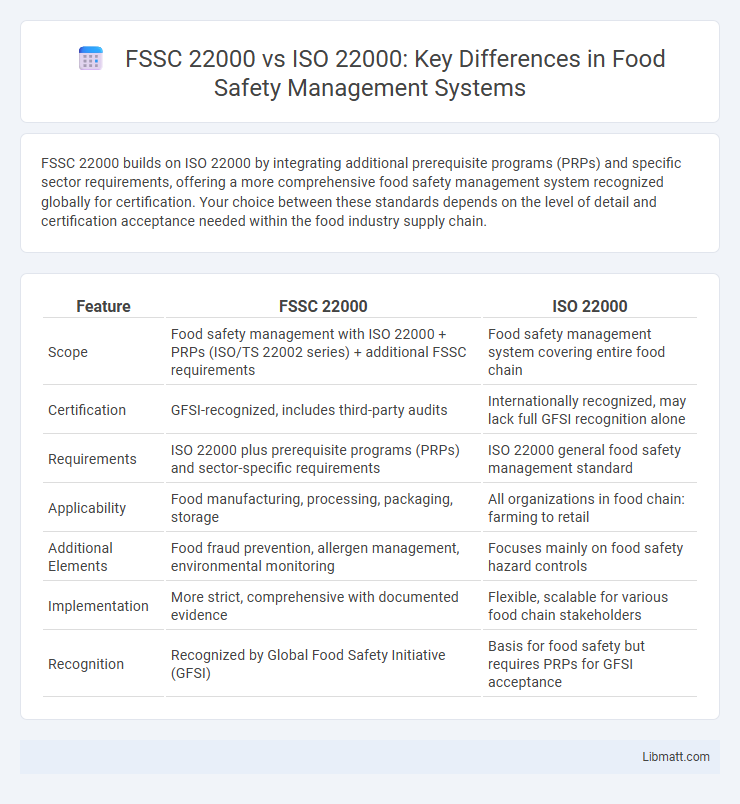
FSSC 22000 builds on ISO 22000 by integrating additional prerequisite programs (PRPs) and specific sector requirements, offering a more comprehensive food safety management system recognized globally for certification. Your choice between these standards depends on the level of detail and certification acceptance needed within the food industry supply chain.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | FSSC 22000 | ISO 22000 |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Food safety management with ISO 22000 + PRPs (ISO/TS 22002 series) + additional FSSC requirements | Food safety management system covering entire food chain |
| Certification | GFSI-recognized, includes third-party audits | Internationally recognized, may lack full GFSI recognition alone |
| Requirements | ISO 22000 plus prerequisite programs (PRPs) and sector-specific requirements | ISO 22000 general food safety management standard |
| Applicability | Food manufacturing, processing, packaging, storage | All organizations in food chain: farming to retail |
| Additional Elements | Food fraud prevention, allergen management, environmental monitoring | Focuses mainly on food safety hazard controls |
| Implementation | More strict, comprehensive with documented evidence | Flexible, scalable for various food chain stakeholders |
| Recognition | Recognized by Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI) | Basis for food safety but requires PRPs for GFSI acceptance |
Introduction to FSSC 22000 and ISO 22000
FSSC 22000 is a comprehensive food safety certification scheme based on ISO 22000, complemented by additional prerequisite programs (PRPs) and sector-specific requirements to meet global food industry demands. ISO 22000 sets the international standard for food safety management systems, focusing on hazard analysis and critical control points (HACCP) principles to ensure safe food production. Understanding these standards helps your organization implement effective food safety controls aligned with industry best practices and regulatory expectations.
Overview of Food Safety Management Systems
FSSC 22000 and ISO 22000 are internationally recognized Food Safety Management Systems (FSMS) designed to ensure food safety and compliance throughout the supply chain. ISO 22000 provides a framework integrating HACCP principles with prerequisite programs, while FSSC 22000 builds on ISO 22000 by incorporating additional sector-specific requirements and GFSI benchmarking. Organizations seeking certification often prefer FSSC 22000 for its comprehensive approach, recognized globally for enhancing food safety culture and risk management.
