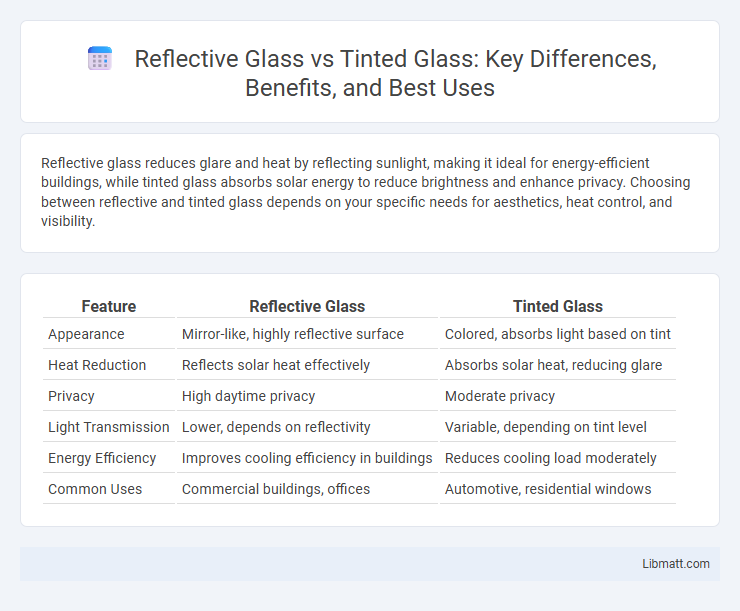
Reflective glass reduces glare and heat by reflecting sunlight, making it ideal for energy-efficient buildings, while tinted glass absorbs solar energy to reduce brightness and enhance privacy. Choosing between reflective and tinted glass depends on your specific needs for aesthetics, heat control, and visibility.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Reflective Glass | Tinted Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Mirror-like, highly reflective surface | Colored, absorbs light based on tint |
| Heat Reduction | Reflects solar heat effectively | Absorbs solar heat, reducing glare |
| Privacy | High daytime privacy | Moderate privacy |
| Light Transmission | Lower, depends on reflectivity | Variable, depending on tint level |
| Energy Efficiency | Improves cooling efficiency in buildings | Reduces cooling load moderately |
| Common Uses | Commercial buildings, offices | Automotive, residential windows |
Introduction to Reflective and Tinted Glass
Reflective glass features a metallic coating that reduces solar heat gain and increases privacy by reflecting light, making it ideal for commercial buildings and energy-efficient designs. Tinted glass incorporates color pigments to absorb sunlight, lowering glare and UV radiation while enhancing aesthetic appeal for residential and automotive applications. Both types improve energy efficiency but differ in their mechanisms and visual effects.
How Reflective Glass Works
Reflective glass works by using a thin metallic coating on one side of the glass pane, which reflects solar radiation and reduces heat transfer into buildings. This coating not only enhances energy efficiency but also maintains visibility from the inside while offering external privacy. You experience lower cooling costs and improved comfort as reflective glass helps control glare and solar heat gain.
How Tinted Glass Works
Tinted glass works by incorporating certain metal oxides or dyes into the glass during manufacturing, which absorb a portion of the visible light spectrum and reduce glare and heat transmission. This absorption capability helps block ultraviolet (UV) rays and solar heat, improving energy efficiency and comfort inside buildings or vehicles. Unlike reflective glass, tinted glass does not create a mirror-like surface but offers a more subtle, colored shading effect while maintaining visibility.
Key Differences Between Reflective and Tinted Glass
Reflective glass has a metallic coating that reduces solar heat gain by reflecting sunlight, while tinted glass absorbs solar radiation to reduce glare and heat inside buildings. Reflective glass offers higher privacy during the day due to its mirror-like appearance, whereas tinted glass provides a subtler shading effect without significantly altering external visibility. Your choice between reflective or tinted glass depends on desired thermal performance, privacy needs, and aesthetic preferences.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Reflective glass offers superior energy efficiency by reducing solar heat gain through its metallic coating, which reflects a significant portion of sunlight and lowers cooling costs. Tinted glass absorbs and blocks some solar radiation, providing moderate heat reduction but less effective glare control compared to reflective glass. Your choice should consider the climate and building orientation to maximize energy savings with the appropriate glass type.
Privacy and Aesthetic Considerations
Reflective glass enhances privacy by mirroring the exterior view, preventing outsiders from seeing inside during daylight hours, while offering a sleek, modern aesthetic that complements commercial buildings. Tinted glass reduces glare and solar heat gain, providing moderate privacy with a subtle, colored appearance that suits residential applications. Your choice between reflective and tinted glass should balance privacy needs and design preferences, ensuring optimal function and style for your space.
Cost Factors and Maintenance
Reflective glass typically incurs higher initial costs due to its specialized coatings that enhance energy efficiency and glare reduction, whereas tinted glass offers a more affordable option with basic sun control properties. Maintenance for reflective glass requires careful cleaning to preserve its reflective coating, often involving non-abrasive materials and mild detergents, while tinted glass demands less delicate upkeep, tolerating conventional cleaning methods. Both glass types contribute to energy savings, but reflective glass may provide longer-term value despite its higher upfront investment.
Applications in Architecture and Interior Design
Reflective glass enhances building energy efficiency by reducing solar heat gain and glare, making it ideal for commercial facades and high-rise buildings in urban environments. Tinted glass is preferred in residential and interior designs for privacy and aesthetic appeal, offering various color options that complement modern and traditional styles while controlling natural light. Both types contribute to sustainability by improving thermal insulation and reducing HVAC costs in architectural projects.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Reflective glass significantly reduces energy consumption by blocking solar heat gain, lowering cooling demands in buildings and thus decreasing carbon emissions. Tinted glass also improves energy efficiency by absorbing solar radiation but may reduce natural daylight, potentially increasing artificial lighting use. Choosing reflective glass over tinted glass enhances sustainability through better thermal regulation and lower environmental impact associated with energy use.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Project
Reflective glass offers superior solar control and energy efficiency by reflecting a significant portion of sunlight, making it ideal for commercial buildings in hot climates. Tinted glass reduces glare and heat by absorbing solar radiation while maintaining color aesthetics, suitable for residential projects seeking privacy and style. Evaluate climate, building orientation, and design preferences to select the optimal glass that balances energy savings, light transmission, and appearance.
reflective glass vs tinted glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com