP by mandating a comprehensive hazard analysis that addresses known and reasonably foreseeable hazards across the entire supply chain, including intentional adulteration and radiological threats. The HARPC approach requires continuous monitoring and verification, aligning with FDA's FSMA requirements, to mitigate risks more broadly and enhance overall food safety control systems.
Documentation and Compliance Standards
HACCP requires detailed documentation of hazard analysis, critical control points, monitoring procedures, and corrective actions to ensure compliance with food safety standards like FDA and USDA regulations. HARPC, mandated by the FDA under the Food Safety Modernization Act, expands documentation to include risk-based preventive controls, supplier verification, and comprehensive record-keeping for all food safety hazards. Your compliance strategy must align with the specific documentation and regulatory frameworks to meet inspection and audit requirements effectively.
Industry Applications: When to Use HACCP or HARPC
HACCP is primarily used in the food industry to identify and control biological, chemical, and physical hazards during food production, ensuring food safety compliance for manufacturers and processors. HARPC, mandated by the FDA under the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA), applies broadly to food facilities and emphasizes proactive risk-based preventive controls, including supply chain oversight and allergen management. Your choice between HACCP and HARPC depends on regulatory requirements and the extent of hazard control needed, with HACCP suited for traditional food safety plans and HARPC for comprehensive risk management in FDA-regulated food businesses.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Food Safety Plan
Selecting the appropriate food safety plan hinges on the specific regulatory requirements and operational scope of a food business. HACCP focuses on identifying and controlling biological, chemical, and physical hazards in food production, making it ideal for traditional food manufacturers and processors. HARPC, mandated by the FDA under the Food Safety Modernization Act, expands preventive controls to include broader risk assessments and supplier verification, which suits facilities handling complex supply chains or higher-risk products.
HACCP vs HARPC Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com