Softwood plywood offers greater flexibility and is typically used for structural purposes like roofing and flooring, while hardwood plywood provides a smoother finish and is preferred for furniture and cabinetry due to its durability and aesthetic appeal. Choosing the right plywood depends on Your project's requirements for strength, appearance, and cost-effectiveness.
Table of Comparison
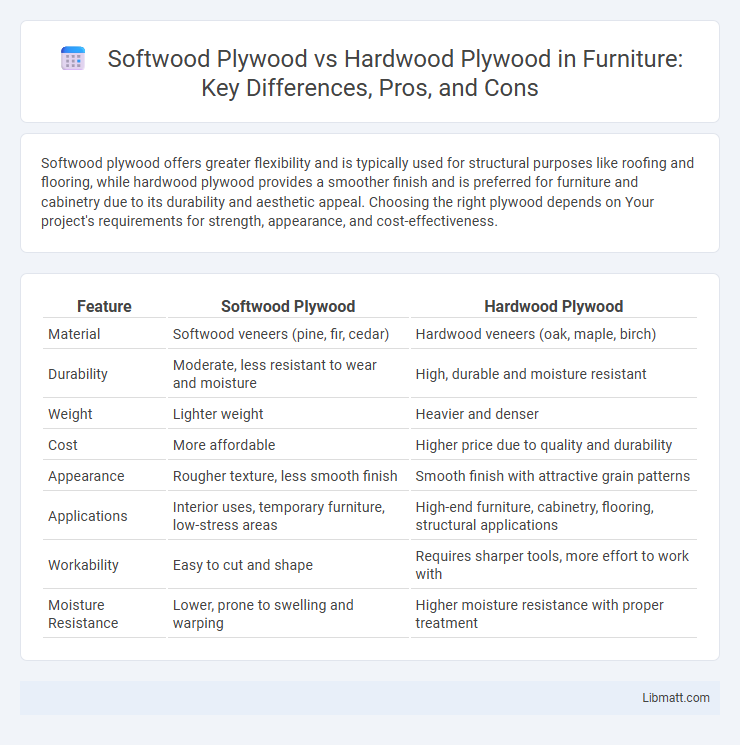
| Feature | Softwood Plywood | Hardwood Plywood |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Softwood veneers (pine, fir, cedar) | Hardwood veneers (oak, maple, birch) |
| Durability | Moderate, less resistant to wear and moisture | High, durable and moisture resistant |
| Weight | Lighter weight | Heavier and denser |
| Cost | More affordable | Higher price due to quality and durability |
| Appearance | Rougher texture, less smooth finish | Smooth finish with attractive grain patterns |
| Applications | Interior uses, temporary furniture, low-stress areas | High-end furniture, cabinetry, flooring, structural applications |
| Workability | Easy to cut and shape | Requires sharper tools, more effort to work with |
| Moisture Resistance | Lower, prone to swelling and warping | Higher moisture resistance with proper treatment |
Introduction to Softwood vs Hardwood Plywood
Softwood plywood is typically made from coniferous trees like pine, cedar, or fir, offering lightweight properties and cost-effectiveness ideal for construction and structural applications. Hardwood plywood derives from deciduous trees such as oak, maple, or birch, providing superior durability, aesthetic appeal, and smooth finishes favored in furniture making and cabinetry. Differences in grain patterns, density, and strength determine the appropriate use cases for softwood versus hardwood plywood in various woodworking projects.
Defining Softwood Plywood
Softwood plywood is manufactured using layers of softwood veneers such as pine, fir, or spruce, providing durability and flexibility ideal for construction and structural applications. Its lightweight nature and resistance to moisture make it suitable for exterior projects and sheathing, differentiating it from hardwood plywood, which is typically used for decorative purposes due to its fine grain and aesthetic appeal. Your choice between softwood and hardwood plywood depends on the required strength, appearance, and intended use of the material.
Understanding Hardwood Plywood
Hardwood plywood is made from thin layers of hardwood veneers glued together, offering superior strength, durability, and a smooth, attractive finish compared to softwood plywood. It is commonly used in furniture making, cabinetry, and interior applications where aesthetics and structural integrity are essential. Understanding hardwood plywood helps you choose the right material for projects requiring a high-quality, long-lasting surface.
Key Material Differences
Softwood plywood is primarily made from softwood species such as pine, fir, or spruce, which provide a lighter, more flexible sheet ideal for construction and sheathing. Hardwood plywood consists of hardwood species like oak, maple, or birch, offering a denser, stronger, and more durable panel suitable for furniture and cabinetry. The grain patterns in hardwood plywood display finer, more intricate textures compared to the coarser, straight grains in softwood plywood, influencing both appearance and performance.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Softwood plywood typically offers greater flexibility and resistance to warping, making it suitable for structural applications requiring moderate strength. Hardwood plywood features denser, tighter grain patterns that provide superior durability and higher load-bearing capacity, ideal for furniture and cabinetry demanding long-lasting performance. The choice between softwood and hardwood plywood depends on the required balance of strength, toughness, and wear resistance in specific construction or design projects.
Common Applications of Each Type
Softwood plywood is commonly used in construction for sheathing, roofing, and subflooring due to its strength, affordability, and lightweight properties. Hardwood plywood finds its primary applications in furniture making, cabinetry, and interior paneling because of its durability, smooth finish, and aesthetic appeal. Both types serve distinct roles in woodworking and building projects based on their material characteristics and performance requirements.
Cost Factors: Softwood vs Hardwood Plywood
Softwood plywood generally costs less than hardwood plywood due to the faster growth and greater availability of softwood species like pine and fir. Hardwood plywood, made from dense species such as oak, maple, or birch, commands a higher price because of its durability, aesthetic appeal, and longer production time. Factors influencing cost differences include raw material scarcity, manufacturing complexity, and intended application strength requirements.
Workability and Finishing Options
Softwood plywood offers superior workability due to its lighter weight and softer fibers, allowing easier cutting, shaping, and nailing, making it ideal for structural applications and simple finishes. Hardwood plywood, composed of dense, fine-grained wood veneers like oak or maple, provides a smooth surface ideal for high-quality staining, painting, and intricate detailing, enhancing aesthetic appeal in cabinetry and furniture. The finishing options on hardwood plywood are more diverse and refined due to its uniform texture and resistance to dents, while softwood plywood typically requires additional surface treatment for a polished look.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Softwood plywood is generally more sustainable due to faster growth rates of softwood species like pine, leading to quicker replenishment and lower carbon footprint during production. Hardwood plywood, often sourced from slower-growing species, may contribute to deforestation and habitat loss if not harvested responsibly, impacting its environmental viability. Your choice in plywood can influence forest conservation efforts; opting for FSC-certified or recycled content products helps reduce ecological impact.
Which Plywood Should You Choose?
Softwood plywood, made from coniferous trees like pine and fir, offers lightweight strength and affordability, making it ideal for construction and structural projects. Hardwood plywood, crafted from deciduous trees such as oak or maple, provides superior durability, smooth finish, and aesthetic appeal, perfect for furniture and cabinetry. Your choice depends on the project's requirements for strength, appearance, and budget, ensuring the right plywood matches your specific application.
softwood plywood vs hardwood plywood Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com