Heat insulating glass minimizes heat transfer to maintain indoor temperatures, enhancing energy efficiency and comfort by reducing heating and cooling costs. UV insulating glass protects your interiors from harmful ultraviolet rays, preventing fading and damage to furnishings while preserving natural light.
Table of Comparison
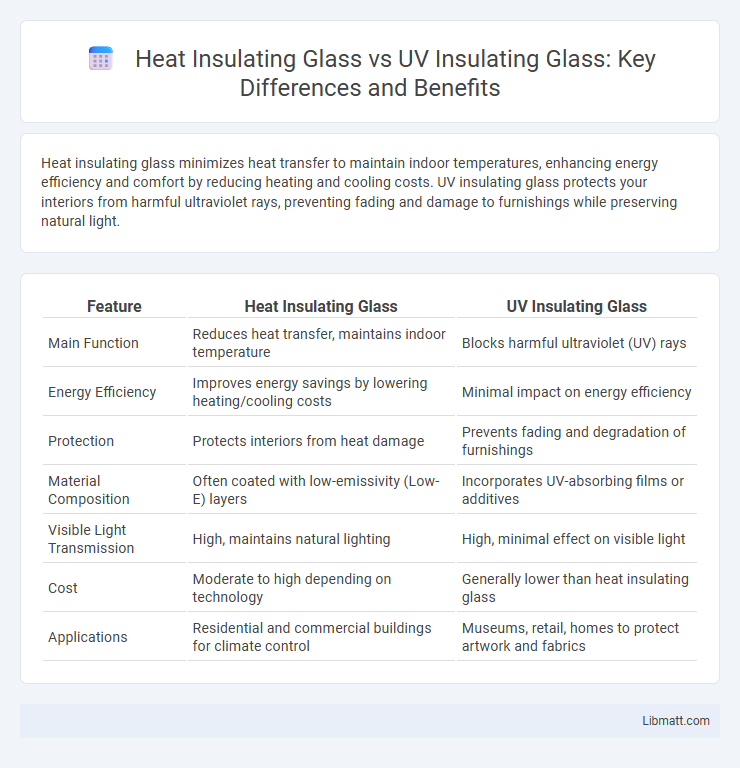
| Feature | Heat Insulating Glass | UV Insulating Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Main Function | Reduces heat transfer, maintains indoor temperature | Blocks harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays |
| Energy Efficiency | Improves energy savings by lowering heating/cooling costs | Minimal impact on energy efficiency |
| Protection | Protects interiors from heat damage | Prevents fading and degradation of furnishings |
| Material Composition | Often coated with low-emissivity (Low-E) layers | Incorporates UV-absorbing films or additives |
| Visible Light Transmission | High, maintains natural lighting | High, minimal effect on visible light |
| Cost | Moderate to high depending on technology | Generally lower than heat insulating glass |
| Applications | Residential and commercial buildings for climate control | Museums, retail, homes to protect artwork and fabrics |
Introduction to Insulating Glass Technologies
Heat insulating glass employs low-emissivity coatings and gas fills like argon to minimize thermal transfer, enhancing energy efficiency in buildings. UV insulating glass integrates specialized layers that block ultraviolet radiation, protecting interiors from fading and sun damage while allowing visible light transmission. These technologies address distinct needs: thermal insulation reduces heating and cooling costs, while UV protection preserves materials and occupant comfort.
What is Heat Insulating Glass?
Heat insulating glass is specially designed to reduce heat transfer between the interior and exterior, enhancing energy efficiency and indoor comfort by reflecting infrared radiation while allowing visible light to pass through. This type of glass often incorporates multiple layers with low-emissivity (Low-E) coatings and gas fills, such as argon or krypton, to minimize heat loss in colder months and reduce heat gain during warmer weather. Your choice of heat insulating glass can significantly lower energy costs and improve thermal performance compared to standard or UV insulating glass, which primarily blocks ultraviolet rays to protect interiors from fading.
Understanding UV Insulating Glass
UV insulating glass blocks harmful ultraviolet rays, preventing skin damage and fading of interior furnishings by filtering out UV radiation up to 99%. Unlike heat insulating glass, which primarily reduces heat transfer through low-emissivity coatings and argon gas fills, UV insulating glass specifically targets UV light without significantly affecting visible light transmission. This specialized glazing enhances occupant comfort and protects interior materials while maintaining natural daylight.
Key Differences: Heat vs. UV Insulation
Heat insulating glass primarily reduces solar heat gain by reflecting and absorbing infrared radiation, enhancing energy efficiency and indoor comfort. UV insulating glass blocks harmful ultraviolet rays to protect interiors from fading and damage caused by prolonged sun exposure. Your choice between the two depends on whether thermal regulation or UV protection is the priority for your space.
Energy Efficiency and Performance
Heat insulating glass significantly enhances energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer through windows, maintaining indoor temperatures and lowering heating and cooling costs. UV insulating glass primarily blocks harmful ultraviolet rays, protecting interiors from fading while providing moderate thermal insulation. Combining both types offers superior performance by optimizing energy savings and minimizing UV damage.
Applications in Residential and Commercial Buildings
Heat insulating glass enhances energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer, making it ideal for residential windows and commercial facades to lower heating and cooling costs. UV insulating glass protects interiors from harmful ultraviolet rays, preserving furnishings, artwork, and flooring in homes and office spaces. Combined use in building envelopes improves occupant comfort, extends material lifespan, and supports sustainable design goals.
Impact on Indoor Comfort and Safety
Heat insulating glass significantly improves indoor comfort by reducing heat transfer, maintaining stable indoor temperatures, and lowering energy consumption for heating and cooling systems. UV insulating glass focuses on blocking harmful ultraviolet rays, protecting interior furnishings from fading and occupants from UV-related health risks. Combining both types of glass enhances safety by providing thermal insulation while reducing UV exposure, promoting a healthier and more comfortable indoor environment.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Heat insulating glass typically features multiple layers with gas fills like argon or krypton, enhancing durability by reducing thermal stress and condensation, which minimizes maintenance needs over time. UV insulating glass incorporates special coatings to block harmful ultraviolet rays while maintaining transparency, but these coatings may degrade or require periodic inspection and cleaning to preserve effectiveness. Both types demand regular maintenance; however, heat insulating glass generally offers longer-lasting performance in extreme climates due to its robust construction.
Environmental and Health Benefits
Heat insulating glass reduces energy consumption by minimizing heat transfer, which lowers greenhouse gas emissions and decreases reliance on fossil fuels, contributing to environmental sustainability. UV insulating glass blocks harmful ultraviolet rays, protecting interior furnishings from fading and preventing skin damage, thereby promoting healthier indoor environments. Both types of glass enhance energy efficiency and occupant well-being, supporting eco-friendly building practices and improved health outcomes.
Choosing the Right Insulating Glass for Your Needs
Heat insulating glass effectively reduces energy consumption by minimizing heat transfer, making it ideal for climates with significant temperature fluctuations. UV insulating glass blocks harmful ultraviolet rays, protecting interiors from fading and damage while maintaining natural light. Selecting the right insulating glass depends on prioritizing thermal regulation for energy savings or UV protection to preserve furnishings and health.
heat insulating glass vs UV insulating glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com