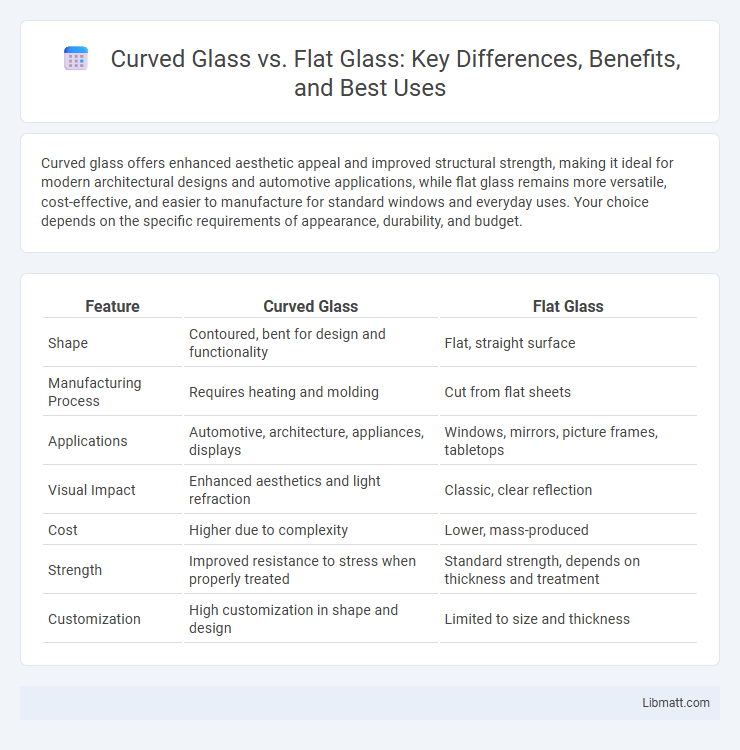
Curved glass offers enhanced aesthetic appeal and improved structural strength, making it ideal for modern architectural designs and automotive applications, while flat glass remains more versatile, cost-effective, and easier to manufacture for standard windows and everyday uses. Your choice depends on the specific requirements of appearance, durability, and budget.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Curved Glass | Flat Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Contoured, bent for design and functionality | Flat, straight surface |
| Manufacturing Process | Requires heating and molding | Cut from flat sheets |
| Applications | Automotive, architecture, appliances, displays | Windows, mirrors, picture frames, tabletops |
| Visual Impact | Enhanced aesthetics and light refraction | Classic, clear reflection |
| Cost | Higher due to complexity | Lower, mass-produced |
| Strength | Improved resistance to stress when properly treated | Standard strength, depends on thickness and treatment |
| Customization | High customization in shape and design | Limited to size and thickness |
Introduction to Curved Glass vs Flat Glass
Curved glass offers enhanced aesthetic appeal and structural flexibility compared to flat glass, allowing for innovative architectural designs and improved wind resistance. Flat glass remains the standard choice for conventional windows and facades due to its ease of manufacturing and cost efficiency. Advances in glass bending technology have significantly increased the feasibility of curved glass in modern construction projects.
Key Differences Between Curved and Flat Glass
Curved glass provides enhanced aesthetics and greater structural strength due to its shape, making it ideal for modern architectural designs and automotive applications. Flat glass offers simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and ease of installation, commonly used in windows, doors, and basic facades. The manufacturing process for curved glass involves bending and tempering techniques, while flat glass is produced through float glass methods, influencing their performance and application versatility.
Aesthetic Appeal: Curved Glass vs Flat Glass
Curved glass offers a sleek, modern aesthetic that enhances architectural designs with smooth, flowing lines, creating a dynamic and visually appealing effect that flat glass cannot replicate. Flat glass provides a classic, minimalist look with clean, straight edges suitable for traditional or simple designs, making it easier to install and maintain. Your choice between curved and flat glass will significantly impact the visual statement and style of your building or interior space.
Structural Strength and Durability
Curved glass exhibits enhanced structural strength due to its arch-like shape that evenly distributes stress, making it more resistant to impacts and deformation compared to flat glass. Its durability is superior in applications subject to high wind loads, vibrations, or pressure variations, often used in automotive and architectural designs for improved safety. Your choice between curved and flat glass should consider these factors to ensure optimal performance in demanding environments.
Applications in Architecture and Interior Design
Curved glass enhances architectural and interior design by offering sleek, modern aesthetics that create fluid, dynamic spaces unlike traditional flat glass. Its applications range from elegant facades and skylights to custom shower enclosures and curved glass walls, allowing architects and designers to push the boundaries of creative expression and spatial functionality. Your projects benefit from curved glass's ability to maximize natural light and provide panoramic views while maintaining structural integrity and energy efficiency.
Energy Efficiency and Insulation
Curved glass offers superior energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer through its shape, which minimizes air gaps and enhances insulation compared to flat glass. Its ability to conform to architectural designs allows for better thermal performance, reducing energy costs in heating and cooling. You can improve your building's overall energy consumption by choosing curved glass that maximizes insulation properties.
Manufacturing Process: Curved vs Flat Glass
Curved glass manufacturing involves heating flat glass to precise temperatures, followed by bending it over molds to achieve the desired curvature, requiring controlled cooling to maintain strength and shape. Flat glass production typically involves the float glass process, where molten glass spreads over a molten tin bath, resulting in uniform thickness and flatness without additional shaping. The complexity of curved glass production increases costs and time due to specialized equipment and exact temperature control compared to the relatively straightforward flat glass manufacturing.
Cost Comparison: Curved and Flat Glass
Curved glass typically costs significantly more than flat glass due to the specialized manufacturing processes and materials required to achieve its shape. Flat glass benefits from mass production techniques that lower its price, making it a more budget-friendly option for standard applications. If your project involves unique architectural designs or automotive needs, the higher cost of curved glass may be justified by its aesthetic and functional advantages.
Maintenance and Longevity
Curved glass typically requires specialized cleaning tools and techniques to prevent damage to its delicate contour, while flat glass is easier to maintain with standard cleaning methods. Your investment in curved glass can offer enhanced durability due to its structural strength, which often resists impacts and environmental stress better than flat glass. Regular maintenance tailored to the glass type ensures optimal longevity and preserves aesthetic appeal over time.
Choosing the Right Glass: Factors to Consider
Curved glass offers enhanced aesthetic appeal and structural benefits for modern architecture, while flat glass remains cost-effective and easier to install. Your decision should consider factors such as design complexity, load-bearing requirements, and budget constraints. Assessing these elements ensures the right balance between functionality and visual impact in your project.
curved glass vs flat glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com