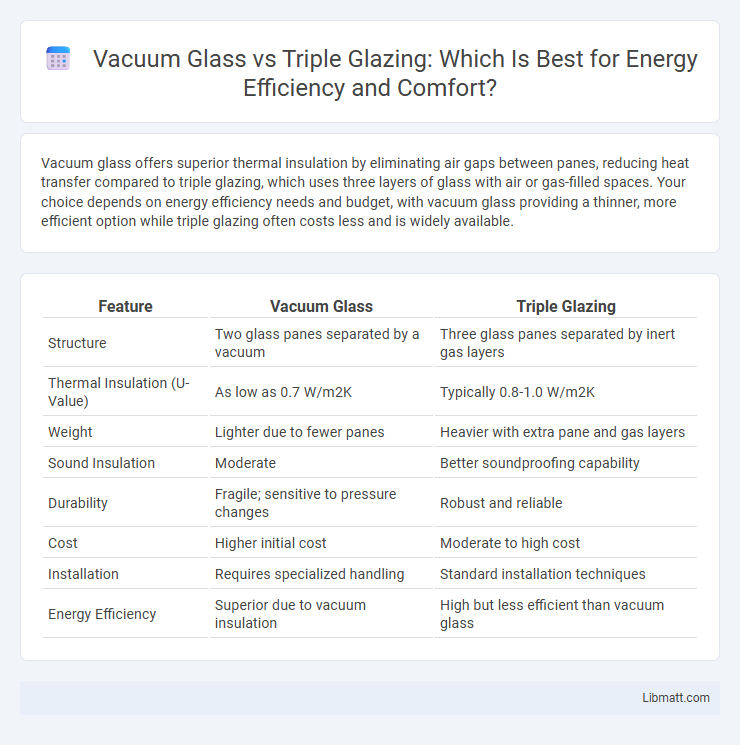
Vacuum glass offers superior thermal insulation by eliminating air gaps between panes, reducing heat transfer compared to triple glazing, which uses three layers of glass with air or gas-filled spaces. Your choice depends on energy efficiency needs and budget, with vacuum glass providing a thinner, more efficient option while triple glazing often costs less and is widely available.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vacuum Glass | Triple Glazing |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Two glass panes separated by a vacuum | Three glass panes separated by inert gas layers |
| Thermal Insulation (U-Value) | As low as 0.7 W/m2K | Typically 0.8-1.0 W/m2K |
| Weight | Lighter due to fewer panes | Heavier with extra pane and gas layers |
| Sound Insulation | Moderate | Better soundproofing capability |
| Durability | Fragile; sensitive to pressure changes | Robust and reliable |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Moderate to high cost |
| Installation | Requires specialized handling | Standard installation techniques |
| Energy Efficiency | Superior due to vacuum insulation | High but less efficient than vacuum glass |
Introduction to Vacuum Glass and Triple Glazing
Vacuum glass consists of two glass panes separated by a vacuum layer, significantly reducing heat transfer and improving insulation performance. Triple glazing features three glass layers separated by inert gas-filled spaces, providing enhanced thermal efficiency and soundproofing compared to double glazing. Both technologies aim to increase energy efficiency in buildings by minimizing heat loss through windows.
How Vacuum Glass Works
Vacuum glass consists of two glass panes separated by a narrow vacuum gap that eliminates heat transfer through conduction and convection, providing superior insulation compared to triple glazing. The vacuum layer acts as a barrier to thermal energy, significantly reducing heat loss and enhancing energy efficiency in buildings. Your choice of vacuum glass ensures optimal thermal performance while maintaining clear visibility and reducing condensation issues.
The Structure of Triple Glazing
Triple glazing consists of three glass panes separated by air or gas-filled spaces, typically argon or krypton, to enhance insulation and reduce heat transfer. The structure improves thermal efficiency by creating multiple barriers against temperature fluctuations, making it suitable for colder climates. Your choice of triple glazing can significantly impact energy savings and soundproofing compared to other window technologies like vacuum glass.
Thermal Insulation Performance
Vacuum glass offers superior thermal insulation performance compared to traditional triple glazing due to its minimal air gap, which eliminates heat conduction and convection inside the pane. Triple glazing improves insulation by using three layers of glass separated by inert gas-filled spaces, but the presence of multiple gas layers still allows some thermal transfer. Your choice of vacuum glass can reduce heat loss significantly, resulting in enhanced energy efficiency and lower heating costs in colder climates.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Vacuum glass offers superior energy efficiency compared to triple glazing due to its extremely low thermal conductivity, achieved by creating a near vacuum between two glass panes that minimizes heat transfer. Triple glazing relies on three glass panes separated by insulating gas, enhancing thermal insulation but still allowing more conduction and convection than vacuum glass. Your choice impacts overall energy savings, with vacuum glass providing better performance in reducing heat loss and improving insulation in extreme climates.
Acoustic Insulation Capabilities
Vacuum glass provides superior acoustic insulation by eliminating the air gap that allows sound waves to pass through, significantly reducing noise transmission compared to triple glazing. Triple glazing enhances soundproofing by using three glass panes and gas-filled spaces, but vacuum glass's near-vacuum layer offers an unmatched barrier against external noise. Your choice between vacuum glass and triple glazing should consider the level of sound reduction needed, with vacuum glass typically delivering better performance in high-noise environments.
Thickness and Weight Differences
Vacuum glass typically measures around 6 to 10 millimeters in thickness, making it thinner compared to triple glazing, which usually ranges between 24 to 36 millimeters due to its three glass panes and air or gas-filled layers. The reduced thickness of vacuum glass results in a lighter overall weight, often cutting down the load by up to 40% compared to traditional triple glazed windows. This weight difference makes vacuum glass an ideal choice for retrofit projects and applications where structural support is limited.
Durability and Longevity
Vacuum glass and triple glazing both offer enhanced durability and longevity compared to standard windows, with vacuum glass typically providing superior resistance to thermal stress and moisture intrusion due to its sealed vacuum gap. Triple glazing features three panes of glass separated by insulating gas layers, which improves thermal performance but may have a shorter lifespan if seals degrade over time. Your choice between vacuum glass and triple glazing should consider the expected maintenance requirements and environmental conditions to ensure optimal durability and long-term energy efficiency.
Cost Analysis: Vacuum Glass vs. Triple Glazing
Vacuum glass typically incurs higher upfront costs compared to triple glazing due to advanced manufacturing techniques and specialized materials. Your choice impacts long-term savings, as vacuum glass offers superior thermal insulation and space efficiency, potentially reducing energy bills more effectively than triple glazing. When conducting a cost analysis, factor in installation expenses, durability, and energy performance to determine the best value for your building needs.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Project
Vacuum glass offers superior thermal insulation with a slim profile, making it ideal for projects where space efficiency and high energy performance are critical. Triple glazing enhances soundproofing and durability with multiple glass layers, suitable for colder climates requiring robust insulation. Your project's specific needs for energy savings, noise reduction, and design constraints will determine whether vacuum glass or triple glazing is the better choice.
vacuum glass vs triple glazing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com