Peak season harvests usually yield higher quality crops due to optimal weather conditions and ample sunlight, ensuring maximum nutritional value and market demand. Off-season harvests may involve increased labor and cost but offer opportunities for niche markets and continuous supply, benefiting your overall agricultural strategy.
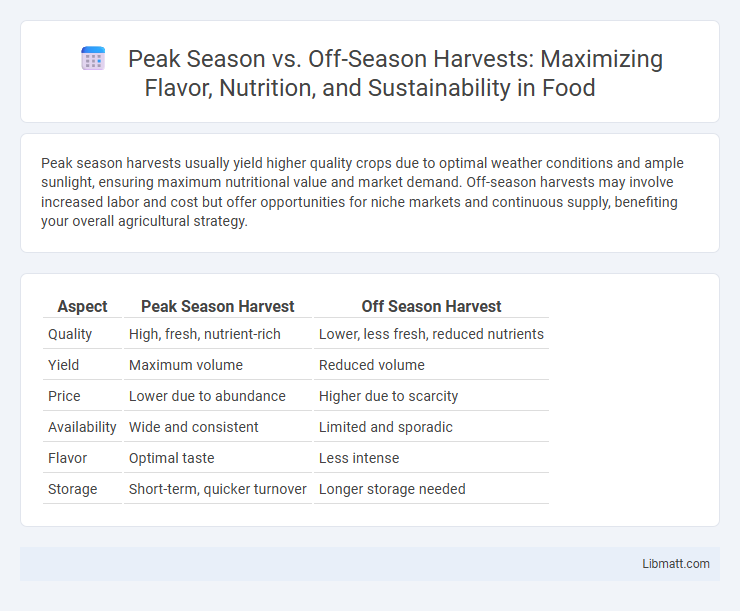
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Peak Season Harvest | Off Season Harvest |
|---|---|---|
| Quality | High, fresh, nutrient-rich | Lower, less fresh, reduced nutrients |
| Yield | Maximum volume | Reduced volume |
| Price | Lower due to abundance | Higher due to scarcity |
| Availability | Wide and consistent | Limited and sporadic |
| Flavor | Optimal taste | Less intense |
| Storage | Short-term, quicker turnover | Longer storage needed |
Understanding Peak Season and Off Season Harvests
Peak season harvests occur when crop yields reach their maximum due to optimal weather conditions and soil fertility, offering the highest quality and quantity of produce. Off season harvests take place outside these ideal periods, often requiring specialized techniques such as greenhouse cultivation or irrigation to sustain crop growth. Understanding the differences between these harvest periods is crucial for optimizing supply chains, pricing strategies, and market availability.
Key Differences Between Peak and Off Season Yields
Peak season harvests generate significantly higher yields due to optimal weather conditions and plant maturity, enhancing fruit size and quality. Off season harvests often result in lower yields with smaller, less flavorful produce caused by suboptimal temperatures and reduced sunlight. Crop management strategies must adjust to these variations to maximize productivity and maintain market supply throughout the year.
Impact on Crop Quality and Quantity
Peak season harvests typically yield higher quantities of crops due to optimal weather and growing conditions, resulting in fresher and more vibrant produce. Off-season harvests may face challenges like reduced crop size and lower nutrient content because of unfavorable climates or artificial growing methods. Your choice between peak and off-season harvesting directly affects the balance of crop quality and quantity for your agricultural goals.
Pricing Trends During Different Harvest Seasons
Peak season harvests typically drive higher market prices due to increased demand and limited supply. Off-season harvests often result in lower prices as producers aim to sell surplus stock and maintain cash flow. Seasonal price fluctuations significantly impact profitability for farmers and influence consumer purchasing patterns.
Farmer Strategies for Seasonal Harvest Optimization
Farmers implement precise planting schedules and crop selection to maximize yield during peak season harvests, leveraging favorable weather conditions and market demand. During the off season, they utilize greenhouse technologies and crop rotation techniques to maintain soil health and extend productivity. These strategies optimize resource use, reduce risk, and ensure consistent supply throughout the year.
Effects on Supply Chains and Distribution
Peak season harvests generate high volumes of produce, causing supply chains to strain under increased demand for labor, transportation, and storage capacity. Off season harvests typically yield lower quantities, allowing for steadier distribution but often requiring specialized logistics to maintain freshness and quality. Fluctuations between peak and off season periods challenge supply chain efficiency, impacting inventory management, pricing strategies, and delivery schedules.
Consumer Preferences: Freshness and Availability
Peak season harvests provide consumers with the freshest produce at optimal availability, meeting high demand with ripe, nutrient-rich fruits and vegetables. Off-season harvests often rely on storage or importation, which can affect the freshness and limit the variety available to you. Consumer preferences typically favor peak season items for their superior flavor and quality, influencing purchasing decisions.
Environmental Considerations by Season
Peak season harvests often lead to increased environmental strain due to intensified water usage, soil degradation, and heightened pesticide application to meet high demand. Off-season harvests can reduce pressure on natural resources by allowing soil recovery, minimizing water consumption, and decreasing the need for chemical inputs. Seasonal differences significantly impact biodiversity, carbon emissions, and ecosystem health in agricultural zones.
Profitability Analysis: Peak vs Off Season
Peak season harvests typically yield higher profitability due to increased demand and premium pricing, resulting in greater revenue per unit. Off season harvests present cost advantages through lower input expenses and less competition, but often face reduced market prices, impacting overall profit margins. Your strategic timing in balancing peak and off season harvests can optimize cash flow and maximize annual profitability.
Future Trends in Seasonal Harvesting Practices
Emerging future trends in seasonal harvesting practices emphasize advanced technology integration, such as AI-driven crop monitoring and precision agriculture, to optimize yield during both peak and off seasons. You can expect an increase in controlled environment agriculture, including vertical farming and greenhouse systems, enabling year-round production regardless of traditional seasonal constraints. Sustainable resource management and climate-resilient crop varieties will play a crucial role in adapting harvest schedules to shifting environmental conditions.
Peak Season vs Off Season Harvest Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com