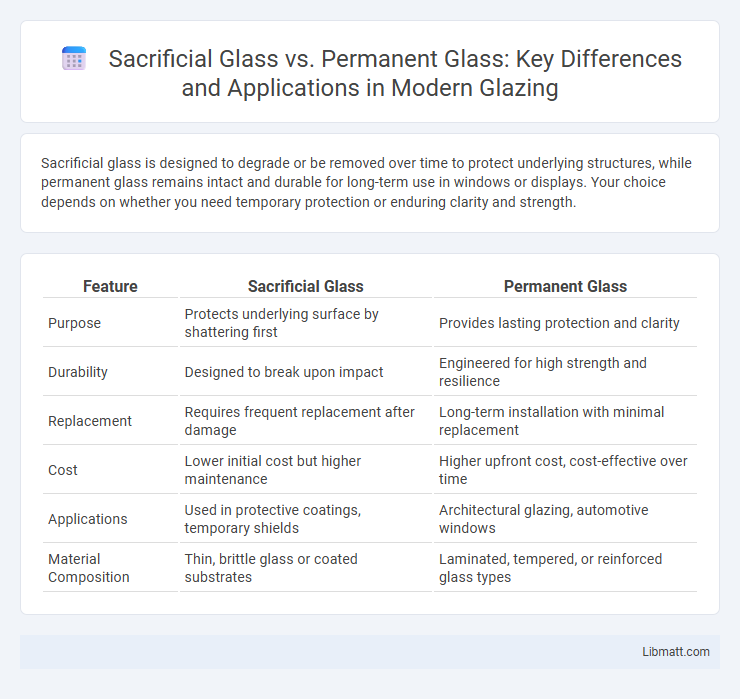
Sacrificial glass is designed to degrade or be removed over time to protect underlying structures, while permanent glass remains intact and durable for long-term use in windows or displays. Your choice depends on whether you need temporary protection or enduring clarity and strength.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sacrificial Glass | Permanent Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Protects underlying surface by shattering first | Provides lasting protection and clarity |
| Durability | Designed to break upon impact | Engineered for high strength and resilience |
| Replacement | Requires frequent replacement after damage | Long-term installation with minimal replacement |
| Cost | Lower initial cost but higher maintenance | Higher upfront cost, cost-effective over time |
| Applications | Used in protective coatings, temporary shields | Architectural glazing, automotive windows |
| Material Composition | Thin, brittle glass or coated substrates | Laminated, tempered, or reinforced glass types |
Understanding Sacrificial Glass: Definition and Purpose
Sacrificial glass is designed to absorb damage and degrade over time, protecting the underlying permanent glass from scratches, etching, or other environmental impacts. This type of glass acts as a replaceable layer that preserves the clarity and integrity of the permanent glass beneath. Its primary purpose is to extend the lifespan and maintain the aesthetic quality of permanent glass installations.
What is Permanent Glass? Key Features Explained
Permanent glass is a durable window material designed to resist scratches and damage over time, ensuring long-lasting clarity and strength. Key features include enhanced impact resistance, low maintenance requirements, and superior weatherproof properties that protect against environmental wear. Your investment in permanent glass guarantees sustained performance and aesthetic appeal compared to sacrificial glass, which sacrifices its surface layer to absorb damage.
Sacrificial Glass vs Permanent Glass: Material Differences
Sacrificial glass is engineered with a sacrificial layer that absorbs impacts and scratches, preserving the underlying surface to extend the glass's lifespan in high-wear environments. Permanent glass, constructed from tempered or laminated materials, offers durable protection without a replaceable layer, providing long-term strength but increased vulnerability to permanent damage. The material differences mainly lie in the presence of a sacrificial coating in sacrificial glass, which is absent in permanent glass, influencing maintenance requirements and overall durability.
Installation Processes: A Comparative Overview
Sacrificial glass installation typically involves applying a protective film that gradually degrades to shield the surface from damage, requiring precise alignment and controlled curing times. Permanent glass installation demands robust anchoring systems and often entails specialized framing techniques to ensure long-term structural integrity and weather resistance. Both methods require professional expertise, but permanent glass installation generally involves a more complex and time-intensive process compared to the relatively straightforward sacrificial glass application.
Cost Analysis: Budget Considerations for Both Glass Types
Sacrificial glass generally presents lower upfront costs but may incur higher long-term expenses due to periodic replacement needs, whereas permanent glass commands a higher initial investment with reduced maintenance costs over time. Evaluating your budget should factor in the frequency of replacement and durability requirements, as sacrificial glass suits short-term projects while permanent glass offers cost efficiency for extended use. Understanding these cost dynamics ensures informed financial planning tailored to your specific application.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Sacrificial glass is designed with a protective layer that deliberately corrodes or wears away to safeguard the main structure, requiring periodic replacement to maintain clarity and functionality. Permanent glass offers superior durability with inherent resistance to environmental stressors, reducing the need for frequent maintenance or replacement. Maintenance for sacrificial glass involves regular inspection and cleaning to prevent premature wear, whereas permanent glass demands minimal upkeep, enhancing long-term structural integrity and cost efficiency.
Applications: Where to Use Sacrificial vs Permanent Glass
Sacrificial glass is ideal for environments prone to high abrasion or vandalism, such as storefronts, bus shelters, and public kiosks, where it can absorb impacts and be replaced easily to maintain clarity and safety. Permanent glass is best suited for architectural features requiring long-term durability and minimal maintenance, including windows, facades, and balustrades in residential and commercial buildings. Your choice depends on balancing the need for protection and ease of replacement with the demand for lasting structural integrity and aesthetic appeal.
Safety and Security: Performance Comparison
Sacrificial glass offers enhanced safety by absorbing impacts and preventing shattering, making it ideal for temporary protection against vandalism or debris. Permanent glass, engineered with laminated or tempered layers, provides long-term security with high resistance to forced entry and environmental stress. The choice between sacrificial and permanent glass depends on balancing immediate impact absorption with durable structural integrity for sustained safety performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Sacrificial glass, designed to degrade or be replaced over time, often results in higher waste and more frequent resource consumption, impacting landfill volumes and carbon emissions. Permanent glass, with its durability and recyclability, supports sustainability by reducing the demand for raw materials and minimizing waste generation over the product's lifespan. Your choice of permanent glass contributes to lower environmental impact through enhanced energy efficiency and longer service life.
Choosing the Right Glass: Factors to Consider
Selecting between sacrificial glass and permanent glass hinges on factors such as durability, maintenance, and intended lifespan. Sacrificial glass offers a protective layer that absorbs environmental damage, ideal for applications requiring regular replacement to preserve underlying surfaces. Permanent glass provides long-term structural integrity and clarity, making it suitable for installations where minimal upkeep and enduring performance are prioritized.
sacrificial glass vs permanent glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com