Sapphire glass offers superior scratch resistance and clarity compared to Gorilla Glass, making it ideal for luxury watches and high-end smartphones. Gorilla Glass provides excellent impact resistance and durability at a lower cost, ensuring your device remains protected from drops and everyday wear.
Table of Comparison
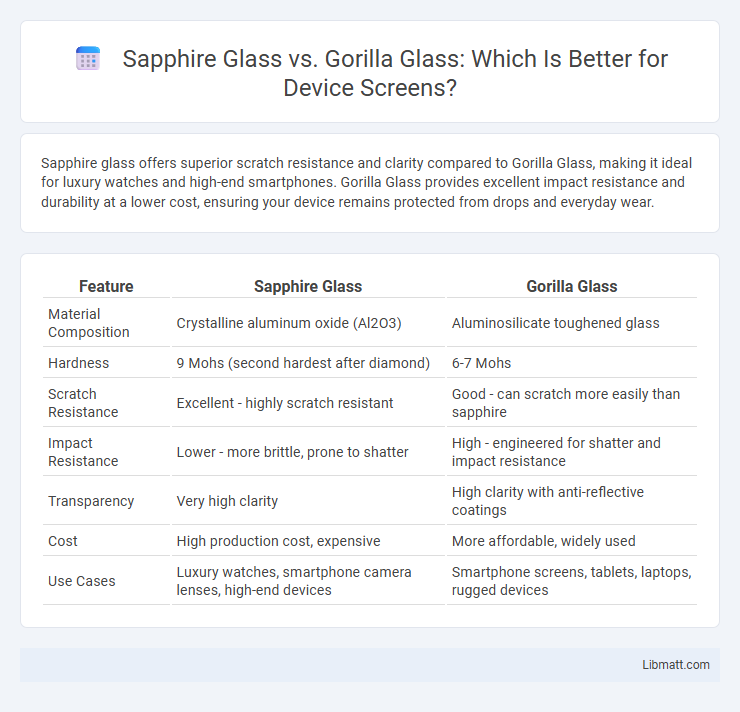
| Feature | Sapphire Glass | Gorilla Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Crystalline aluminum oxide (Al2O3) | Aluminosilicate toughened glass |
| Hardness | 9 Mohs (second hardest after diamond) | 6-7 Mohs |
| Scratch Resistance | Excellent - highly scratch resistant | Good - can scratch more easily than sapphire |
| Impact Resistance | Lower - more brittle, prone to shatter | High - engineered for shatter and impact resistance |
| Transparency | Very high clarity | High clarity with anti-reflective coatings |
| Cost | High production cost, expensive | More affordable, widely used |
| Use Cases | Luxury watches, smartphone camera lenses, high-end devices | Smartphone screens, tablets, laptops, rugged devices |
Introduction to Sapphire Glass and Gorilla Glass
Sapphire glass is an ultra-hard, synthetic material made from crystallized aluminum oxide, known for its exceptional scratch resistance and durability in high-end watch faces and smartphone cameras. Gorilla Glass, developed by Corning, is an alkali-aluminosilicate sheet glass engineered for enhanced toughness, impact resistance, and flexibility, widely used in consumer electronics like smartphones and tablets. Both materials offer unique advantages in protective screen technology, with sapphire glass excelling in scratch resistance and Gorilla Glass providing superior impact protection and shatter resistance.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Sapphire glass is composed of crystallized aluminum oxide (Al2O3) and is manufactured through a high-temperature crystallization process called the Kyropoulos method, resulting in a dense, scratch-resistant surface. Gorilla Glass is an alkali-aluminosilicate sheet glass produced by Corning using an ion-exchange process that strengthens the glass by replacing smaller sodium ions with larger potassium ions. Your choice between these materials depends on the balance between scratch resistance and impact durability required for your device.
