Security glass offers enhanced impact resistance and shatterproof qualities, ideal for protecting against break-ins and harsh weather, while laminated glass features a durable interlayer that holds shards together upon breaking, providing superior safety and noise reduction. Choosing the right option depends on your specific needs for strength, safety, and sound insulation in your space.
Table of Comparison
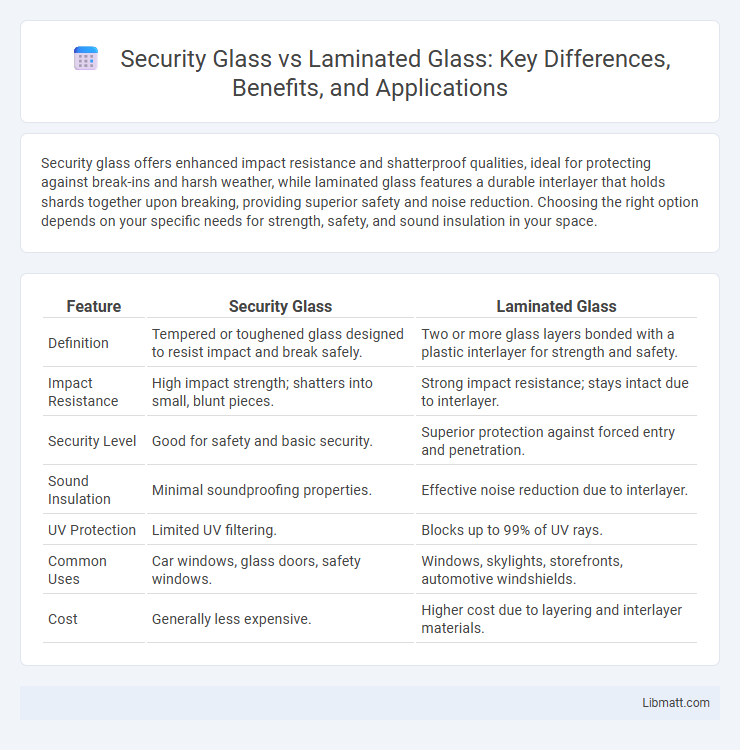
| Feature | Security Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tempered or toughened glass designed to resist impact and break safely. | Two or more glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer for strength and safety. |
| Impact Resistance | High impact strength; shatters into small, blunt pieces. | Strong impact resistance; stays intact due to interlayer. |
| Security Level | Good for safety and basic security. | Superior protection against forced entry and penetration. |
| Sound Insulation | Minimal soundproofing properties. | Effective noise reduction due to interlayer. |
| UV Protection | Limited UV filtering. | Blocks up to 99% of UV rays. |
| Common Uses | Car windows, glass doors, safety windows. | Windows, skylights, storefronts, automotive windshields. |
| Cost | Generally less expensive. | Higher cost due to layering and interlayer materials. |
Understanding Security Glass: An Overview
Security glass is engineered to withstand impact and provide enhanced protection against break-ins, often featuring multiple layers fused together to absorb shock and resist shattering. Laminated glass, a key type of security glass, consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, which holds the glass fragments in place if broken, reducing the risk of injury and intrusion. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right glass solution to safeguard your property effectively.
What Is Laminated Glass? Key Features Explained
Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded together with an interlayer, typically made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), providing enhanced safety by holding the glass shards in place upon impact. Its key features include improved sound insulation, UV protection, and superior resistance to penetration, making it ideal for automotive windshields and architectural applications. Unlike standard security glass, laminated glass maintains structural integrity even when broken, reducing the risk of injury and unauthorized access.
Primary Differences Between Security Glass and Laminated Glass
Security glass and laminated glass both enhance safety but differ primarily in construction and impact resistance; security glass typically combines tempered glass layers with a plastic interlayer for high strength, while laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded by a resilient interlayer that holds shards together upon breakage. Laminated glass excels in preventing penetration and reducing injury risk due to its ability to remain intact when cracked, whereas security glass offers superior resistance to impact and forced entry. Choosing the right option depends on your specific needs for durability, safety, and protection against different types of threats.
Safety Performance Comparison: Breakage and Impact Resistance
Security glass offers superior breakage resistance with higher impact strength, designed to withstand forced entry and blunt impacts, while laminated glass excels in safety by holding shards together upon breakage, preventing injury. Laminated glass incorporates a plastic interlayer that absorbs impacts and maintains structural integrity even when cracked, reducing the risk of penetration. Your choice between security glass and laminated glass should consider whether impact resistance or shard containment is the priority for your safety requirements.
Security Levels: Protection Against Theft and Vandalism
Security glass offers high resistance to impact, making it ideal for protecting against break-ins and vandalism by preventing easy penetration. Laminated glass contains a durable interlayer that holds shards together when broken, maintaining a barrier that deters theft and prolongs intrusion time. Your choice depends on the desired level of security, with laminated glass excelling in safety retention while security glass maximizes force resistance.
Acoustic and Thermal Insulation: Which Glass Performs Better?
Laminated glass outperforms security glass in acoustic insulation due to its interlayer, which absorbs sound vibrations and reduces noise transmission effectively. For thermal insulation, laminated glass also provides superior performance by minimizing heat transfer, helping maintain your indoor temperature and improving energy efficiency. Security glass primarily offers impact resistance but lacks the enhanced soundproofing and thermal benefits found in laminated glass.
Applications and Use Cases: Where Each Glass Type Excels
Security glass, known for its impact resistance and ability to withstand forced entry, is ideal for high-risk areas such as bank teller windows, storefronts, and vehicle windshields. Laminated glass excels in applications requiring both safety and sound insulation, commonly used in residential windows, skylights, and automotive windshields to prevent shattering and reduce noise pollution. While security glass prioritizes protection against break-ins, laminated glass is preferred where occupant safety and acoustic comfort are essential.
Cost Comparison: Which Glass Offers Better Value?
Security glass typically costs more upfront due to its enhanced strength and ability to withstand high impact, making it ideal for high-risk environments. Laminated glass offers better long-term value by combining affordability with durability, as its multiple layers hold shards together upon breakage, reducing injury risks and maintenance expenses. Choosing laminated glass often results in lower overall costs while still providing effective security and safety benefits.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Security glass requires professional installation to ensure proper fit and maximum impact resistance, often involving heavy-duty frames and specialized sealing techniques. Laminated glass, while also needing expert installation, typically demands less structural reinforcement and allows easier replacement of damaged interlayers without full panel removal. Maintenance for security glass involves routine inspections for frame integrity and impact damage, whereas laminated glass maintenance focuses on preserving the interlayer's clarity and preventing delamination caused by moisture or UV exposure.
Choosing the Right Glass: Security Glass vs. Laminated Glass
Security glass offers enhanced impact resistance by combining multiple layers of tempered or heat-strengthened glass, ideal for high-risk areas requiring maximum protection against break-ins or blasts. Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with a durable polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, providing excellent safety by holding shards together upon impact and enhancing sound insulation. Selecting between security glass and laminated glass depends on the required level of force resistance, safety needs, and specific application such as commercial entrances, automotive glazing, or hurricane-prone regions.
security glass vs laminated glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com