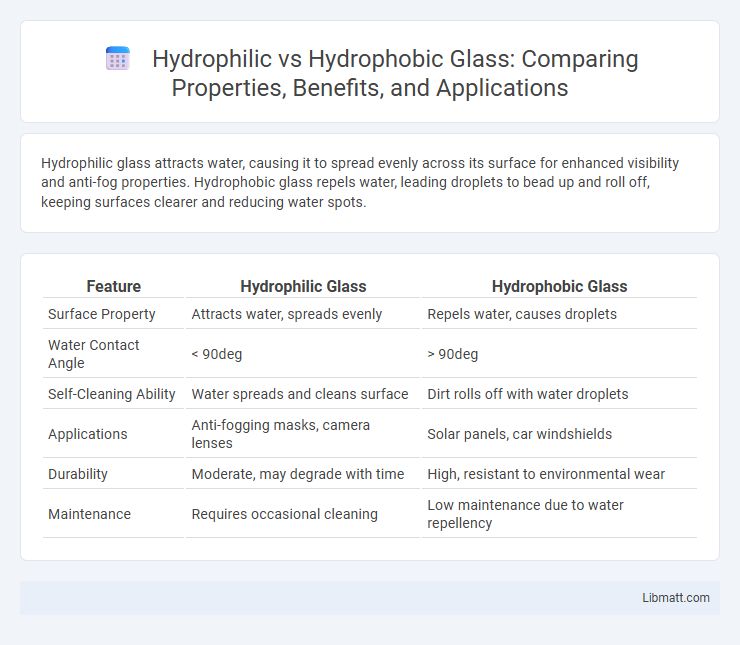
Hydrophilic glass attracts water, causing it to spread evenly across its surface for enhanced visibility and anti-fog properties. Hydrophobic glass repels water, leading droplets to bead up and roll off, keeping surfaces clearer and reducing water spots.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hydrophilic Glass | Hydrophobic Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Property | Attracts water, spreads evenly | Repels water, causes droplets |
| Water Contact Angle | < 90deg | > 90deg |
| Self-Cleaning Ability | Water spreads and cleans surface | Dirt rolls off with water droplets |
| Applications | Anti-fogging masks, camera lenses | Solar panels, car windshields |
| Durability | Moderate, may degrade with time | High, resistant to environmental wear |
| Maintenance | Requires occasional cleaning | Low maintenance due to water repellency |
Understanding Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Glass
Hydrophilic glass features a surface that attracts water molecules, causing water to spread evenly and form a thin, uniform layer, enhancing clarity and reducing fogging. Hydrophobic glass repels water, resulting in water droplets beading and rolling off quickly, which improves water drainage and reduces staining. Understanding these properties is crucial for applications in automotive, architectural, and optical industries where moisture control is essential.
Key Differences Between Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Glass
Hydrophilic glass exhibits a high surface energy that attracts water molecules, causing water to spread evenly across its surface, which enhances visibility and self-cleaning properties. Hydrophobic glass, in contrast, has a low surface energy that repels water, resulting in water droplets forming beads that roll off, reducing watermarks and improving corrosion resistance. These differences impact applications in optics, medical devices, and automotive industries where water interaction and surface cleanliness are critical.
Surface Properties and Water Interaction
Hydrophilic glass exhibits a high surface energy that attracts water molecules, causing water to spread evenly and form a thin film on the surface, enhancing transparency and reducing fogging. Hydrophobic glass has a low surface energy that repels water, leading to the formation of discrete droplets that easily roll off, promoting self-cleaning and water resistance. These contrasting surface properties determine their applications in environments requiring anti-fog coatings or water-repellent treatments.
Manufacturing Processes and Technology
Hydrophilic glass is typically manufactured using processes such as chemical vapor deposition or plasma treatment to coat the surface with titanium dioxide, enhancing its water-attracting properties. Hydrophobic glass involves the application of fluoropolymer or silane-based coatings through spray, dip, or vapor deposition techniques that create a water-repellent surface. Understanding these advanced manufacturing technologies allows you to select the appropriate glass type for applications requiring specific wetting behaviors.
Applications of Hydrophilic Glass
Hydrophilic glass is widely used in applications requiring enhanced wettability and anti-fog properties, such as in automotive windshields, optical lenses, and solar panels. Its ability to spread water evenly across surfaces prevents droplets from forming, improving visibility and light transmission. Medical devices and self-cleaning surfaces also benefit from hydrophilic coatings due to their moisture-attracting nature.
Applications of Hydrophobic Glass
Hydrophobic glass is widely used in applications requiring water repellency, such as automotive windshields, solar panels, and optical lenses, where it helps maintain clarity by preventing water spots and fogging. This type of glass reduces maintenance efforts and enhances visibility in wet conditions, making it ideal for outdoor surfaces exposed to rain or humidity. Your choice of hydrophobic glass can significantly improve performance and durability in environments prone to moisture.
Performance in Real-World Conditions
Hydrophilic glass enhances visibility in wet conditions by causing water to spread evenly across the surface, reducing water droplets that can obstruct your view. Hydrophobic glass repels water, causing droplets to bead up and roll off quickly, which is especially effective during heavy rain or when driving at high speeds. In real-world conditions, hydrophobic glass tends to offer better self-cleaning properties, while hydrophilic glass excels in maintaining clearer surfaces during light rain or fog.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Hydrophilic glass requires less frequent cleaning as water spreads evenly across its surface, preventing water spots and allowing rain to wash away dirt effectively. Hydrophobic glass repels water, causing droplets to bead and roll off, which can reduce dirt adhesion but may need more regular wiping to remove stubborn residues. Overall, hydrophilic surfaces minimize maintenance through self-cleaning properties, while hydrophobic coatings demand periodic upkeep to maintain their water-repellent performance.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Hydrophilic glass features a surface that attracts water, promoting self-cleaning by allowing water to spread evenly and remove dirt, which enhances its durability over time. Hydrophobic glass repels water, causing droplets to bead and roll off, reducing water spots but potentially requiring more frequent cleaning that can affect its lifespan. You can expect hydrophilic glass to maintain clearer visibility longer in wet environments, while hydrophobic glass may experience longer durability in dry conditions due to less surface wear from frequent cleaning.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Needs
Hydrophilic glass features a surface that attracts water, causing it to spread evenly and reduce fogging, making it ideal for applications requiring clear visibility in humid environments, such as bathroom mirrors and car windshields. Hydrophobic glass repels water, causing droplets to bead and roll off, enhancing water resistance and cleanliness, which benefits outdoor signage, solar panels, and smartphone screens. Selecting the right glass depends on environmental conditions and desired maintenance levels, with hydrophilic glass suited for moisture control and hydrophobic glass preferred for water repellency and self-cleaning properties.
hydrophilic glass vs hydrophobic glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com