Sous vide and confit are two precise cooking techniques that emphasize low-temperature methods to enhance flavor and texture; sous vide uses vacuum-sealed bags cooked in a water bath at a controlled temperature, ensuring even doneness, while confit involves slow-cooking food submerged in fat, traditionally duck or other meats, to achieve tender, flavorful results. You can choose sous vide for consistent texture and exact cooking or confit for rich, preserved flavors and a silky finish.
Table of Comparison
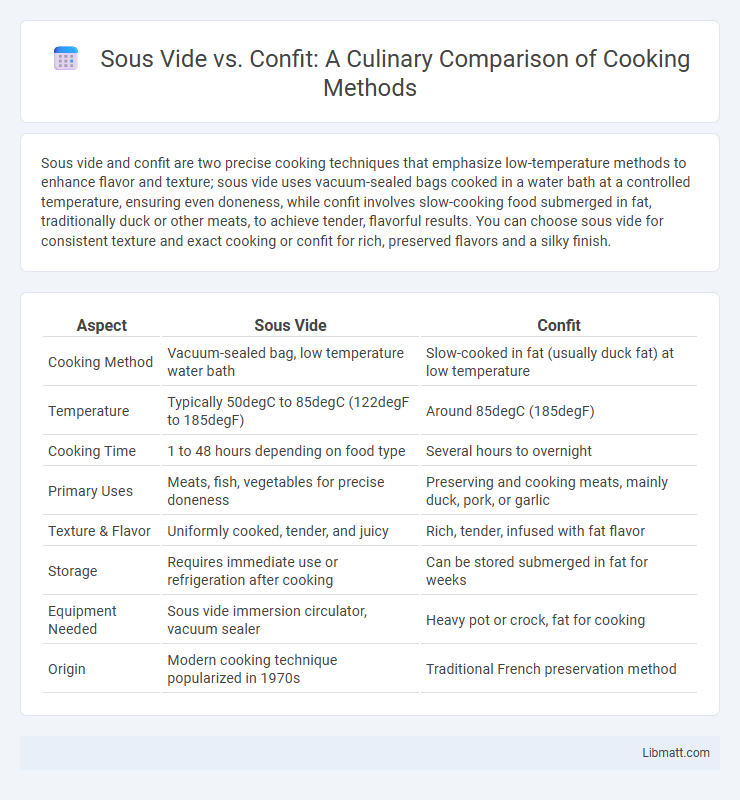
| Aspect | Sous Vide | Confit |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Vacuum-sealed bag, low temperature water bath | Slow-cooked in fat (usually duck fat) at low temperature |
| Temperature | Typically 50degC to 85degC (122degF to 185degF) | Around 85degC (185degF) |
| Cooking Time | 1 to 48 hours depending on food type | Several hours to overnight |
| Primary Uses | Meats, fish, vegetables for precise doneness | Preserving and cooking meats, mainly duck, pork, or garlic |
| Texture & Flavor | Uniformly cooked, tender, and juicy | Rich, tender, infused with fat flavor |
| Storage | Requires immediate use or refrigeration after cooking | Can be stored submerged in fat for weeks |
| Equipment Needed | Sous vide immersion circulator, vacuum sealer | Heavy pot or crock, fat for cooking |
| Origin | Modern cooking technique popularized in 1970s | Traditional French preservation method |
Introduction to Sous Vide and Confit
Sous vide is a precise cooking technique where food is vacuum-sealed and cooked in a controlled water bath at a consistent low temperature to ensure even doneness and enhanced flavor retention. Confit, a traditional French method, involves slow-cooking food submerged in fat at low temperatures, resulting in tender, flavorful dishes with a rich texture. Your choice between sous vide and confit depends on desired texture and flavor profiles, with sous vide offering precision and confit emphasizing preservation and richness.
Historical Background of Both Techniques
Sous vide, developed in the mid-1970s by French engineer and researcher Dr. Bruno Goussault, revolutionized precise temperature cooking by immersing vacuum-sealed food in a water bath, ensuring consistent doneness and texture. Confit, originating in medieval France, traditionally involves slow-cooking meat, usually duck or goose, in its own fat to preserve it before refrigeration existed, showcasing early methods of food preservation. Both techniques exemplify French culinary innovation where sous vide reflects modern scientific approach, while confit preserves ancestral slow-cooking artistry.
