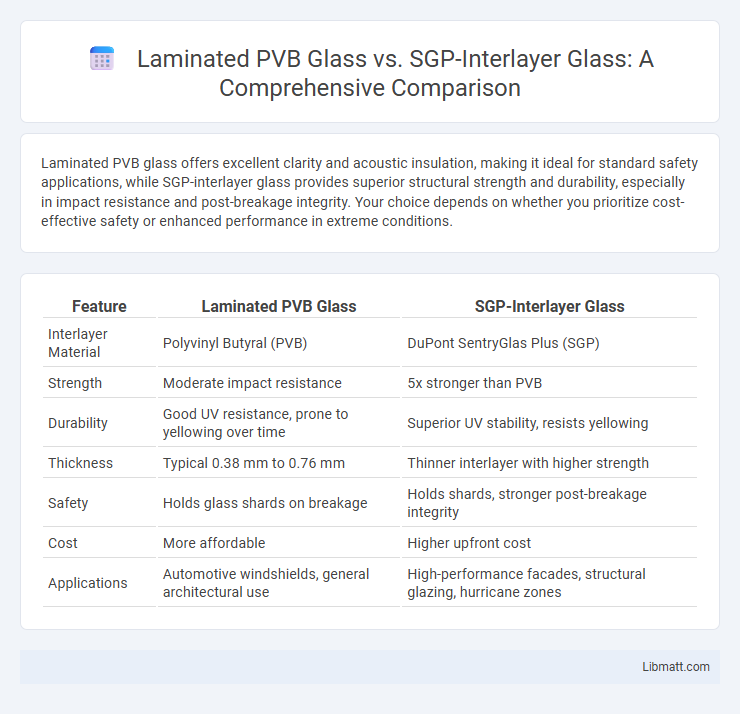
Laminated PVB glass offers excellent clarity and acoustic insulation, making it ideal for standard safety applications, while SGP-interlayer glass provides superior structural strength and durability, especially in impact resistance and post-breakage integrity. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize cost-effective safety or enhanced performance in extreme conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Laminated PVB Glass | SGP-Interlayer Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Interlayer Material | Polyvinyl Butyral (PVB) | DuPont SentryGlas Plus (SGP) |
| Strength | Moderate impact resistance | 5x stronger than PVB |
| Durability | Good UV resistance, prone to yellowing over time | Superior UV stability, resists yellowing |
| Thickness | Typical 0.38 mm to 0.76 mm | Thinner interlayer with higher strength |
| Safety | Holds glass shards on breakage | Holds shards, stronger post-breakage integrity |
| Cost | More affordable | Higher upfront cost |
| Applications | Automotive windshields, general architectural use | High-performance facades, structural glazing, hurricane zones |
Introduction to Laminated Glass Technologies
Laminated PVB glass features a polyvinyl butyral interlayer known for its excellent impact resistance and clarity, commonly used in automotive and architectural applications. SGP-interlayer glass utilizes a stronger, more durable SentryGlas Plus material, offering enhanced structural performance, improved safety, and superior resistance to moisture and delamination. Your choice between these laminated glass technologies depends on the demands for strength, longevity, and application-specific performance.
What is PVB Interlayer Glass?
PVB interlayer glass consists of multiple glass layers bonded together with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer that enhances impact resistance, sound insulation, and safety. This type of laminated glass absorbs energy upon impact, preventing shards from dispersing, making it ideal for automotive windshields and architectural applications. Choosing between PVB and SGP interlayer glass depends on factors like durability, clarity, and structural performance to best suit your project's needs.
Understanding SGP Interlayer Glass
SGP interlayer glass offers superior strength, durability, and clarity compared to traditional laminated PVB glass due to its polyvinyl butyral composite structure with enhanced tensile strength. This type of glass provides better impact resistance, improved post-breakage integrity, and higher moisture resistance, making it ideal for safety-critical applications in architecture and automotive industries. The superior bonding and rigidity of SGP interlayer glass result in longer lifespan and enhanced performance under extreme conditions.
Mechanical Strength: PVB vs SGP Glass
SGP (SentryGlas Plus) interlayer glass offers superior mechanical strength compared to traditional PVB (Polyvinyl Butyral) laminated glass, exhibiting up to 5 times greater tear resistance and enhanced stiffness. This increased durability results in better load-bearing capacity, improved impact resistance, and longer lifespan under stress, making SGP glass suitable for structural applications requiring higher safety standards. PVB glass, while effective for basic safety and sound insulation, typically demonstrates lower strength and aging resistance than SGP glass, limiting its use in high-performance environments.
Security and Impact Resistance Comparison
Laminated PVB glass offers moderate security and impact resistance by holding glass fragments together upon breakage, reducing injury risk. SGP-interlayer glass, made with a stronger SentryGlas Plus layer, delivers superior impact resistance and enhanced security, with higher tensile strength and improved post-breakage integrity. This makes SGP glass ideal for applications requiring maximum protection against forced entry and severe impact events.
Edge Stability and Durability Insights
Laminated PVB glass offers moderate edge stability but can be prone to moisture absorption, potentially compromising long-term durability. In contrast, SGP-interlayer glass provides superior edge stability due to its higher tear strength and enhanced resistance to moisture, ensuring improved durability in harsh environmental conditions. Your choice of glass should consider the demanding requirements of edge performance and lifespan, making SGP an ideal option for applications needing robust edge durability.
Performance in Extreme Weather Conditions
Laminated PVB glass provides reliable impact resistance and UV protection but may delaminate or lose clarity under prolonged exposure to extreme heat and moisture. SGP-interlayer glass delivers superior structural strength, enhanced durability, and exceptional resistance to wind pressure, high impacts, and temperature fluctuations commonly found in hurricanes and seismic zones. Architectural applications demanding maximum safety and longevity often prefer SGP glass for extreme weather resilience and sustained optical clarity.
Acoustic Properties: PVB vs SGP
Laminated PVB glass offers effective sound insulation by absorbing and dampening noise vibrations, making it suitable for reducing everyday environmental sounds. SGP-interlayer glass enhances acoustic performance with superior strength and stiffness, which improves sound transmission loss and provides better noise reduction in high-impact or high-vibration settings. SGP's higher modulus contributes to less glass vibration, resulting in improved acoustic isolation compared to traditional PVB interlayers.
Typical Applications of PVB and SGP Glass
Laminated PVB glass is commonly used in automotive windshields, residential windows, and commercial storefronts due to its excellent sound insulation and impact resistance. SGP-interlayer glass is preferred in high-performance architectural applications such as hurricane-resistant windows, skylights, and facades because of its superior strength, durability, and clarity. Both materials offer safety benefits, but SGP glass provides enhanced post-breakage integrity and longer lifespan in demanding environments.
Choosing the Right Interlayer for Your Project
Choosing the right interlayer for your project depends on the desired performance and safety characteristics, with laminated PVB glass offering excellent clarity and sound insulation, while SGP-interlayer glass provides superior strength and impact resistance. PVB interlayers are widely used for applications needing flexibility and cost-effectiveness, whereas SGP interlayers excel in structural applications requiring enhanced durability and post-breakage integrity. Understanding project requirements such as load resistance, safety standards, and longevity helps determine the most suitable glass interlayer solution.
Laminated PVB glass vs SGP-interlayer glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com