Cluster glass offers enhanced insulation and energy efficiency by incorporating multiple glass panes separated by air or gas layers, while laminated glass provides superior safety and soundproofing with its interlayer that holds shards together upon impact. Choosing between cluster glass and laminated glass depends on whether your priority is thermal performance or impact resistance and security.
Table of Comparison
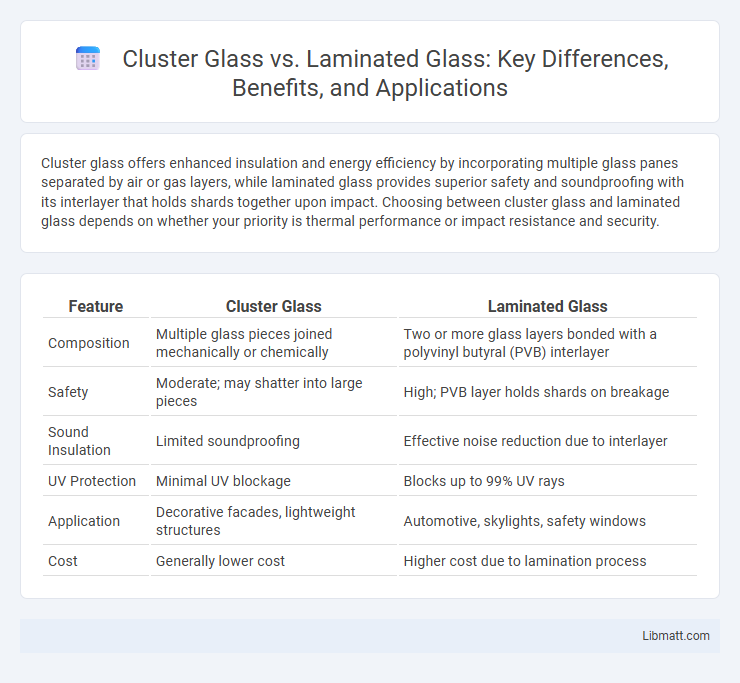
| Feature | Cluster Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Multiple glass pieces joined mechanically or chemically | Two or more glass layers bonded with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer |
| Safety | Moderate; may shatter into large pieces | High; PVB layer holds shards on breakage |
| Sound Insulation | Limited soundproofing | Effective noise reduction due to interlayer |
| UV Protection | Minimal UV blockage | Blocks up to 99% UV rays |
| Application | Decorative facades, lightweight structures | Automotive, skylights, safety windows |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to lamination process |
Introduction to Cluster Glass and Laminated Glass
Cluster glass consists of multiple small glass pieces fused together, creating a unique pattern that enhances aesthetic appeal and provides moderate safety. Laminated glass features two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, offering superior impact resistance and shatterproof properties. The structural differences between cluster glass and laminated glass determine their specific applications in architecture, automotive, and safety industries.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Cluster glass consists of multiple smaller glass pieces fused together through a heat treatment process, enhancing strength and creating unique visual effects. Laminated glass is made by sandwiching a plastic interlayer, usually polyvinyl butyral (PVB), between two or more glass sheets, bonded under heat and pressure to improve safety and durability. Your choice depends on the desired combination of aesthetic appeal and impact resistance required for your application.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Cluster glass offers enhanced strength due to its multiple layers fused together, making it highly resistant to impact and thermal stress. Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, providing excellent durability and superior resistance to shattering upon impact. Your choice between cluster glass and laminated glass should consider the specific strength and durability requirements of your project for optimal performance.
Safety Features and Performance
Cluster glass offers enhanced safety by utilizing multiple small glass units that distribute impact forces more effectively, reducing the risk of injury from sharp shards. Laminated glass incorporates a durable interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB), which holds the glass fragments together upon breakage, preventing glass from shattering and causing harm. Both types improve safety performance, but laminated glass is especially effective in impacting structural integrity and security in automotive and architectural applications.
Acoustic and Thermal Insulation Properties
Cluster glass offers superior acoustic insulation due to multiple air gaps between the glass layers, effectively reducing noise transmission and enhancing soundproofing in buildings. Laminated glass provides excellent thermal insulation by combining glass layers with a plastic interlayer that reduces heat transfer and improves energy efficiency. Both cluster and laminated glass contribute significantly to controlling indoor temperatures and minimizing external noise, making them ideal for environments requiring enhanced comfort and energy savings.
Applications in Architecture and Automotive
Cluster glass offers enhanced insulation and soundproofing, making it ideal for energy-efficient architectural designs, especially in commercial buildings and skyscrapers. Laminated glass provides superior safety and UV protection, commonly used in automotive windshields and architectural applications requiring impact resistance, such as skylights and glass facades. Both types optimize safety and performance but serve distinct roles based on structural and environmental demands.
Cost Considerations and Budgeting
Cluster glass typically offers a more cost-effective solution compared to laminated glass due to its simpler manufacturing process and lower material costs. Laminated glass involves multiple layers bonded with a plastic interlayer, which increases both production expenses and installation complexity, impacting your overall budget. Choosing between these options requires balancing upfront costs with long-term durability and safety benefits.
Maintenance and Longevity
Cluster glass offers lower maintenance due to its unified structure, reducing the risk of cracks and leaks compared to laminated glass. Laminated glass, while providing enhanced safety by holding shattered pieces together, requires more frequent inspections and potential seal replacements to maintain its integrity over time. Both materials benefit from regular cleaning, but cluster glass generally ensures longer-lasting durability with less upkeep in high-exposure environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cluster glass often has a lower environmental impact due to its use of smaller, modular glass pieces that reduce raw material consumption and facilitate recycling. Laminated glass, while durable and offering enhanced safety, typically requires more energy-intensive production processes and can be challenging to recycle due to the interlayer materials. Sustainable construction projects increasingly favor cluster glass for its potential to minimize waste and promote circular economy practices in the glass industry.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Project
Cluster glass offers superior sound insulation and thermal performance, making it ideal for projects requiring enhanced energy efficiency and noise reduction. Laminated glass provides excellent safety features with its shatter-resistant interlayer, perfect for applications demanding impact resistance and security. Selecting between cluster and laminated glass depends on balancing project priorities such as energy efficiency, safety, and acoustic requirements.
cluster glass vs laminated glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com