Toughened glass and tempered glass are essentially the same, both undergoing a heat treatment process that increases their strength and safety compared to regular glass. Your choice between the two terms typically depends on regional preferences, but both offer superior resistance to impact and, when broken, shatter into small, less harmful pieces.
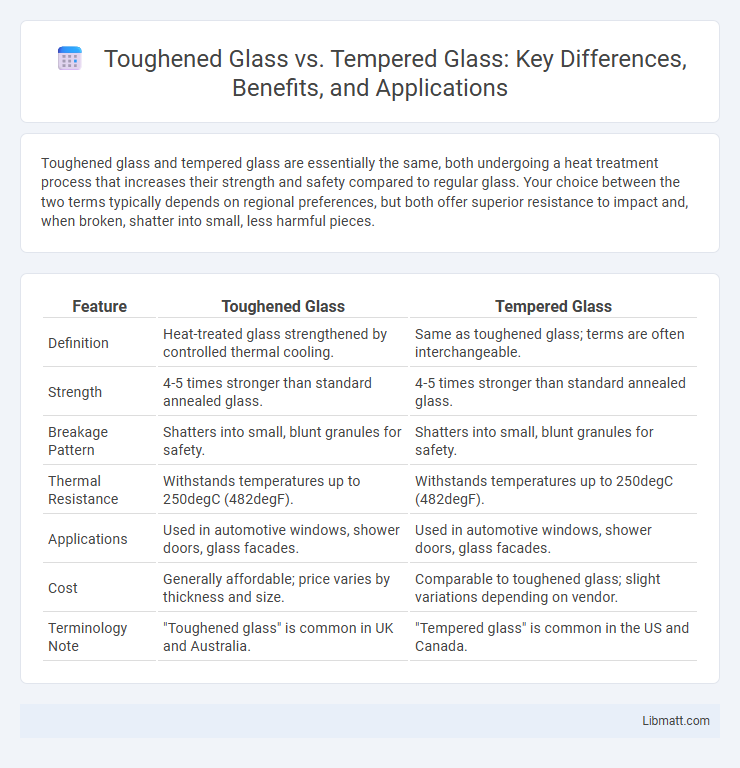
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Toughened Glass | Tempered Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Heat-treated glass strengthened by controlled thermal cooling. | Same as toughened glass; terms are often interchangeable. |
| Strength | 4-5 times stronger than standard annealed glass. | 4-5 times stronger than standard annealed glass. |
| Breakage Pattern | Shatters into small, blunt granules for safety. | Shatters into small, blunt granules for safety. |
| Thermal Resistance | Withstands temperatures up to 250degC (482degF). | Withstands temperatures up to 250degC (482degF). |
| Applications | Used in automotive windows, shower doors, glass facades. | Used in automotive windows, shower doors, glass facades. |
| Cost | Generally affordable; price varies by thickness and size. | Comparable to toughened glass; slight variations depending on vendor. |
| Terminology Note | "Toughened glass" is common in UK and Australia. | "Tempered glass" is common in the US and Canada. |
Understanding Toughened Glass
Toughened glass, also known as tempered glass, undergoes a specialized thermal treatment process that increases its strength compared to standard annealed glass. This glass is heated to approximately 620degC and then rapidly cooled, resulting in a surface compression layer that enhances durability and resistance to impact and thermal stress. Toughened glass is widely used in applications requiring high safety standards, such as automotive windows, shower doors, and architectural facades.
What is Tempered Glass?
Tempered glass is a type of safety glass processed by controlled thermal or chemical treatments to increase its strength compared to normal glass. This treatment causes the outer surfaces to compress and the inner core to tension, making tempered glass up to four times stronger and resistant to impact, heat, and stress. You can recognize tempered glass by its characteristic break pattern, which shatters into small, blunt pieces, reducing the risk of injury.
Key Differences Between Toughened and Tempered Glass
Toughened glass and tempered glass are essentially the same, both referring to glass that has been heat-treated to increase its strength and safety. The key difference lies primarily in terminology: "toughened" is commonly used in Europe and Asia, while "tempered" is the preferred term in North America. Your choice between the two terms depends on regional preferences, but both types offer enhanced durability, shatter resistance, and improved safety for architectural and automotive applications.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Toughened glass and tempered glass often refer to the same material, produced through a thermal tempering process involving rapid cooling after heating to around 620degC, which increases surface compression and enhances strength. The key manufacturing difference lies in nomenclature rather than technique, as both undergo heating and quenching steps to improve mechanical and thermal resistance. Unlike laminated glass, toughened or tempered glass cannot be cut or drilled after treatment without shattering, making precise fabrication essential before the tempering process.
Strength and Durability: Toughened vs Tempered Glass
Toughened glass and tempered glass both undergo heat treatment to enhance their strength and durability, making them significantly stronger than regular glass. Toughened glass is heated to a higher temperature and cooled rapidly, resulting in greater resistance to impact and thermal stress, ideal for safety applications. Your choice between the two should consider the specific strength requirements, with tempered glass offering reliable durability for everyday use, while toughened glass is suited for more demanding environments requiring maximum toughness.
Safety Features and Breakage Patterns
Toughened glass and tempered glass are essentially the same, both designed with enhanced safety features that increase strength by rapid cooling during manufacturing. When broken, tempered glass shatters into small, blunt granules rather than sharp shards, minimizing injury risks in automotive, architectural, and furniture applications. This controlled breakage pattern is a critical safety advantage over regular glass, making tempered (toughened) glass the preferred option for environments requiring high impact resistance and safety compliance.
Applications: Where to Use Each Glass Type
Toughened glass and tempered glass are often used interchangeably but serve distinct applications based on safety and strength requirements. Toughened glass is ideal for architectural elements like windows, facades, and doors where high impact resistance and thermal stability are crucial. Tempered glass is commonly used in automotive windows, shower doors, and glass furniture, providing enhanced safety by shattering into small, blunt pieces to protect you from injury.
Cost Comparison and Affordability
Toughened glass and tempered glass actually refer to the same heat-treated safety glass, so their cost differences are minimal or nonexistent. Pricing varies mainly based on thickness, size, and supplier rather than the glass type, making affordability largely dependent on project specifications. Generally, both toughened and tempered glass offer a cost-effective safety solution compared to laminated glass or other enhanced safety options.
Pros and Cons of Toughened and Tempered Glass
Toughened glass and tempered glass are often used interchangeably, but tempered glass undergoes a controlled thermal or chemical treatment to improve strength, offering high resistance to impact and thermal stress. Toughened glass provides enhanced durability and safety by shattering into small, blunt pieces on breakage, minimizing injury risks, but it can be more expensive and difficult to cut or modify after processing. Your choice depends on the balance between safety requirements, application needs, and cost considerations.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Needs
Toughened glass and tempered glass both offer enhanced strength and safety compared to regular glass, making them ideal for various architectural and automotive applications. Tempered glass undergoes rapid cooling after heating, resulting in increased resistance to impact and thermal stress, while toughened glass is manufactured using controlled heat treatment to achieve similar durability. Your choice depends on specific requirements such as impact resistance, thermal tolerance, and application environment to ensure optimal performance and safety.
toughened glass vs tempered glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com