Acoustic laminated glass is specially designed to reduce noise transmission through its multiple sound-dampening layers, making it ideal for environments where sound insulation is crucial. Standard laminated glass provides basic safety and security benefits by holding shattered glass together but does not offer the enhanced acoustic properties found in acoustic laminated glass.
Table of Comparison
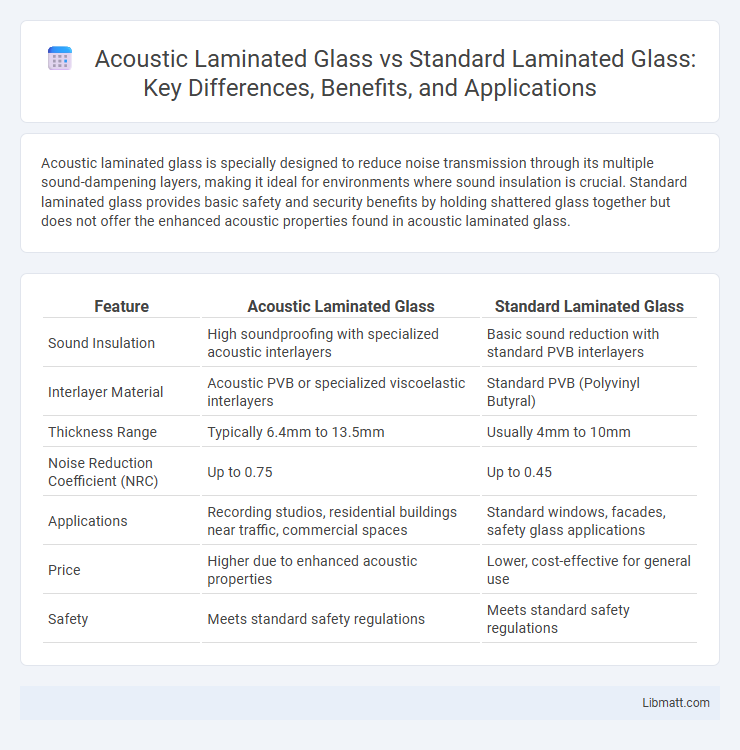
| Feature | Acoustic Laminated Glass | Standard Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Sound Insulation | High soundproofing with specialized acoustic interlayers | Basic sound reduction with standard PVB interlayers |
| Interlayer Material | Acoustic PVB or specialized viscoelastic interlayers | Standard PVB (Polyvinyl Butyral) |
| Thickness Range | Typically 6.4mm to 13.5mm | Usually 4mm to 10mm |
| Noise Reduction Coefficient (NRC) | Up to 0.75 | Up to 0.45 |
| Applications | Recording studios, residential buildings near traffic, commercial spaces | Standard windows, facades, safety glass applications |
| Price | Higher due to enhanced acoustic properties | Lower, cost-effective for general use |
| Safety | Meets standard safety regulations | Meets standard safety regulations |
Introduction to Laminated Glass Types
Acoustic laminated glass features specialized interlayers designed to reduce sound transmission, making it ideal for noise-sensitive environments. Standard laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer, providing safety and shatter resistance without significant soundproofing benefits. Your choice between these glass types depends on the desired balance of acoustic insulation and safety performance.
What Is Standard Laminated Glass?
Standard laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded together with an interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB), providing enhanced safety and durability compared to regular glass. This construction helps hold the glass fragments in place when shattered, reducing the risk of injury and improving security. Your choice of standard laminated glass offers fundamental noise reduction and UV protection, though it may not perform as well acoustically as specialized acoustic laminated glass.
What Is Acoustic Laminated Glass?
Acoustic laminated glass consists of multiple glass layers bonded with a specialized noise-reducing interlayer designed to absorb and dampen sound vibrations, significantly improving sound insulation compared to standard laminated glass. Standard laminated glass typically uses a single polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer primarily for safety and impact resistance, without enhanced acoustic properties. Acoustic laminated glass is ideal for environments requiring superior noise control, such as urban buildings and recording studios.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Acoustic laminated glass is manufactured by incorporating specialized sound-damping interlayers such as polyvinyl butyral (PVB) with viscoelastic properties, enhancing its ability to reduce noise transmission compared to standard laminated glass. Standard laminated glass typically uses conventional PVB interlayers focused primarily on safety and impact resistance rather than acoustic performance. The manufacturing process for acoustic laminated glass demands precise lamination techniques and controlled temperature and pressure settings to optimize sound insulation without compromising clarity or strength.
Sound Insulation Performance
Acoustic laminated glass offers superior sound insulation performance compared to standard laminated glass due to its specialized interlayer materials designed to absorb and dampen sound vibrations. Typical acoustic laminates use viscoelastic interlayers that significantly reduce noise transmission across a broad frequency range, particularly low and mid frequencies essential for urban environments. Standard laminated glass, while providing basic noise reduction, lacks these enhanced acoustic properties, making acoustic laminated glass the preferred choice for improved soundproofing in residential and commercial applications.
Safety and Security Differences
Acoustic laminated glass features enhanced inner layers designed to absorb and reduce sound transmission, providing superior noise insulation compared to standard laminated glass. Both types incorporate a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, which enhances safety by holding glass fragments together upon impact, but acoustic laminated glass typically uses thicker or multiple PVB layers, increasing its resistance to breakage and intrusion. This construction not only improves soundproofing but also elevates security by making forced entry more difficult than with standard laminated glass.
Energy Efficiency and UV Protection
Acoustic laminated glass enhances energy efficiency by providing superior insulation that reduces heat transfer compared to standard laminated glass, lowering your heating and cooling costs. It also offers advanced UV protection, blocking up to 99% of harmful ultraviolet rays, which helps prevent interior fading and damage. This combination makes acoustic laminated glass an optimal choice for maintaining indoor comfort and protecting furnishings effectively.
Application Scenarios for Each Glass Type
Acoustic laminated glass is ideal for environments requiring enhanced sound insulation, such as recording studios, conference rooms, and urban residential buildings near busy roads or airports. Standard laminated glass suits general safety and security applications like storefronts, vehicle windshields, and schools, where impact resistance and basic noise reduction are sufficient. Selecting the appropriate type depends on balancing noise control needs with safety and budget considerations.
Cost Analysis and Budget Considerations
Acoustic laminated glass typically incurs higher costs compared to standard laminated glass due to its specialized sound-dampening interlayers designed to reduce noise transmission. Budget considerations must factor in the long-term benefits of improved acoustic insulation, which can lead to energy savings and increased property value despite the initial investment. Standard laminated glass offers a more economical option but may require supplementary soundproofing measures, potentially increasing overall expenses.
Choosing the Right Laminated Glass for Your Needs
Acoustic laminated glass features a specialized interlayer designed to reduce noise transmission, making it ideal for environments requiring enhanced sound insulation such as offices, homes near busy roads, or recording studios. Standard laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded with a plastic interlayer, providing safety and basic noise reduction but lacking the superior soundproofing qualities of acoustic variants. Selecting the right laminated glass involves evaluating noise reduction needs, safety requirements, and budget constraints to ensure optimal performance and comfort.
Acoustic laminated glass vs standard laminated glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com