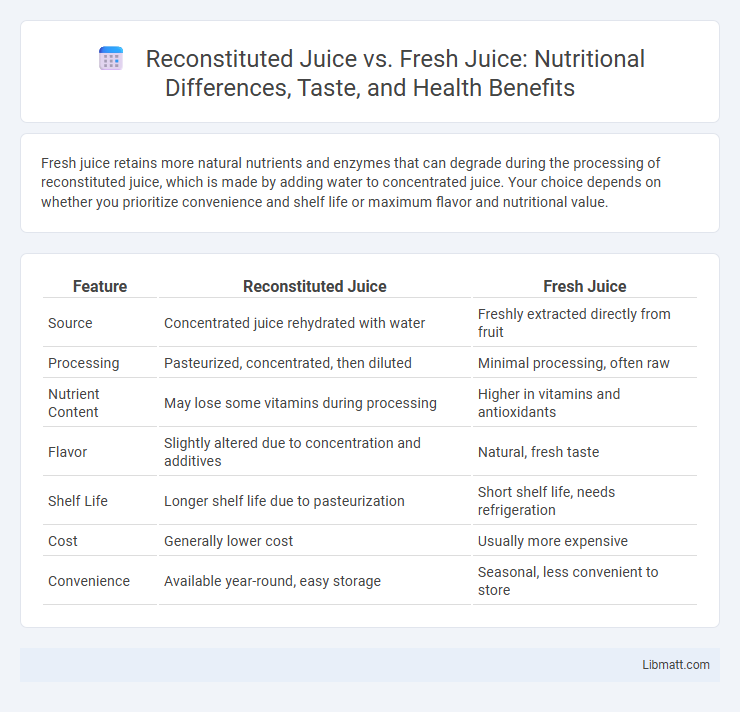
Fresh juice retains more natural nutrients and enzymes that can degrade during the processing of reconstituted juice, which is made by adding water to concentrated juice. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize convenience and shelf life or maximum flavor and nutritional value.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Reconstituted Juice | Fresh Juice |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Concentrated juice rehydrated with water | Freshly extracted directly from fruit |
| Processing | Pasteurized, concentrated, then diluted | Minimal processing, often raw |
| Nutrient Content | May lose some vitamins during processing | Higher in vitamins and antioxidants |
| Flavor | Slightly altered due to concentration and additives | Natural, fresh taste |
| Shelf Life | Longer shelf life due to pasteurization | Short shelf life, needs refrigeration |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Usually more expensive |
| Convenience | Available year-round, easy storage | Seasonal, less convenient to store |
Introduction to Reconstituted and Fresh Juice
Reconstituted juice is made by adding water to concentrated fruit juice, preserving its flavor and nutrients while offering longer shelf life and convenience. Fresh juice is extracted directly from fruits without processing or additives, providing a natural taste and higher vitamin content. Consumers often choose fresh juice for its purity, whereas reconstituted juice offers affordability and ease of storage.
What is Reconstituted Juice?
Reconstituted juice is made by adding water back to concentrated fruit juice, restoring it to its original liquid form after water removal during processing. This method allows for easier storage and transportation of juice concentrate, reducing weight and volume. Although reconstituted juice contains the same natural fruit components, its flavor and nutritional profile may differ slightly from fresh juice due to processing and concentration.
What Defines Fresh Juice?
Fresh juice is defined by its extraction directly from fruits or vegetables without any processing methods such as concentration, freezing, or addition of preservatives. It retains natural nutrients, flavors, and enzymes, offering a taste and health profile closest to the original produce. You benefit from higher vitamin content and antioxidants in fresh juice compared to reconstituted juice, which is often diluted and altered during manufacturing.
Nutritional Differences Compared
Reconstituted juice often contains fewer nutrients than fresh juice due to processing methods that can reduce vitamin C and antioxidants. Fresh juice retains more natural enzymes, phytonutrients, and higher levels of potassium and folate, contributing to better overall nutritional value. However, some reconstituted juices are fortified with vitamins to partially restore nutrient content lost during concentration and storage.
Taste and Flavor: A Direct Comparison
Reconstituted juice often has a more uniform but less vibrant taste due to pasteurization and concentration processes that can diminish natural flavor compounds. Fresh juice delivers a richer, more complex flavor profile with brighter, fresher notes and a natural sweetness that reconstituted juice rarely achieves. The subtle aroma and mouthfeel of fresh juice make it preferable for consumers seeking authentic taste experiences.
Shelf Life and Storage Requirements
Reconstituted juice typically has a longer shelf life than fresh juice due to pasteurization and packaging methods that inhibit microbial growth, allowing it to be stored unopened at room temperature for several months. Fresh juice requires refrigeration and has a much shorter shelf life, often lasting only 2 to 3 days before spoilage occurs because it lacks preservatives and is more prone to oxidation. Understanding these differences can help you choose the best option for your storage needs and consumption timeline.
Additives and Preservatives: What’s Inside?
Reconstituted juice often contains additives and preservatives such as vitamin C (ascorbic acid) to maintain color and flavor, along with stabilizers to improve texture and shelf life. Fresh juice, by contrast, is free from artificial preservatives and retains natural enzymes and nutrients without added chemicals. Choosing fresh juice can help you avoid synthetic additives commonly found in reconstituted options, supporting a cleaner, more natural beverage.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Reconstituted juice significantly reduces environmental impact by utilizing concentrated juice which lowers transportation weight and packaging needs, leading to decreased carbon emissions compared to fresh juice. The production process of reconstituted juice often supports sustainability by minimizing food waste through extended shelf life and efficient resource use. Your preference for reconstituted juice can contribute to a smaller ecological footprint while still enjoying nutritious options.
Cost Comparison: Which is More Economical?
Reconstituted juice generally costs less than fresh juice due to lower transportation and storage expenses, as it involves concentrated juice mixed with water, reducing volume and extending shelf life. Fresh juice typically incurs higher costs because of the need for rapid processing, refrigeration, and shorter shelf life, increasing wastage and logistical expenses. For budget-conscious consumers, reconstituted juice offers a more economical option without sacrificing essential nutrients, whereas fresh juice appeals more to those prioritizing flavor and freshness despite a higher price.
Making the Healthiest Choice
Choosing between reconstituted juice and fresh juice hinges on nutritional retention and ingredient quality; fresh juice typically retains more vitamins, antioxidants, and enzymes due to minimal processing. Reconstituted juice, made by adding water to concentrated juice, may lose some nutrients during processing but often includes added sugars and preservatives impacting health negatively. For the healthiest choice, prioritize fresh juice with no added sugars or additives, ensuring maximum nutrient density and natural benefits.
Reconstituted Juice vs Fresh Juice Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com