Fire-rated glass is designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of flames and smoke during a fire, providing crucial safety in emergency situations. Tempered glass offers enhanced strength and shatter resistance for everyday safety but does not provide the same level of fire protection as fire-rated glass.
Table of Comparison
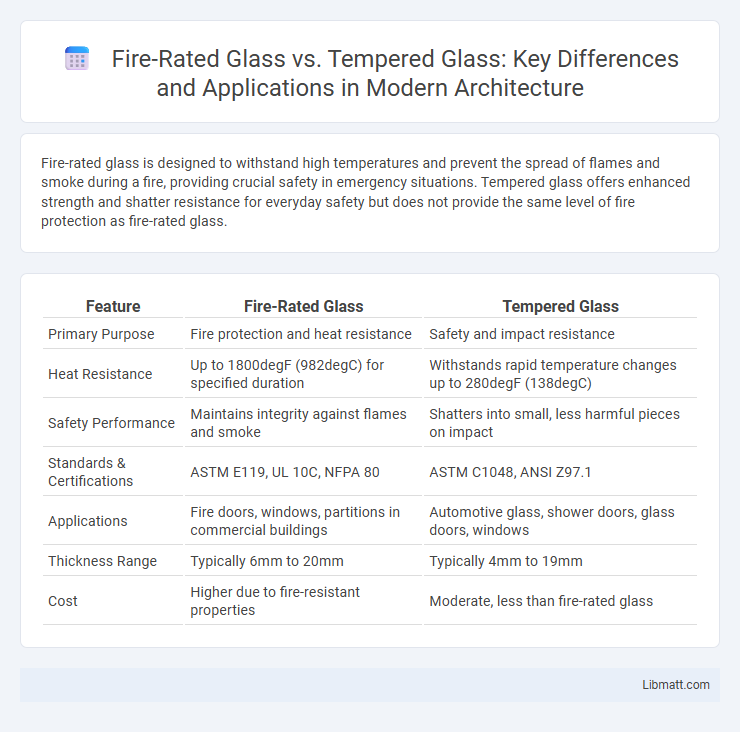
| Feature | Fire-Rated Glass | Tempered Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Fire protection and heat resistance | Safety and impact resistance |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 1800degF (982degC) for specified duration | Withstands rapid temperature changes up to 280degF (138degC) |
| Safety Performance | Maintains integrity against flames and smoke | Shatters into small, less harmful pieces on impact |
| Standards & Certifications | ASTM E119, UL 10C, NFPA 80 | ASTM C1048, ANSI Z97.1 |
| Applications | Fire doors, windows, partitions in commercial buildings | Automotive glass, shower doors, glass doors, windows |
| Thickness Range | Typically 6mm to 20mm | Typically 4mm to 19mm |
| Cost | Higher due to fire-resistant properties | Moderate, less than fire-rated glass |
Introduction to Fire-Rated Glass and Tempered Glass
Fire-rated glass is specifically engineered to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of fire, offering crucial time for evacuation and property protection. Tempered glass, on the other hand, undergoes thermal treatment to improve strength and shatter into small, safer pieces without fire-resistance properties. Your choice between fire-rated and tempered glass depends on safety requirements, building codes, and the intended application.
Defining Fire-Rated Glass
Fire-rated glass is specially engineered to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of fire and smoke, maintaining its integrity during fire emergencies. Unlike tempered glass, which is heat-strengthened for impact resistance but lacks fire resistance, fire-rated glass typically contains multiple layers, including intumescent materials that expand under heat to block flames. Choosing fire-rated glass enhances your building's safety by meeting stringent fire codes and providing critical time for evacuation and fire control.
Defining Tempered Glass
Tempered glass is a type of safety glass processed with controlled thermal or chemical treatments to increase its strength compared to regular glass. It is designed to shatter into small, blunt pieces rather than sharp shards, enhancing safety during impact. While tempered glass provides durability and resistance to breakage, it does not offer the fire protection that fire-rated glass is specifically engineered to deliver.
Core Differences: Fire Resistance vs. Strength
Fire-rated glass is specifically engineered to withstand extreme heat and prevent the spread of flames and smoke for a designated period, making it essential for fire safety compliance in buildings. Tempered glass, in contrast, is heat-treated for enhanced strength and shatters into small, less harmful pieces upon impact, but does not offer significant fire resistance. Your choice between these glass types should depend on whether fire containment or durability is the primary concern in your application.
Applications of Fire-Rated Glass
Fire-rated glass is crucial in applications requiring both visibility and enhanced fire protection, such as in fire doors, partitions, and windows in commercial buildings, hospitals, and schools. This type of glass can withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of flames and smoke, meeting strict building codes and safety regulations. Choosing fire-rated glass for your project ensures compliance with fire safety standards while maintaining aesthetic transparency.
Applications of Tempered Glass
Tempered glass is primarily used in applications requiring enhanced strength and safety, such as automobile windows, shower doors, and building facades. Its ability to shatter into small, blunt pieces reduces injury risk, making it ideal for areas prone to impact. Your choice of tempered glass ensures durability and compliance with safety standards in both residential and commercial environments.
Safety Standards and Certification
Fire-rated glass meets rigorous safety standards such as UL 9, NFPA 80, and ASTM E119, ensuring it can withstand high temperatures and prevent fire spread for specified durations. Tempered glass complies with safety certifications like ANSI Z97.1 and CPSC 16 CFR 1201, designed primarily to resist impact and reduce injury risk upon breakage but lacks fire resistance properties. Fire-rated glass undergoes stringent testing to maintain structural integrity in fire scenarios, making it essential for building codes requiring passive fire protection.
Cost Considerations and Budget Impact
Fire-rated glass typically incurs higher costs than tempered glass due to its specialized materials and certification requirements, impacting your project's budget significantly. While tempered glass is more affordable and widely available, it lacks the fire-resistance properties essential for safety compliance in certain building codes. Balancing the initial investment against long-term safety benefits is crucial when choosing between fire-rated and tempered glass for your construction needs.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Fire-rated glass installation demands strict adherence to fire-resistance standards, requiring precise fitting within fire-rated frames to maintain integrity during high heat exposure. Maintenance involves regular inspections for cracks or seal failures to ensure continued fire protection performance. Tempered glass installation is more flexible and straightforward, focusing on safety and impact resistance, with minimal ongoing maintenance beyond standard cleaning and damage checks.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Project
Fire-rated glass provides superior heat resistance and maintains integrity during fire exposure, making it essential for passive fire protection in commercial and residential buildings. Tempered glass offers enhanced strength and safety through controlled breakage patterns, ideal for impact resistance but not suitable for fire containment. Selecting the right glass depends on project requirements such as fire code compliance, safety standards, and specific environmental conditions.
fire-rated glass vs tempered glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com