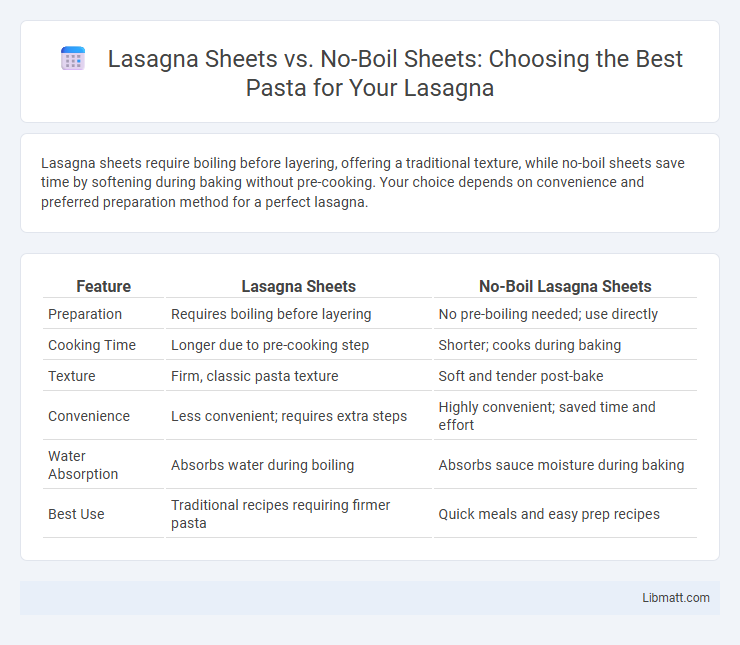
Lasagna sheets require boiling before layering, offering a traditional texture, while no-boil sheets save time by softening during baking without pre-cooking. Your choice depends on convenience and preferred preparation method for a perfect lasagna.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lasagna Sheets | No-Boil Lasagna Sheets |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation | Requires boiling before layering | No pre-boiling needed; use directly |
| Cooking Time | Longer due to pre-cooking step | Shorter; cooks during baking |
| Texture | Firm, classic pasta texture | Soft and tender post-bake |
| Convenience | Less convenient; requires extra steps | Highly convenient; saved time and effort |
| Water Absorption | Absorbs water during boiling | Absorbs sauce moisture during baking |
| Best Use | Traditional recipes requiring firmer pasta | Quick meals and easy prep recipes |
Introduction to Lasagna Sheets
Lasagna sheets are essential components in traditional lasagna recipes, providing structure and texture to the layered dish. Standard lasagna sheets require boiling before assembling, ensuring they soften and cook properly during baking. No-boil sheets, made thinner with ingredients that absorb moisture from sauces, save preparation time while allowing you to create a delicious lasagna without pre-cooking.
What Are Traditional Lasagna Sheets?
Traditional lasagna sheets are thin, flat pasta sheets made primarily from durum wheat semolina and water, designed to be boiled or par-cooked before assembling a lasagna. These sheets absorb sauces and flavors during baking, resulting in a tender and cohesive texture. Your choice between traditional and no-boil sheets depends on preferred preparation time and textural outcome in the finished dish.
What Are No-Boil Lasagna Sheets?
No-boil lasagna sheets are pre-cooked pasta sheets designed to eliminate the need for boiling before assembling a lasagna. Made from durum wheat flour and water, these sheets absorb sauce moisture during baking, softening efficiently in the oven. They offer convenience and reduce preparation time compared to traditional lasagna sheets that require boiling.
Texture and Taste Differences
Lasagna sheets typically offer a firmer, al dente texture and a more pronounced wheat flavor after baking, while no-boil sheets absorb more sauce and moisture, resulting in a softer, almost creamy texture. The traditional sheets benefit from pre-cooking or boiling, which intensifies their taste and maintains structure, whereas no-boil sheets simplify preparation but may yield a slightly different taste profile due to their increased starch content and faster hydration. Choosing between them affects the final dish's mouthfeel and subtle flavor nuances, allowing you to tailor lasagna texture and taste to your preference.
Ease of Preparation
No-boil lasagna sheets simplify meal preparation by eliminating the need for pre-cooking, allowing them to absorb sauce and cook directly in the oven. Traditional lasagna sheets require boiling before layering, which adds an extra step and time to the cooking process. Choosing no-boil sheets reduces overall preparation time and minimizes cleanup, enhancing kitchen efficiency.
Cooking Time Comparison
Lasagna sheets typically require boiling for 8 to 10 minutes before assembling, extending the overall cooking process compared to no-boil sheets, which are designed to soften during baking and eliminate the pre-cooking step. No-boil lasagna sheets cut down total preparation and cooking time by absorbing moisture from sauces and oven heat, usually baking fully within 45 to 60 minutes. Choosing no-boil sheets streamlines the process, making it more efficient without sacrificing texture or flavor in the finished lasagna.
Sauce and Liquid Absorption
Lasagna sheets require pre-cooking to absorb enough sauce and liquid, ensuring they soften properly during baking without becoming overly mushy. No-boil sheets are designed with a porous texture that absorbs sauce and liquid directly while baking, allowing them to cook thoroughly without pre-soaking. Choosing between lasagna sheets and no-boil sheets depends on the desired texture and convenience, with no-boil sheets offering a quicker preparation by effectively managing sauce absorption within the oven.
Nutritional Comparison
Lasagna sheets and no-boil sheets differ primarily in texture and preparation but share similar basic nutritional profiles, including calories, carbohydrates, and protein content. No-boil sheets often contain slightly more sodium due to pre-treatment for quicker cooking, which can impact your daily sodium intake if consumed in large quantities. Choosing between the two depends on your cooking preference and nutritional priorities, but both provide a good source of complex carbohydrates essential for energy.
Best Dishes for Each Type
Traditional lasagna sheets are ideal for classic baked lasagna recipes that require boiling to achieve the perfect texture, such as meat or vegetable lasagnas with rich tomato sauces. No-boil lasagna sheets excel in quick and convenient dishes like layered casseroles or microwave-friendly lasagnas, absorbing moisture directly from the sauce and reducing prep time. Your choice between these sheets depends on whether you prioritize authentic texture or speedy meal preparation.
Which Lasagna Sheet Should You Choose?
Choosing between traditional lasagna sheets and no-boil sheets depends on preparation time and desired texture; traditional sheets require pre-cooking and yield a firmer bite, while no-boil sheets absorb sauce directly and offer convenience with a softer result. No-boil sheets are ideal for quick meals and layered sauces with ample moisture, whereas traditional sheets suit recipes calling for precise texture control and less watery sauces. Consider cooking preferences, sauce consistency, and desired lasagna firmness to select the best sheet type for your dish.
Lasagna Sheet vs No-Boil Sheet Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com