Core Similarities Between FSSC 22000 and ISO 22000
FSSC 22000 and ISO 22000 share core similarities such as both frameworks being based on the ISO 22000 food safety management system standard, emphasizing hazard analysis and critical control points (HACCP) principles. Each standard requires systematic processes for identifying, controlling, and monitoring food safety risks to ensure product safety throughout the supply chain. Both certifications promote continuous improvement through management review, verification, and validation activities aligning with international food safety requirements.
Key Differences in Certification Requirements
FSSC 22000 certification incorporates ISO 22000 requirements with additional prerequisites such as PAS 223 for food packaging and sector-specific prerequisite programs (PRPs), making it more comprehensive. ISO 22000 focuses primarily on the food safety management system framework, emphasizing hazard analysis and critical control points (HACCP) principles without mandatory sector-specific PRPs. FSSC 22000 also mandates a more rigorous third-party audit process and is recognized by the Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI), unlike ISO 22000 alone.
Scope and Applicability in the Food Industry
FSSC 22000 is a comprehensive certification scheme designed specifically for the food industry, integrating ISO 22000 with additional prerequisite programs (PRPs) tailored for food manufacturing, packaging, and storage sectors. ISO 22000 provides a broad food safety management framework applicable across the entire food supply chain, including primary producers, manufacturers, and distributors, but does not include sector-specific PRPs. FSSC 22000's expanded scope ensures stricter compliance and suitability for organizations aiming for internationally recognized GFSI benchmarking, while ISO 22000 offers flexible implementation adaptable to diverse food safety risks and operational sizes.
Integration with Other Management Systems
FSSC 22000 integrates seamlessly with ISO 22000 by incorporating ISO standards alongside technical specifications for prerequisite programs, enabling comprehensive food safety management aligned with other management systems such as ISO 9001. This integration facilitates unified documentation, consistent risk management, and streamlined audits across quality, environmental, and occupational health and safety standards. Organizations adopting FSSC 22000 benefit from enhanced compatibility and operational efficiency within their existing integrated management system frameworks.
Documentation and Implementation Processes
FSSC 22000 builds upon ISO 22000 by integrating additional requirements such as prerequisite programs (PRPs) and sector-specific technical specifications, resulting in more comprehensive documentation that meets food safety management system certification standards. The implementation process of FSSC 22000 demands a thorough risk assessment and control measures aligned with PAS 220, ensuring stricter compliance and enhanced traceability compared to the foundational ISO 22000 framework. Your organization benefits from FSSC 22000's structured approach to documentation, which facilitates smoother audits and stronger food safety culture.
Audit and Compliance Procedures
FSSC 22000 integrates ISO 22000 standards with additional prerequisite programs and sector-specific requirements, leading to more rigorous audit and compliance procedures compared to ISO 22000 alone. Your audit process under FSSC 22000 involves detailed assessments of food safety management systems alongside verification of prerequisite programs and compliance with PAS 220 or ISO/TS 22002-1, enhancing overall supply chain integrity. This results in a comprehensive audit scope that ensures stronger adherence to food safety regulations and greater consumer confidence.
Benefits of FSSC 22000 vs ISO 22000
FSSC 22000 offers enhanced credibility by integrating ISO 22000 with sector-specific prerequisite programs (PRPs), ensuring comprehensive food safety management in manufacturing environments. It provides greater market recognition and global acceptance due to its alignment with GFSI (Global Food Safety Initiative) requirements, which ISO 22000 alone does not guarantee. This certification enables organizations to demonstrate robust risk control and continuous improvement, fostering stronger customer confidence and supply chain transparency.
Choosing the Right Standard for Your Organization
Choosing between FSSC 22000 and ISO 22000 depends on your organization's specific food safety management needs and certification goals. FSSC 22000 incorporates ISO 22000 requirements with additional prerequisite programs and sector-specific standards, offering a more comprehensive approach for companies seeking wider market recognition and compliance with GFSI benchmarks. Evaluating your supply chain complexity and customer expectations will help determine the most suitable standard for your operational success.
FSSC 22000 vs ISO 22000 Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com