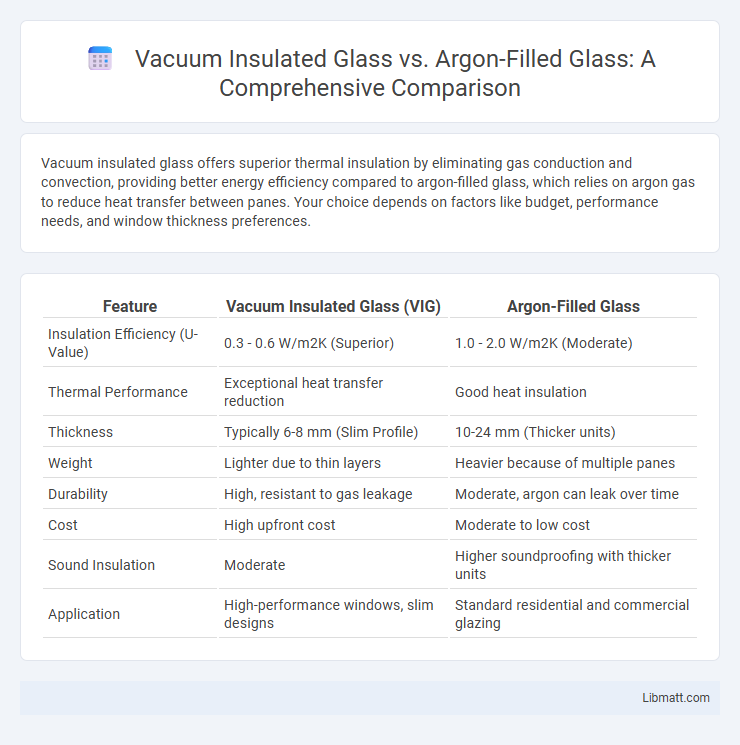
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation by eliminating gas conduction and convection, providing better energy efficiency compared to argon-filled glass, which relies on argon gas to reduce heat transfer between panes. Your choice depends on factors like budget, performance needs, and window thickness preferences.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vacuum Insulated Glass (VIG) | Argon-Filled Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Insulation Efficiency (U-Value) | 0.3 - 0.6 W/m2K (Superior) | 1.0 - 2.0 W/m2K (Moderate) |
| Thermal Performance | Exceptional heat transfer reduction | Good heat insulation |
| Thickness | Typically 6-8 mm (Slim Profile) | 10-24 mm (Thicker units) |
| Weight | Lighter due to thin layers | Heavier because of multiple panes |
| Durability | High, resistant to gas leakage | Moderate, argon can leak over time |
| Cost | High upfront cost | Moderate to low cost |
| Sound Insulation | Moderate | Higher soundproofing with thicker units |
| Application | High-performance windows, slim designs | Standard residential and commercial glazing |
Introduction to Vacuum Insulated Glass and Argon-Filled Glass
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) features a vacuum space between two glass panes, dramatically reducing heat transfer by eliminating gas molecules that conduct heat, resulting in superior thermal insulation compared to traditional glazing. Argon-filled glass contains argon gas, an inert and low-conductivity gas, between double or triple panes to enhance insulation by reducing heat transfer through convection and conduction. Both technologies aim to improve energy efficiency in windows, with VIG offering higher performance in thermal resistance and thinner profile solutions than argon-filled units.
Composition and Structure: How Each Technology Works
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) consists of two glass panes separated by a thin vacuum space that eliminates heat transfer through conduction and convection, enhancing thermal insulation. Argon-filled glass uses a gas-filled cavity between panes, where argon gas reduces heat transfer more effectively than air due to its lower thermal conductivity. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize maximum insulation with vacuum technology or a cost-effective option using argon gas for better energy efficiency.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) offers superior thermal insulation compared to argon-filled glass by minimizing heat transfer through the vacuum layer, effectively eliminating convective and conductive heat loss. Argon-filled glass improves insulation by filling the space between panes with argon gas, reducing thermal conductivity better than air but not as effectively as a vacuum. Your choice of glazing impacts energy efficiency significantly, with VIG providing enhanced performance in extreme temperature conditions.
Soundproofing Capabilities: Which Glass is Quieter?
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior soundproofing capabilities by eliminating the air gap found in argon-filled glass, significantly reducing noise transmission. Argon-filled glass provides decent sound insulation, but its gas layer cannot match the vacuum's ability to block sound vibrations effectively. For your quiet comfort, vacuum insulated glass is the optimal choice for maximizing noise reduction in windows.
Energy Efficiency: Reducing Heating and Cooling Costs
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation by eliminating heat transfer through conduction and convection, significantly reducing heating and cooling costs compared to argon-filled glass. Argon gas improves energy efficiency by slowing heat transfer between panes, but vacuum insulation achieves lower U-values, enhancing overall building performance. Investing in vacuum insulated glass results in greater energy savings and improved temperature regulation for residential and commercial properties.
Durability and Lifespan of Both Glass Types
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior durability and a longer lifespan due to its airtight vacuum space that prevents moisture buildup and minimizes heat transfer. Argon-filled glass, while effective in thermal insulation, may experience gas leakage over time, reducing its insulating performance and lifespan. Your choice between these glass types impacts long-term energy efficiency and maintenance needs in windows and doors.
Installation Process and Compatibility
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) requires precise installation techniques to maintain the vacuum seal and prevent damage, typically necessitating specialized frames and expert handling to ensure long-term durability. Argon-filled glass offers greater compatibility with conventional window frames and standard installation methods, making it easier to retrofit into existing structures without extensive modifications. Both glazing types demand professional installation to optimize thermal performance, but argon-filled glass provides more flexibility for a wider range of architectural applications.
Cost Differences and Long-Term Value
Vacuum insulated glass typically has a higher upfront cost compared to argon-filled glass due to advanced manufacturing processes and superior thermal insulation properties. Argon-filled glass offers a more affordable initial investment but may have lower long-term energy savings due to slightly reduced insulation performance. Over time, vacuum insulated glass provides greater energy efficiency and durability, resulting in enhanced long-term value despite the higher initial price.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal performance by minimizing heat transfer without the need for greenhouse gases, making it a more sustainable choice compared to argon-filled glass, which relies on argon gas that may leak over time, reducing efficiency. The production of vacuum insulated glass uses fewer resources and extends product lifespan, lowering its overall carbon footprint. Your choice of vacuum insulated glass contributes to long-term environmental benefits through enhanced energy savings and reduced reliance on escaped insulating gases.
Ideal Applications: Choosing the Right Glass for Your Needs
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and is ideal for extreme climates or high-performance building envelopes requiring maximum energy efficiency. Argon-filled glass provides excellent insulation at a lower cost, making it suitable for moderate climate zones and residential windows aiming to balance performance and affordability. Your choice depends on the climate severity, budget constraints, and specific energy-saving goals to optimize comfort and cost-effectiveness.
vacuum insulated glass vs argon-filled glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com