Wired glass provides enhanced fire resistance and security by embedding a wire mesh within the glass, making it ideal for safety applications but prone to shattering upon impact. Polycarbonate glazing offers superior impact resistance and lightweight durability, perfect for environments requiring high strength and vandal resistance, although it may scratch more easily than glass.
Table of Comparison
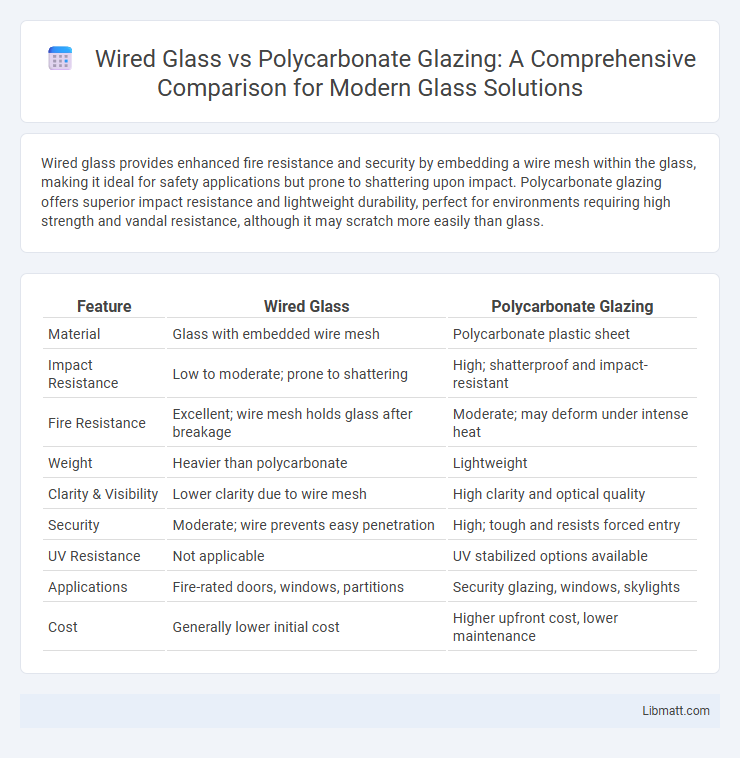
| Feature | Wired Glass | Polycarbonate Glazing |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Glass with embedded wire mesh | Polycarbonate plastic sheet |
| Impact Resistance | Low to moderate; prone to shattering | High; shatterproof and impact-resistant |
| Fire Resistance | Excellent; wire mesh holds glass after breakage | Moderate; may deform under intense heat |
| Weight | Heavier than polycarbonate | Lightweight |
| Clarity & Visibility | Lower clarity due to wire mesh | High clarity and optical quality |
| Security | Moderate; wire prevents easy penetration | High; tough and resists forced entry |
| UV Resistance | Not applicable | UV stabilized options available |
| Applications | Fire-rated doors, windows, partitions | Security glazing, windows, skylights |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher upfront cost, lower maintenance |
Introduction to Wired Glass and Polycarbonate Glazing
Wired glass features embedded metal mesh within the glass, providing enhanced fire resistance and preventing shattering during impact, commonly used in fire-rated doors and windows. Polycarbonate glazing is a lightweight, high-impact resistant thermoplastic material known for superior durability and UV protection, ideal for security barriers and skylights. Both materials offer distinct advantages based on the specific safety, security, and environmental requirements of architectural glazing applications.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Wired glass is composed of annealed glass embedded with a metal wire mesh, created through a high-temperature lamination process that fuses the wire grid within the glass for added fire resistance and safety reinforcement. Polycarbonate glazing consists of thermoplastic polymer sheets manufactured via extrusion or casting, offering exceptional impact resistance and lightweight properties through a process that involves heating and molding the polycarbonate resin. The differences in materials and production methods directly influence the performance characteristics, with wired glass excelling in fire protection and polycarbonate providing superior impact strength and flexibility.
Safety and Impact Resistance
Wired glass offers moderate safety by preventing glass shattering but is prone to breakage upon high-impact forces, potentially causing injury. Polycarbonate glazing provides superior impact resistance, with high tensile strength and shatterproof properties, making it ideal for environments requiring enhanced security and protection. Its ability to absorb impact energy without breaking significantly reduces the risk of injury compared to wired glass.
Fire Protection Capabilities
Wired glass offers excellent fire protection capabilities by maintaining structural integrity and preventing the spread of flames and smoke during a fire, making it compliant with many fire safety codes. Polycarbonate glazing, while highly impact-resistant and lightweight, generally provides less fire resistance and may not meet stringent fire protection standards for certain applications. Your choice should consider the specific fire safety requirements of the building to ensure optimal protection.
Optical Clarity and Aesthetics
Wired glass offers moderate optical clarity but features embedded wire mesh that can distort vision and reduce light transmission, affecting overall aesthetics. Polycarbonate glazing delivers superior optical clarity with high transparency and minimal distortion, maintaining visual quality over time. This makes polycarbonate the preferred choice for applications requiring clear sightlines and modern appearance.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation
Polycarbonate glazing offers superior thermal insulation compared to wired glass, with a typical U-value ranging from 2.7 to 3.0 W/m2K, reducing heat transfer and improving energy efficiency. Acoustic insulation is also enhanced in polycarbonate panels, providing noise reduction benefits up to 28-32 dB, while wired glass generally offers lower soundproofing performance around 20-25 dB. The multi-layer structure of polycarbonate contributes to its better performance in both thermal retention and sound attenuation.
Applications in Architectural Design
Wired glass is commonly used in architectural designs where fire resistance and safety are critical, such as in fire-rated doors, windows, and partitions within commercial buildings. Polycarbonate glazing offers exceptional impact resistance and is ideal for applications requiring high durability and security, including skylights, curtain walls, and protective barriers in both residential and commercial structures. Your choice depends on balancing fire safety standards and impact resistance needs to meet specific building code requirements.
Cost Comparison and Longevity
Wired glass generally offers a lower upfront cost compared to polycarbonate glazing, making it a budget-friendly option for basic safety and fire-resistant applications. However, polycarbonate glazing provides significantly greater longevity due to its superior impact resistance and UV protection, reducing replacement and maintenance expenses over time. Your choice should factor in long-term durability needs and budget constraints to optimize overall value.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Wired glass installation demands careful handling due to its brittleness and often requires professional glazing techniques to securely fit the glass within metal frames. Polycarbonate glazing is lightweight and more flexible, allowing for easier DIY installation with standard tools and minimal risk of breakage during setup. Your maintenance workload for wired glass includes regular inspection for cracks and chip repair, while polycarbonate requires cleaning to prevent scratching and UV protection treatments to maintain clarity and durability.
Environmental Sustainability and Recycling
Wired glass often contains embedded metal mesh that complicates recycling processes and limits its environmental sustainability due to the difficulty of separating materials. Polycarbonate glazing is highly recyclable and made from durable thermoplastic polymers that reduce environmental impact through longer lifespan and lower energy consumption in manufacturing. The choice of polycarbonate glazing supports greener building practices by enabling efficient recycling and minimizing waste compared to wired glass alternatives.
wired glass vs polycarbonate glazing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com