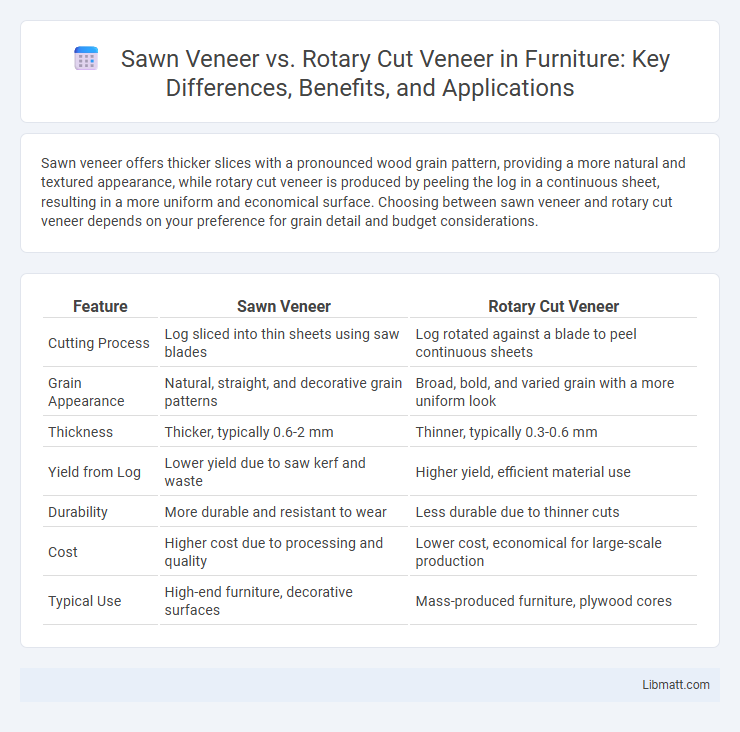
Sawn veneer offers thicker slices with a pronounced wood grain pattern, providing a more natural and textured appearance, while rotary cut veneer is produced by peeling the log in a continuous sheet, resulting in a more uniform and economical surface. Choosing between sawn veneer and rotary cut veneer depends on your preference for grain detail and budget considerations.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sawn Veneer | Rotary Cut Veneer |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Process | Log sliced into thin sheets using saw blades | Log rotated against a blade to peel continuous sheets |
| Grain Appearance | Natural, straight, and decorative grain patterns | Broad, bold, and varied grain with a more uniform look |
| Thickness | Thicker, typically 0.6-2 mm | Thinner, typically 0.3-0.6 mm |
| Yield from Log | Lower yield due to saw kerf and waste | Higher yield, efficient material use |
| Durability | More durable and resistant to wear | Less durable due to thinner cuts |
| Cost | Higher cost due to processing and quality | Lower cost, economical for large-scale production |
| Typical Use | High-end furniture, decorative surfaces | Mass-produced furniture, plywood cores |
Introduction to Veneer Types
Sawn veneer, also known as plain sliced veneer, is created by slicing logs perpendicular to the growth rings, resulting in a straight grain pattern that highlights the natural texture of the wood. Rotary cut veneer involves peeling the log in a continuous spiral, producing a broad, uniform grain pattern ideal for covering large surfaces. Both veneer types are extensively used in furniture manufacturing and architectural paneling, offering distinct aesthetic qualities and material efficiencies.
What is Sawn Veneer?
Sawn veneer is a type of veneer produced by slicing logs into thin sheets using a band saw or plain saw, resulting in a more uniform grain pattern with less variation compared to rotary cut veneer. This method preserves the natural growth rings and character of the wood, making sawn veneers ideal for high-quality furniture and cabinetry where appearance and grain pattern consistency are important. Sawn veneer typically displays a linear, straight grain and is available in various thicknesses to suit different woodworking applications.
What is Rotary Cut Veneer?
Rotary cut veneer is produced by peeling a log on a lathe, creating a continuous sheet of wood with a distinctive, broad grain pattern that follows the growth rings. This method efficiently yields large quantities of veneer, making it ideal for plywood and veneer core panels. The resulting appearance is less uniform than sawn veneer, often showcasing dramatic grain variations and knots.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Sawn veneer is produced by slicing a log perpendicular to its growth rings, resulting in thicker sheets that highlight the wood's natural grain patterns and textures. Rotary cut veneer is manufactured by rotating the log against a blade, peeling continuous thin sheets that maximize yield but often display a less distinct grain appearance. Understanding these manufacturing differences helps you select the veneer type best suited for your project's aesthetic and structural needs.
Visual Appearance Differences
Sawn veneer features a distinctive, irregular grain pattern with varied textures that highlight natural wood markings, offering a more unique and rustic visual appeal. Rotary cut veneer produces a uniform, circular grain pattern with consistent texture, creating a smoother surface ideal for large, continuous panels. The choice between sawn and rotary cut veneer significantly influences the furniture or panel aesthetics, balancing between character-rich visuals and clean, repetitive grain designs.
Strength and Durability Factors
Sawn veneer exhibits greater strength and durability due to its tighter grain pattern, which enhances resistance to warping and splitting. Rotary cut veneer, while more cost-effective and uniform in appearance, tends to have a looser grain structure that may reduce its mechanical strength over time. The denser fiber alignment in sawn veneer provides superior load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for structural applications requiring enhanced durability.
Cost and Affordability
Sawn veneer generally costs more than rotary cut veneer due to its labor-intensive production process and higher-quality appearance. Rotary cut veneer is more affordable, making it suitable for large-scale projects or budget-conscious buyers seeking an economical solution. You can optimize your expenses by choosing rotary cut veneer for cost efficiency or sawn veneer for premium aesthetics.
Common Applications
Sawn veneer is commonly used in high-end furniture, cabinetry, and decorative panels where a distinctive grain pattern and texture are desired, while rotary cut veneer is typically applied in plywood manufacturing and large-scale construction due to its efficient and cost-effective production. The unique grain patterns of sawn veneer enhance aesthetic appeal in luxury interiors, whereas rotary cut veneer offers uniformity and strength essential for structural applications. Both types serve important roles in woodworking, with sawn veneer favored for visual impact and rotary cut veneer prioritized for volume and durability.
Environmental Impact
Sawn veneer typically generates less waste compared to rotary cut veneer, as it involves slicing logs into thin sheets with minimal wood loss, promoting more efficient resource use. Rotary cut veneer often produces higher volumes due to its ability to peel large logs continuously, but this process can lead to increased energy consumption and higher environmental footprints associated with machinery operation. Choosing sawn veneer supports sustainable forestry practices by maximizing wood utilization and reducing the carbon emissions linked to veneer manufacturing processes.
Choosing the Right Veneer
Choosing the right veneer depends on the desired grain pattern and application, with sawn veneer offering straight, linear grain ideal for matching and a premium look. Rotary cut veneer produces broader, more varied patterns suitable for large surface areas and cost-effective projects. Understanding the visual effect and project requirements ensures the optimal balance between aesthetics and budget.
Sawn veneer vs rotary cut veneer Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com