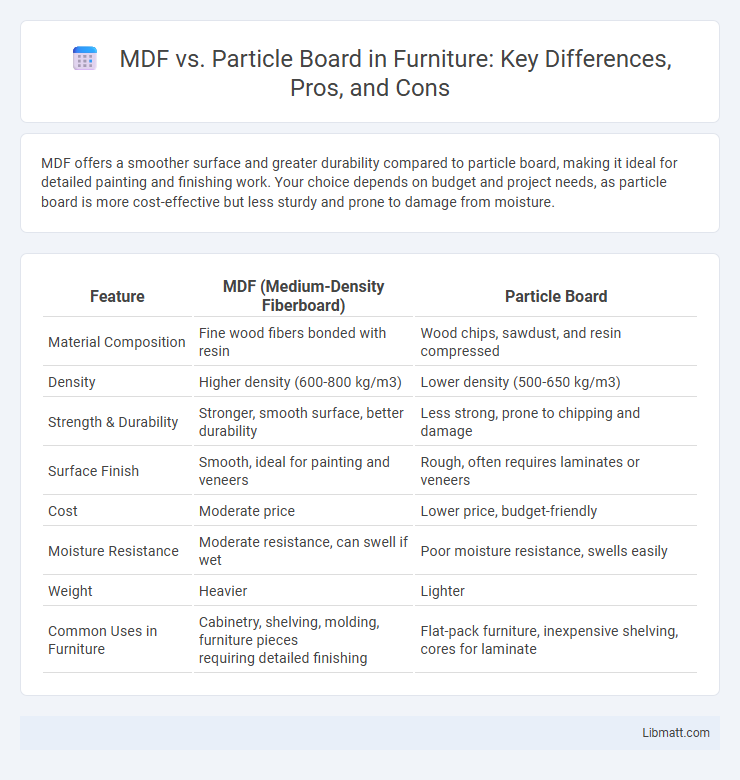
MDF offers a smoother surface and greater durability compared to particle board, making it ideal for detailed painting and finishing work. Your choice depends on budget and project needs, as particle board is more cost-effective but less sturdy and prone to damage from moisture.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | MDF (Medium-Density Fiberboard) | Particle Board |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Fine wood fibers bonded with resin | Wood chips, sawdust, and resin compressed |
| Density | Higher density (600-800 kg/m3) | Lower density (500-650 kg/m3) |
| Strength & Durability | Stronger, smooth surface, better durability | Less strong, prone to chipping and damage |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, ideal for painting and veneers | Rough, often requires laminates or veneers |
| Cost | Moderate price | Lower price, budget-friendly |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate resistance, can swell if wet | Poor moisture resistance, swells easily |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Common Uses in Furniture |
Cabinetry, shelving, molding, furniture pieces requiring detailed finishing |
Flat-pack furniture, inexpensive shelving, cores for laminate |
Introduction to MDF and Particle Board
Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF) and particle board are engineered wood products widely used in furniture and construction. MDF is made from finely ground wood fibers combined with resin and compressed under heat, resulting in a smooth, dense surface ideal for painting and machining. Particle board consists of larger wood chips and particles bonded with adhesive, offering a cost-effective but less durable alternative with a rougher texture.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
MDF (Medium-Density Fiberboard) is made from fine wood fibers combined with resin and wax, compressed under high pressure and heat to form dense, smooth panels. Particle board consists of larger wood chips and shavings mixed with synthetic resin, then pressed and heated to create a lighter, less dense panel. The finer wood fibers and higher compression in MDF result in a stronger, more uniform surface compared to the coarser, more porous structure of particle board.
Strength and Durability Comparison
MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard) offers higher density and uniform strength, making it more durable and resistant to warping compared to particle board, which is composed of larger wood chips and adhesive that result in a more fragile structure. MDF's smooth, solid surface supports heavy loads better and withstands moisture damage moderately well, while particle board tends to swell and degrade when exposed to water. For applications requiring longevity and robustness, MDF is generally the preferred choice due to its superior mechanical properties and structural integrity.
Surface Finish and Appearance
MDF (Medium-Density Fiberboard) offers a smooth, uniform surface that excels in holding paint and laminate finishes without visible grain or knots, resulting in a sleek, consistent appearance. Particle board has a rougher texture with visible wood chips and often requires veneer or laminate coverings to achieve an attractive surface finish. Due to its denser composition, MDF provides superior aesthetic versatility and a more refined look compared to the coarser, less durable particle board.
Cost Differences
MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard) generally costs more than particle board due to its denser composition and smoother finish, making it ideal for detailed woodworking projects. Particle board is the more budget-friendly option, often chosen for inexpensive furniture and cabinetry but is less durable and prone to moisture damage. Your choice between MDF and particle board will depend on balancing cost constraints with the desired strength and finish quality for your project.
Weight and Handling
Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF) typically weighs more than particle board due to its higher density and finer wood fibers. The heavier weight of MDF results in a sturdier feel but can make handling and transportation more challenging compared to the lighter, more maneuverable particle board. Particle board's lower weight allows for easier cutting and installation, especially in large projects or where frequent movement is required.
Moisture and Environmental Resistance
MDF and particle board differ significantly in moisture and environmental resistance; MDF is denser and less porous, offering better resistance to humidity and moisture-related swelling than particle board, which tends to absorb water more easily and deteriorate. Your choice should consider MDF for applications in moderately humid environments, while particle board is more suited for dry, interior settings due to its lower resistance. Environmental factors such as exposure to water vapor or fluctuating humidity levels markedly affect the durability and longevity of both materials.
Applications and Ideal Uses
MDF is ideal for cabinetry, furniture, and intricate molding due to its smooth surface and ability to be easily machined, making it perfect for painted finishes. Particle board suits budget-friendly applications such as shelving, flat-pack furniture, and underlayment where high strength and fine detail are less critical. Your choice between MDF and particle board depends on the balance between durability, cost, and desired finish quality.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
MDF (Medium-Density Fiberboard) generally has a lower environmental impact than particle board due to its higher density, durability, and use of recycled wood fibers, which reduces deforestation. Particle board often uses lower-quality wood waste and formaldehyde-based adhesives, contributing to higher emissions and shorter lifespan, impacting sustainability negatively. Choosing MDF for your projects supports reduced waste and longer product life, enhancing overall environmental responsibility.
Conclusion: Choosing Between MDF and Particle Board
MDF offers a smoother surface, higher density, and better durability compared to particle board, making it ideal for fine woodworking and furniture that demands precision. Particle board is more cost-effective and lighter but less resistant to moisture and mechanical stress, suitable for budget-friendly and non-structural applications. Your choice depends on the project's requirements for strength, finish quality, and budget constraints.
MDF vs Particle Board Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com