Scratch Resistance Comparison
Sapphire glass offers superior scratch resistance with a hardness of 9 on the Mohs scale, making it nearly impervious to everyday scratches from keys or coins, whereas Gorilla Glass typically rates between 6 and 7, providing strong but less durable scratch protection. Despite its hardness, sapphire glass is more brittle and prone to shattering on impact compared to Gorilla Glass's chemically strengthened, flexible design. Devices like luxury watches and some high-end smartphones use sapphire glass for scratch resistance, while Gorilla Glass dominates mainstream smartphone screens for its balance of durability and impact resistance.
Durability and Impact Resistance
Sapphire glass offers superior scratch resistance due to its hardness rating of 9 on the Mohs scale, making it highly durable against abrasions but more brittle under impact. Gorilla Glass, composed of chemically strengthened aluminosilicate, demonstrates enhanced impact resistance by flexing slightly to absorb shocks and resist cracking. While sapphire glass excels in scratch durability, Gorilla Glass provides better overall durability in everyday drops and impacts.
Optical Clarity and Transparency
Sapphire glass offers exceptional optical clarity with a higher refractive index and minimal light distortion, resulting in sharper and more vibrant visuals. Gorilla Glass, while also providing good transparency, tends to have slightly lower optical purity due to its chemical composition and manufacturing process. Both materials ensure excellent screen visibility, but sapphire glass excels in maintaining superior clarity under different lighting conditions.
Weight and Thickness Differences
Sapphire glass is typically denser and heavier than Gorilla Glass, resulting in slightly increased device weight due to its higher aluminum oxide content. Its thickness usually ranges between 0.4 to 1.0 millimeters, often making it more robust but bulkier compared to the thinner 0.2 to 0.6 millimeters thickness of chemically strengthened Gorilla Glass, which uses an aluminosilicate composition. The trade-off between sapphire's superior scratch resistance and Gorilla Glass's lighter, thinner profile influences manufacturers' material choices for smartphones and smartwatches.
Cost Analysis: Production and End-Consumer
Sapphire glass production involves a labor-intensive process with high energy consumption, leading to significantly higher manufacturing costs compared to Gorilla Glass, which uses an ion-exchange strengthening method that is more cost-effective and scalable. For the end-consumer, devices featuring sapphire glass often come at a premium price due to its superior scratch resistance and durability, whereas Gorilla Glass provides a more affordable option with adequate protection for everyday use. Your choice between these materials depends on whether you prioritize cost efficiency or enhanced hardness and luxury in your device's screen protection.
Real-World Applications and Use Cases
Sapphire glass is commonly used in luxury watches and high-end smartphone camera lenses due to its exceptional scratch resistance and durability, making it ideal for small, high-impact surfaces. Gorilla Glass, developed by Corning, dominates smartphone screens, tablets, and laptops, offering a robust, lightweight, and damage-resistant solution optimized for larger touch interfaces. Real-world applications highlight sapphire glass's premium protection in concentrated areas, while Gorilla Glass provides versatile, cost-effective defense across widespread display surfaces.
Pros and Cons of Sapphire Glass vs Gorilla Glass
Sapphire glass offers exceptional scratch resistance and durability, making it ideal for luxury watches and premium smartphones, but it is more expensive and prone to shattering upon impact compared to Gorilla Glass. Gorilla Glass provides superior impact resistance and flexibility at a lower cost, making it widely used in consumer electronics, though it is more susceptible to scratches than sapphire glass. Choosing between sapphire and Gorilla Glass depends on prioritizing scratch resistance versus impact durability and manufacturing costs.
Which is Better: Summary and Recommendation
Sapphire glass offers superior scratch resistance with a hardness rating of 9 on the Mohs scale, making it ideal for luxury watches and premium smartphones where durability against abrasion is critical. Gorilla Glass provides enhanced shatter resistance and flexibility due to its chemically strengthened composition, making it better suited for everyday use in smartphones and tablets exposed to drops and impacts. For devices prioritizing scratch resistance and premium clarity, sapphire glass is recommended, while Gorilla Glass is preferable for cost-effective, impact-resistant protection.
sapphire glass vs Gorilla glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com