Vegan cheese offers a plant-based alternative free from lactose and cholesterol, making it suitable for those with dietary restrictions or ethical concerns. Your choice between vegan and dairy cheese depends on factors like taste preference, nutritional content, and environmental impact.
Table of Comparison
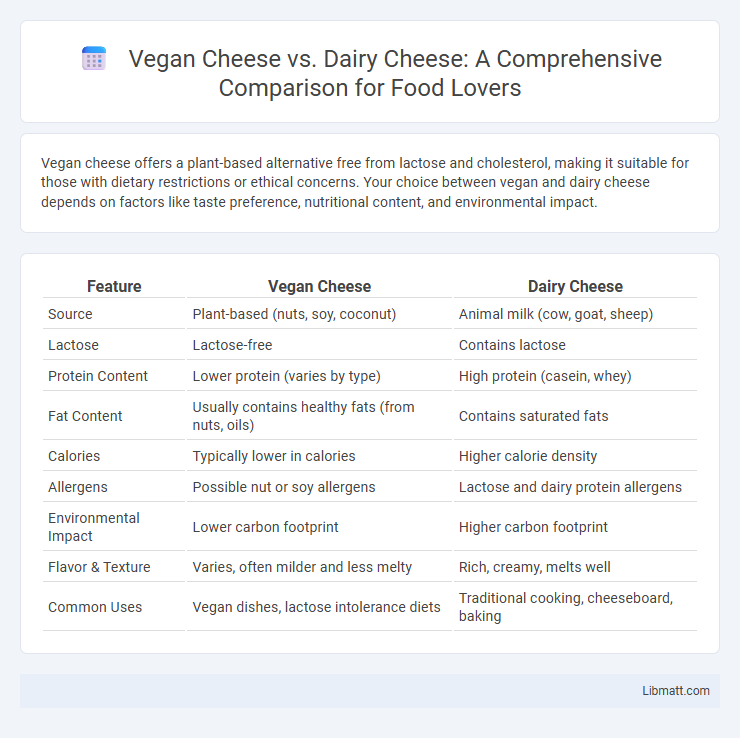
| Feature | Vegan Cheese | Dairy Cheese |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Plant-based (nuts, soy, coconut) | Animal milk (cow, goat, sheep) |
| Lactose | Lactose-free | Contains lactose |
| Protein Content | Lower protein (varies by type) | High protein (casein, whey) |
| Fat Content | Usually contains healthy fats (from nuts, oils) | Contains saturated fats |
| Calories | Typically lower in calories | Higher calorie density |
| Allergens | Possible nut or soy allergens | Lactose and dairy protein allergens |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint | Higher carbon footprint |
| Flavor & Texture | Varies, often milder and less melty | Rich, creamy, melts well |
| Common Uses | Vegan dishes, lactose intolerance diets | Traditional cooking, cheeseboard, baking |
Introduction to Vegan Cheese and Dairy Cheese
Vegan cheese, crafted from plant-based ingredients like nuts, soy, and nutritional yeast, offers a lactose-free alternative to traditional dairy cheese made from animal milk. While dairy cheese provides rich sources of calcium and protein, vegan varieties cater to those avoiding animal products due to dietary restrictions or ethical concerns. Innovations in vegan cheese technology increasingly replicate the texture and flavor profiles of dairy cheese, enhancing its appeal to diverse consumers.
Key Ingredients: Plant-Based vs Animal-Based
Vegan cheese is crafted primarily from plant-based ingredients such as nuts, soy, coconut oil, and nutritional yeast, providing a lactose-free and cholesterol-free alternative. Dairy cheese relies on animal-based components, mainly cow, goat, or sheep milk, containing casein proteins and lactose. Your choice between vegan and dairy cheese depends on dietary preferences, allergies, and ethical considerations related to animal products.
Nutritional Comparison: Protein, Calcium, and Fats
Vegan cheese typically contains lower protein levels compared to dairy cheese, which provides a rich source of complete proteins essential for muscle repair and growth. In terms of calcium, many vegan cheeses are fortified to match or surpass the calcium content found in dairy cheese, supporting bone health effectively. The fat profiles differ significantly; dairy cheese often has higher saturated fat content, while vegan cheeses commonly contain more unsaturated fats, which are considered heart-healthier.
Flavor Profiles: Taste and Texture Differences
Vegan cheese typically offers a mild, nutty, or tangy flavor with a creamy, sometimes crumbly texture derived from plant-based ingredients like nuts, soy, or coconut oil. Dairy cheese provides a richer, more complex taste with varying textures from soft and creamy to hard and crumbly, influenced by fermentation and aging processes. The absence of lactose and casein in vegan cheese results in a less sharp flavor compared to traditional dairy cheese, appealing to those with dietary restrictions.
Health Benefits and Risks
Vegan cheese typically contains lower saturated fat and cholesterol compared to dairy cheese, reducing the risk of heart disease and supporting better cardiovascular health. However, some vegan cheeses may be high in sodium and additives, which can pose health risks if consumed excessively. Dairy cheese provides essential nutrients like calcium and vitamin B12, but its high saturated fat content is linked to increased cholesterol and potential cardiovascular issues.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Vegan cheese significantly reduces your carbon footprint compared to dairy cheese by requiring fewer resources like water and land, and generating lower greenhouse gas emissions during production. Sustainability efforts favor plant-based alternatives, which avoid methane emissions from dairy cows and decrease deforestation linked to livestock farming. Choosing vegan cheese supports environmental conservation and helps mitigate climate change effects tied to traditional dairy practices.
Allergen and Dietary Considerations
Vegan cheese is free from common dairy allergens such as lactose and casein, making it suitable for individuals with lactose intolerance or milk protein allergies. Dairy cheese contains animal-derived proteins that can trigger allergic reactions and is unsuitable for those following vegan or plant-based diets. Both options require careful consideration of ingredients, especially for those with nut or soy allergies often present in vegan cheese formulations.
Culinary Uses: Melting, Cooking, and Pairing
Vegan cheese often excels in cooking versatility, providing smooth melting properties ideal for pizzas, sauces, and grilled dishes, commonly made from nuts or soy. Dairy cheese offers a rich, creamy texture and distinct flavor profiles that enhance baked goods, casseroles, and wine pairings with its unique casein proteins aiding browning and texture. Your choice between vegan and dairy cheese influences culinary outcomes, with vegan options suiting plant-based diets and dairy options favored for traditional recipes requiring complex taste and melt characteristics.
Price and Accessibility
Vegan cheese typically costs more than dairy cheese due to its specialized ingredients and smaller production scale, yet it is increasingly available in mainstream grocery stores and online. Dairy cheese remains widely accessible and generally more affordable, benefiting from large-scale production and established supply chains. You may find your choice influenced by budget constraints and the ease of finding these products in local markets.
Consumer Trends and Future of Cheese
Rising consumer demand for plant-based alternatives has accelerated the growth of vegan cheese, driven by increasing awareness of health, environmental sustainability, and ethical concerns. Market forecasts predict that the global vegan cheese industry will expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 10% through 2030, challenging the traditional dairy cheese sector. Your choice reflects a broader shift toward innovative, allergen-friendly products that align with evolving dietary preferences worldwide.
Vegan Cheese vs Dairy Cheese Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com