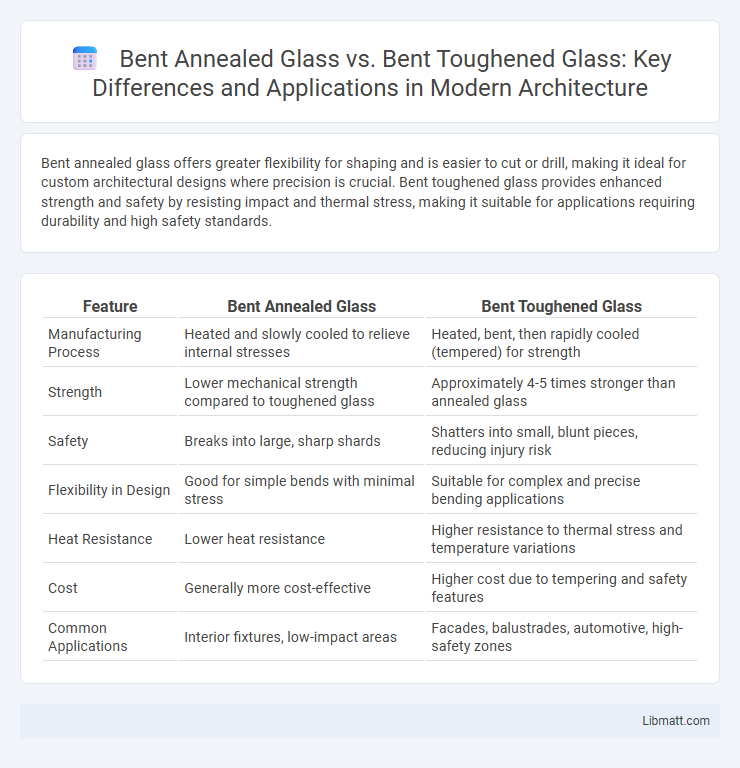
Bent annealed glass offers greater flexibility for shaping and is easier to cut or drill, making it ideal for custom architectural designs where precision is crucial. Bent toughened glass provides enhanced strength and safety by resisting impact and thermal stress, making it suitable for applications requiring durability and high safety standards.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bent Annealed Glass | Bent Toughened Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Heated and slowly cooled to relieve internal stresses | Heated, bent, then rapidly cooled (tempered) for strength |
| Strength | Lower mechanical strength compared to toughened glass | Approximately 4-5 times stronger than annealed glass |
| Safety | Breaks into large, sharp shards | Shatters into small, blunt pieces, reducing injury risk |
| Flexibility in Design | Good for simple bends with minimal stress | Suitable for complex and precise bending applications |
| Heat Resistance | Lower heat resistance | Higher resistance to thermal stress and temperature variations |
| Cost | Generally more cost-effective | Higher cost due to tempering and safety features |
| Common Applications | Interior fixtures, low-impact areas | Facades, balustrades, automotive, high-safety zones |
Introduction to Bent Glass Types
Bent annealed glass offers a smooth curvature formed through controlled cooling, providing flexibility in design applications with moderate strength and safety properties. Bent toughened glass undergoes a heat treatment process that enhances its strength and impact resistance, making it ideal for architectural elements requiring higher durability and safety standards. Your choice between these bent glass types depends on the specific structural requirements and safety considerations of your project.
Overview of Bent Annealed Glass
Bent annealed glass is a type of glass that undergoes a controlled heating and slow cooling process to relieve internal stresses, allowing it to be shaped into curved forms without compromising clarity or strength. It offers excellent optical quality and is commonly used in architectural applications where precise bends and smooth curves are required. Unlike bent toughened glass, bent annealed glass lacks the enhanced impact resistance and thermal strength but provides superior formability and reduced risk of spontaneous breakage.
Overview of Bent Toughened Glass
Bent toughened glass undergoes a heat-strengthening process at temperatures around 600degC, which improves its structural integrity and resistance to impact compared to bent annealed glass. This type of glass is ideal for architectural applications requiring durability and safety, such as curved facades, balustrades, and skylights. The tempering process also enhances thermal resistance, making bent toughened glass suitable for environments with fluctuating temperatures.
Manufacturing Processes: Annealed vs Toughened
Bent annealed glass is manufactured through a controlled slow cooling process that relieves internal stresses, resulting in a glass that is flexible to slight bending but remains fragile under impact. Bent toughened glass undergoes a rapid heating and quenching cycle after bending, producing high compressive surface stresses that significantly increase its strength and impact resistance. Your choice between these manufacturing processes affects safety, durability, and application suitability, with toughened glass providing superior performance in structural and high-stress environments.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Bent toughened glass offers significantly higher strength and durability compared to bent annealed glass due to its tempering process, which increases resistance to impact and thermal stress. Bent annealed glass, while more flexible during bending and less prone to immediate shattering, lacks the enhanced structural integrity of toughened glass, making it more susceptible to breakage under heavy loads or sudden impacts. For applications requiring superior safety and longevity, bent toughened glass is the preferred choice to ensure your installation withstands demanding conditions.
Safety Features and Breakage Behavior
Bent annealed glass offers basic safety with a smooth, slow fracture pattern, reducing immediate injury risks upon breakage but shattering into large, sharp pieces. Bent toughened glass enhances safety by undergoing controlled thermal tempering, causing breakage into small, blunt granules that minimize harm to users. Choosing bent toughened glass increases Your protection in applications where impact resistance and safer breakage behavior are critical.
Applications in Architecture and Design
Bent annealed glass is widely used in architectural applications requiring gentle curves and lower stress tolerance, such as decorative facades, skylights, and interior partitions where flexibility in shaping is essential but impact resistance is moderate. Bent toughened glass, known for its high strength and thermal resistance, is ideal for safety-critical installations like balustrades, curved safety windows, and structural glass elements exposed to wind loads or human impact. In contemporary design, bent toughened glass enables innovative curved forms that meet stringent building codes, while bent annealed glass offers cost-effective solutions for non-load-bearing curved features.
Cost Considerations: Bent Annealed vs Toughened
Bent annealed glass generally costs less than bent toughened glass due to simpler manufacturing processes and lower energy requirements. Toughened glass undergoes an additional tempering step that increases its strength and safety features but significantly raises production costs. For applications prioritizing budget and moderate durability, bent annealed glass offers a cost-effective solution, whereas bent toughened glass justifies higher expenses through enhanced performance and compliance with stringent safety standards.
Aesthetic Differences and Design Flexibility
Bent annealed glass offers smoother, more subtle curves with a softer appearance, making it ideal for designs where elegance and a seamless look are prioritized. Bent toughened glass provides sharper bends and increased strength, allowing for more daring architectural shapes and enhanced safety in structural applications. Your choice depends on whether aesthetic subtlety or rigid design flexibility and durability are more critical for your project.
Choosing the Right Bent Glass for Your Project
Bent annealed glass offers flexibility and ease of shaping, making it ideal for decorative applications where thermal strength is less critical. Bent toughened glass provides enhanced safety and durability due to its heat treatment, suitable for structural projects requiring impact resistance. Your choice between these types depends on the project's safety requirements and the desired balance of form and function.
Bent annealed glass vs bent toughened glass Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com