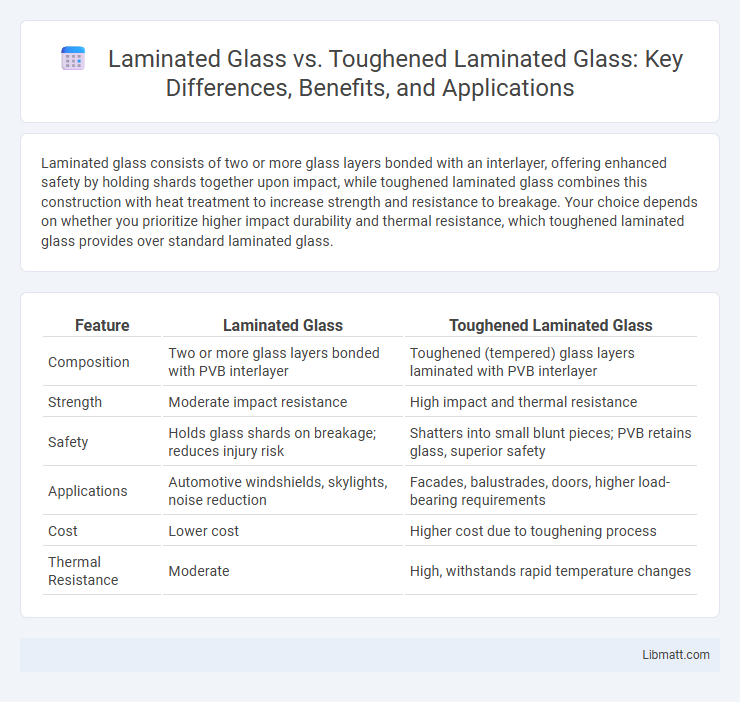
Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, offering enhanced safety by holding shards together upon impact, while toughened laminated glass combines this construction with heat treatment to increase strength and resistance to breakage. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize higher impact durability and thermal resistance, which toughened laminated glass provides over standard laminated glass.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Laminated Glass | Toughened Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Two or more glass layers bonded with PVB interlayer | Toughened (tempered) glass layers laminated with PVB interlayer |
| Strength | Moderate impact resistance | High impact and thermal resistance |
| Safety | Holds glass shards on breakage; reduces injury risk | Shatters into small blunt pieces; PVB retains glass, superior safety |
| Applications | Automotive windshields, skylights, noise reduction | Facades, balustrades, doors, higher load-bearing requirements |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to toughening process |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate | High, withstands rapid temperature changes |
Introduction to Laminated Glass and Toughened Laminated Glass
Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, providing enhanced safety and sound insulation by holding shards together upon impact. Toughened laminated glass combines laminated glass with a toughening process, increasing strength and thermal resistance while maintaining the safety benefits of lamination. This makes toughened laminated glass ideal for high-stress environments requiring durability, such as automotive windshields and architectural applications.
What is Laminated Glass?
Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with an interlayer, typically made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), which enhances safety by holding the shards in place if broken. Toughened laminated glass combines the impact resistance of toughened (tempered) glass with the safety features of laminated glass, offering superior durability and security. You can rely on laminated glass for noise reduction and UV protection, while toughened laminated glass provides increased strength for high-stress environments.
What is Toughened Laminated Glass?
Toughened laminated glass combines the strength of toughened (tempered) glass with the safety features of laminated glass, offering enhanced impact resistance and durability. It consists of two or more layers of toughened glass bonded with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, providing superior shatter resistance and safety by preventing glass fragments from dispersing upon breakage. Commonly used in automotive windshields and high-security architectural applications, toughened laminated glass delivers both structural integrity and protection against forced entry or accidents.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB), through heat and pressure to enhance safety and sound insulation. Toughened laminated glass combines this lamination with a prior toughening process, where the glass is rapidly heated and cooled to increase strength and impact resistance before lamination. This two-step manufacturing process results in glass that offers superior durability, increased resistance to thermal stress, and enhanced safety performance compared to standard laminated glass.
Strength and Durability Differences
Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, providing basic impact resistance and enhanced safety by holding shards together upon breakage. Toughened laminated glass combines the toughness of tempered glass with the safety of lamination, offering significantly higher strength and increased resistance to impact, thermal stress, and breakage. If you require superior durability and enhanced protection for your windows or facades, toughened laminated glass is the optimal choice over standard laminated glass.
Safety Features: Laminated vs Toughened Laminated Glass
Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer that holds shards in place upon impact, reducing injury risk. Toughened laminated glass combines the strength of toughened glass with the safety benefits of lamination, offering enhanced resistance to breakage and preventing dangerous fragments from dispersing. Your choice of toughened laminated glass provides superior safety features for high-risk environments, combining shatter resistance with secure glass retention.
Applications in Architecture and Automotive
Laminated glass provides enhanced safety and noise reduction, making it ideal for architectural applications such as facades, skylights, and balustrades, whereas toughened laminated glass combines the strength of toughened glass with the safety benefits of lamination, offering superior impact resistance and thermal stability. Automotive industry uses laminated glass primarily for windshields due to its ability to hold shards together upon impact, while toughened laminated glass is favored in side and rear windows for increased durability and passenger protection. The integration of toughened laminated glass in both industries supports compliance with stringent safety standards and improves overall structural performance.
Acoustic and Thermal Insulation Properties
Laminated glass offers superior acoustic insulation by effectively dampening sound waves through its interlayer, reducing noise transmission compared to toughened laminated glass, which combines impact resistance with moderate soundproofing characteristics. Toughened laminated glass provides enhanced thermal insulation due to its increased strength and ability to withstand temperature fluctuations, making it suitable for energy-efficient applications where both safety and insulation are critical. Both types optimize thermal performance, but laminated glass excels in soundproofing, while toughened laminated glass balances thermal insulation and structural durability.
Cost Comparison and Economic Considerations
Laminated glass generally costs less than toughened laminated glass due to simpler manufacturing processes and lower material strength requirements. Toughened laminated glass demands additional heat treatment and quality control, increasing production expenses and retail prices. When considering economic factors, laminated glass offers cost efficiency for standard applications, while toughened laminated glass provides better impact resistance worth the higher investment for enhanced safety and durability.
Selecting the Right Glass for Your Project
Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded with an interlayer, providing enhanced safety and noise reduction, while toughened laminated glass combines the strength of toughened glass with the safety features of lamination for superior impact resistance and durability. Your choice depends on project requirements such as safety standards, load-bearing capacity, and environmental conditions, where toughened laminated glass suits high-impact areas and laminated glass excels in sound insulation and UV protection. Evaluating these factors ensures selecting the right glass enhances both performance and safety in your construction or design project.
laminated glass vs toughened laminated glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com