Toughened glass offers increased strength and safety by shattering into small, less harmful pieces upon impact, making it suitable for everyday protection and durability. Bullet resistant glass incorporates multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate, designed to absorb and dissipate the energy from bullets, ensuring higher security for Your property in high-risk environments.
Table of Comparison
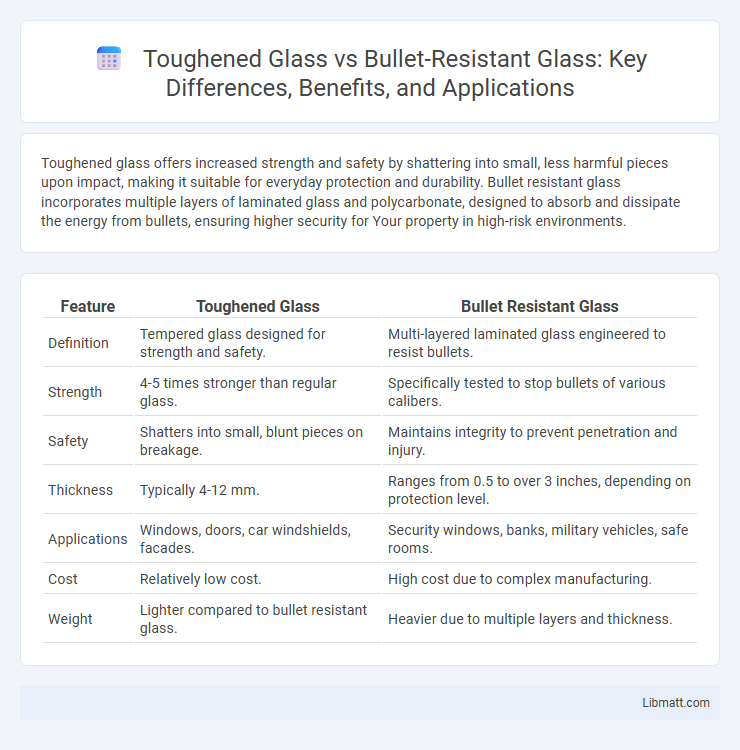
| Feature | Toughened Glass | Bullet Resistant Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tempered glass designed for strength and safety. | Multi-layered laminated glass engineered to resist bullets. |
| Strength | 4-5 times stronger than regular glass. | Specifically tested to stop bullets of various calibers. |
| Safety | Shatters into small, blunt pieces on breakage. | Maintains integrity to prevent penetration and injury. |
| Thickness | Typically 4-12 mm. | Ranges from 0.5 to over 3 inches, depending on protection level. |
| Applications | Windows, doors, car windshields, facades. | Security windows, banks, military vehicles, safe rooms. |
| Cost | Relatively low cost. | High cost due to complex manufacturing. |
| Weight | Lighter compared to bullet resistant glass. | Heavier due to multiple layers and thickness. |
Introduction to Toughened and Bullet Resistant Glass
Toughened glass, also known as tempered glass, undergoes a thermal or chemical treatment to enhance its strength, making it resistant to impact and thermal stress. Bullet resistant glass is specially engineered with multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate to absorb and dissipate the energy from ballistic projectiles, providing enhanced security. Your choice between toughened and bullet resistant glass depends on the level of protection required, whether for everyday safety or high-security applications.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Toughened glass is created by rapidly cooling heated annealed glass, resulting in increased strength through induced surface compression, while bullet resistant glass is a laminated assembly of multiple layers of glass and polycarbonate or other polymers designed to absorb and dissipate ballistic energy. The manufacturing of toughened glass involves thermal tempering, whereas bullet resistant glass requires precision lamination and interlayer bonding to ensure multi-hit resistance. Your choice depends on the required impact protection level, as toughened glass resists shattering but does not stop bullets like the specialized composition of bullet resistant glass.
Key Differences in Strength and Durability
Toughened glass, also known as tempered glass, is designed to be four to five times stronger than standard glass, offering enhanced resistance to impact and thermal stress, but it shatters into small, safe pieces upon breakage. Bullet resistant glass, composed of multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate, is engineered to absorb and disperse the kinetic energy from bullets, preventing penetration and maintaining structural integrity under ballistic impact. The key difference lies in bullet resistant glass's multi-layered construction that provides superior durability and strength specifically against firearm projectiles, whereas toughened glass primarily improves general impact resistance and safety.
Safety Features: Toughened vs Bullet Resistant Glass
Toughened glass offers enhanced safety through its ability to shatter into small, blunt pieces upon impact, minimizing injury risk, while bullet resistant glass is specially engineered with multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate to absorb and disperse bullet energy, preventing penetration. The safety features of bullet resistant glass provide superior protection in high-risk environments by stopping projectiles and reducing harm, whereas toughened glass primarily protects against accidental breakage and blunt force. You should choose based on the level of security required, with bullet resistant glass being the optimal choice for ballistic threats.
Applications in Architecture and Security
Toughened glass, commonly used in architectural applications such as facades, windows, and doors, provides enhanced strength and resistance to impact, making it ideal for everyday safety requirements in commercial and residential buildings. Bullet-resistant glass, designed with multiple laminated layers of polycarbonate and glass, is crucial in security-sensitive environments like government buildings, banks, and armored vehicles, offering protection against ballistic threats. The choice between toughened and bullet-resistant glass hinges on balancing architectural aesthetics with necessary levels of security and threat mitigation.
Impact Resistance and Testing Standards
Toughened glass offers high impact resistance due to its tempering process, adhering to standards like ASTM C1048 which measure strength and thermal durability. Bullet resistant glass, typically composed of laminated layers of polycarbonate and glass, meets stringent testing standards such as UL 752 or NIJ Level III, ensuring it can absorb and dissipate ballistic energy without penetration. The key difference lies in bullet resistant glass's multi-layered construction designed to withstand high-velocity impacts, unlike toughened glass which primarily resists blunt force impact.
Cost Comparison and Affordability
Toughened glass typically costs significantly less than bullet resistant glass due to simpler manufacturing processes and materials. Bullet resistant glass, designed with multiple layers of polycarbonate and laminated glass, involves higher production costs that impact affordability for consumers and businesses. Budget-conscious projects prioritize toughened glass for cost efficiency, while high-security needs justify the premium price of bullet resistant glass.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Toughened glass installation requires standard framing techniques and regular inspections to detect chips or cracks that could compromise safety. Bullet resistant glass demands specialized mounting systems to support its multi-layered structure and periodic maintenance to ensure seals remain intact and resistant to impact. Both types benefit from professional installation, but bullet resistant glass mandates stricter adherence to guidelines due to its complex composition and higher safety requirements.
Limitations and Vulnerabilities
Toughened glass offers high strength and shatter resistance but is vulnerable to high-velocity impacts that can cause it to break into sharp fragments. Bullet resistant glass, composed of multiple laminated layers including polycarbonate, can absorb and disperse ballistic energy, yet it has limitations against prolonged or multiple gunfire hits and large-caliber rounds. Your choice must consider that while bullet resistant glass provides superior security against firearms, it is often thicker, heavier, and more expensive than toughened glass, with vulnerabilities to certain types of optical delamination and impact fatigue.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Needs
Toughened glass offers high strength and shatter resistance, making it ideal for everyday safety applications such as windows and doors. Bullet resistant glass combines multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate to provide protection against firearm projectiles, suitable for security-sensitive environments like banks or government buildings. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing impact resistance requirements with budget and specific use cases, ensuring optimal safety and performance.
toughened glass vs bullet resistant glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com