Key Equipment and Tools Needed
Sous vide requires an immersion circulator, a precise temperature-controlled water bath, and vacuum-sealed bags to ensure even cooking and moisture retention. Confit demands a heavy-duty, oven-safe pot or slow cooker with a tight-fitting lid, along with ample fat, such as duck fat, to submerge and cook the food slowly at low temperatures. Both techniques benefit from thermometers, but sous vide emphasizes digital precision, whereas confit centers on consistent low heat and fat immersion.
Step-by-Step Sous Vide Cooking Process
Sous vide cooking involves vacuum-sealing food and immersing it in a precisely controlled water bath at a consistent low temperature, typically between 130degF to 190degF (54degC to 88degC), for an extended period to achieve even doneness. The process steps include seasoning the food, vacuum-sealing in a plastic pouch, setting the immersion circulator to the desired temperature, cooking for the recommended time depending on the protein or vegetable, and finally searing or finishing the food to develop texture and flavor. This method contrasts with confit, which slow-cooks food submerged in fat at slightly higher temperatures, focusing on preservation and rich flavor development.
Traditional Confit Preparation Method
Traditional confit preparation involves slowly cooking meat, typically duck or pork, submerged in its own fat at low temperatures for several hours. This method preserves the meat and enhances tenderness by sealing it in fat, preventing exposure to air and bacteria. Sous vide offers a modern alternative by cooking vacuum-sealed food in temperature-controlled water, yet the authentic confit technique remains valued for its rich flavor and texture.
Flavor Profiles: Sous Vide vs Confit
Sous vide cooking preserves the natural flavors and moisture of food by cooking it in a precisely controlled water bath at low temperatures, resulting in tender, evenly cooked dishes with enhanced subtlety and depth. Confit, a traditional method of slow-cooking meat in its own fat, imparts rich, savory flavors and a distinctive, slightly caramelized texture due to the extended cooking time and fat immersion. Your choice between sous vide and confit will influence the intensity and complexity of the flavor profile, with sous vide offering purity and precision, while confit provides boldness and richness.
Texture and Mouthfeel Comparison
Sous Vide technique ensures precise temperature control, resulting in consistently tender and evenly cooked textures that preserve the natural moisture of ingredients. In contrast, Confit involves slow cooking in fat at low temperatures, producing a rich, silky mouthfeel with a slightly crisp exterior due to fat immersion. Your choice between Sous Vide and Confit will impact how tender or rich the texture and mouthfeel of your dish ultimately become.
Nutritional Differences and Benefits
Sous vide cooking preserves nutrients by using precise, low-temperature water baths that minimize nutrient loss, retaining vitamins and minerals more effectively than traditional methods. Confit involves slow cooking in fat, increasing calorie and fat content, which enhances flavor but may contribute to higher saturated fat intake. Sous vide offers a healthier option by reducing oxidation and nutrient degradation, while confit provides richer taste profiles with potentially less nutritional balance.
Common Dishes and Recipe Ideas
Sous vide excels in cooking proteins like steak, chicken breast, and fish to precise temperatures, resulting in tender, evenly cooked dishes such as sous vide salmon or steak au poivre. Confit is traditionally used for preserving meats like duck or pork by slow-cooking them in their own fat, ideal for rich recipes like duck confit or garlic confit potatoes. Your choice depends on whether you prefer the convenience and precision of sous vide or the deep, savory flavors offered by confit recipes.
Choosing Between Sous Vide and Confit
Choosing between sous vide and confit depends on texture and flavor preferences; sous vide offers precise temperature control for tender, evenly cooked results, while confit involves slow cooking in fat, imparting rich, preserved flavors and a silky texture. Sous vide suits delicate proteins and vegetables that benefit from exact doneness, whereas confit is ideal for preserving and enriching fatty meats like duck legs. Home cooks and chefs prioritize sous vide for consistency and health-conscious cooking, while confit appeals for traditional recipes and deeply infused flavors.
Sous Vide vs Confit Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com