Reflective glass features a metallic coating that reduces heat and glare by reflecting sunlight, making it ideal for energy-efficient windows and privacy while maintaining external visibility. Mirror glass has a silvered backing that produces a high-quality, true reflection, perfect for decorative, safety, or signaling purposes, but it does not offer the same solar control benefits as reflective glass.
Table of Comparison
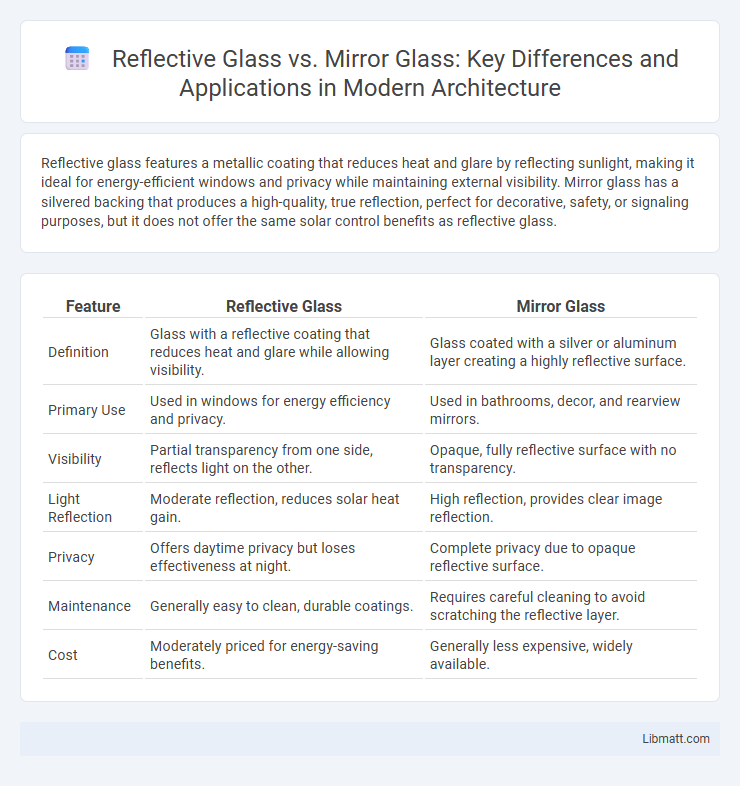
| Feature | Reflective Glass | Mirror Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Glass with a reflective coating that reduces heat and glare while allowing visibility. | Glass coated with a silver or aluminum layer creating a highly reflective surface. |
| Primary Use | Used in windows for energy efficiency and privacy. | Used in bathrooms, decor, and rearview mirrors. |
| Visibility | Partial transparency from one side, reflects light on the other. | Opaque, fully reflective surface with no transparency. |
| Light Reflection | Moderate reflection, reduces solar heat gain. | High reflection, provides clear image reflection. |
| Privacy | Offers daytime privacy but loses effectiveness at night. | Complete privacy due to opaque reflective surface. |
| Maintenance | Generally easy to clean, durable coatings. | Requires careful cleaning to avoid scratching the reflective layer. |
| Cost | Moderately priced for energy-saving benefits. | Generally less expensive, widely available. |
Introduction to Reflective Glass and Mirror Glass
Reflective glass is specially coated to reduce glare and improve energy efficiency by reflecting sunlight while allowing natural light to pass through, making it ideal for architectural applications. Mirror glass, often coated on the back side with a reflective metallic layer, provides a clear and sharp reflection used primarily for decorative and functional purposes. Both types serve distinct roles in design and functionality, with reflective glass emphasizing solar control and mirror glass focusing on image clarity.
Definition and Composition Differences
Reflective glass consists of a transparent substrate coated with a thin metallic layer that reflects light while allowing partial transmission, commonly used in architectural and solar applications. Mirror glass, in contrast, features a glass base with a highly reflective silver or aluminum backing that produces a clear and accurate reflection by fully blocking light transmission. Your choice between reflective and mirror glass depends on whether transparency or precise reflection is more critical for your project's functionality.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Reflective glass is produced by depositing a thin metallic or dielectric coating on one side of a transparent glass substrate, allowing partial light transmission and reflection, which is common in energy-efficient windows and architectural applications. Mirror glass involves applying a silver or aluminum reflective layer, often backed with protective paint, to achieve nearly 100% reflection used in decorative and functional mirrors. Your choice depends on desired light control and durability, as manufacturing processes influence optical performance and resistance to environmental factors.
Key Optical Properties
Reflective glass typically features a metallic coating that controls light transmission and reflection, offering high reflectivity while allowing partial transparency, ideal for energy-efficient windows and privacy functions. Mirror glass provides near-total reflectance with minimal light transmission, producing clear and accurate reflections essential for personal grooming and decorative purposes. Your choice depends on whether you need visibility through the glass or a precise, opaque reflection.
Applications in Architecture and Design
Reflective glass is commonly used in architectural facades to improve energy efficiency by reducing solar heat gain and enhancing natural light control, making it ideal for commercial and residential buildings. Mirror glass, with its high reflectivity and aesthetic appeal, is favored in interior design for decorative wall finishes, bathroom mirrors, and artistic installations, contributing to visual space expansion and elegance. Both materials play crucial roles in modern architecture by balancing functionality with aesthetic enhancement, addressing thermal performance and interior ambiance needs.
Energy Efficiency and Thermal Performance
Reflective glass enhances energy efficiency by reducing solar heat gain through its coated surface, minimizing indoor temperature fluctuations and lowering cooling costs. Mirror glass, while providing privacy and aesthetic appeal, typically lacks the advanced coatings that improve thermal performance, resulting in less effective heat management. Choosing reflective glass can significantly improve a building's insulation properties and contribute to sustainable energy use.
Aesthetics and Visual Appeal
Reflective glass offers a sleek, modern aesthetic with a subtle tint that enhances natural light while maintaining privacy, making your space feel open and sophisticated. Mirror glass provides a clear, crisp reflection ideal for decorative and functional purposes, adding brightness and depth to interiors. Choosing between reflective and mirror glass depends on whether you prioritize privacy and light control or sharp visual clarity and decorative impact.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Reflective glass offers enhanced durability due to its tempered or laminated construction, making it resistant to impact, scratches, and weather conditions compared to traditional mirror glass. Mirror glass, often made from thin glass with a reflective backing, requires careful maintenance to prevent tarnishing and damage to the reflective surface. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize a robust, low-maintenance solution or the classic clarity and finish of mirror glass.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Reflective glass generally costs more than mirror glass due to its specialized coating that controls light transmission and heat reflection, enhancing energy efficiency. Mirror glass is widely available and typically less expensive, making it a popular choice for decorative and functional applications. Availability of reflective glass can be limited depending on the required specifications and geographic location, impacting project budgets and timelines.
Choosing Between Reflective Glass and Mirror Glass
Choosing between reflective glass and mirror glass depends on your desired balance of privacy, aesthetics, and light control. Reflective glass offers a one-way visibility effect by reflecting exterior images while allowing you to see outside, making it ideal for daytime privacy and energy efficiency. Mirror glass provides a solid reflective surface with no transparency, often used for decorative or functional purposes where complete reflection is needed.
reflective glass vs mirror glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com