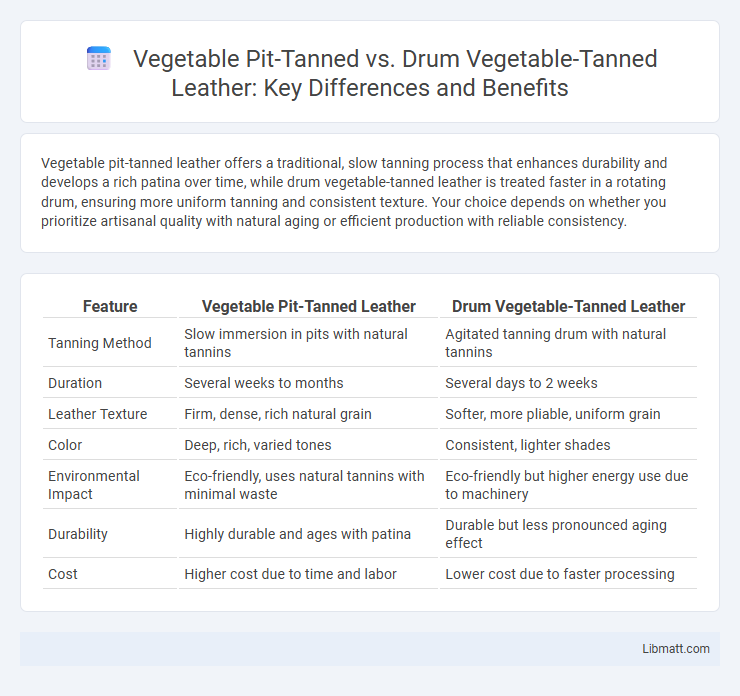
Vegetable pit-tanned leather offers a traditional, slow tanning process that enhances durability and develops a rich patina over time, while drum vegetable-tanned leather is treated faster in a rotating drum, ensuring more uniform tanning and consistent texture. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize artisanal quality with natural aging or efficient production with reliable consistency.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vegetable Pit-Tanned Leather | Drum Vegetable-Tanned Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Tanning Method | Slow immersion in pits with natural tannins | Agitated tanning drum with natural tannins |
| Duration | Several weeks to months | Several days to 2 weeks |
| Leather Texture | Firm, dense, rich natural grain | Softer, more pliable, uniform grain |
| Color | Deep, rich, varied tones | Consistent, lighter shades |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, uses natural tannins with minimal waste | Eco-friendly but higher energy use due to machinery |
| Durability | Highly durable and ages with patina | Durable but less pronounced aging effect |
| Cost | Higher cost due to time and labor | Lower cost due to faster processing |
Introduction to Vegetable Tanning Methods
Vegetable pit-tanned leather involves soaking hides in large pits filled with natural tannins from tree bark and plant extracts, resulting in a slow, traditional tanning process that enhances durability and distinct character. Drum vegetable-tanned leather uses rotating drums that accelerate tannin penetration, offering more consistent tanning outcomes and reduced processing time. Both methods harness natural tannins but differ in processing techniques, impacting texture, flexibility, and environmental footprint.
What is Pit Vegetable Tanning?
Pit vegetable tanning is a traditional method where hides are submerged in large earthen pits filled with natural tannins extracted from tree bark, leaves, and fruits, allowing a slow and thorough tanning process that enhances the leather's durability and develops a rich patina over time. Unlike drum vegetable tanning, which uses rotating drums for faster tannin penetration, pit tanning can take several months, producing leather with a firmer texture and distinctive character. You can expect pit-tanned leather to have a deeper, more natural scent and superior aging qualities compared to drum-tanned leather.
What is Drum Vegetable Tanning?
Drum vegetable tanning is a process where hides are treated in large rotating drums filled with natural tannins derived from tree bark and plant extracts, resulting in a more consistent and flexible leather compared to traditional pit vegetable tanning. The tumbling action allows tannins to penetrate the hide evenly, producing durable leather with enhanced softness and a uniform texture. Your choice of drum vegetable-tanned leather ensures a high-quality, eco-friendly material prized for its strength and natural finish.
Key Differences: Pit-tanned vs Drum Vegetable-tanned
Pit-tanned leather undergoes a slow, traditional tanning process in sunken pits where hides are immersed for months, resulting in a more natural, supple texture with rich character and unique color variations. Drum vegetable-tanned leather is treated in large rotating drums, allowing for a more controlled, uniform tanning process that produces consistent thickness and a smoother finish ideal for precise craftsmanship. Your choice between pit-tanned and drum vegetable-tanned leather depends on whether you prioritize artisanal uniqueness and aging character or reliable uniformity and production efficiency.
Leather Quality and Durability Comparison
Vegetable pit-tanned leather undergoes a slow, traditional tanning process that enhances its natural texture and develops a rich patina over time, resulting in superior leather quality with unique character. Drum vegetable-tanned leather is tanned faster in rotating drums, producing more uniform and consistent hides but slightly less depth in texture and patina development. Both methods yield durable leather, yet pit-tanned leather tends to be more robust and ages gracefully, while drum vegetable-tanned leather offers reliable strength with a smoother finish ideal for mass production.
Environmental Impact of Each Tanning Method
Vegetable pit-tanned leather uses traditional natural tannins in earthen pits, allowing slow absorption that reduces chemical runoff and lowers water pollution, making it more environmentally friendly but resource intensive. Drum vegetable-tanned leather accelerates the process in rotating drums, increasing tannin penetration but consuming more energy and generating higher wastewater loads requiring treatment. Your choice affects ecological footprint: pit tanning offers a sustainable, low-impact option, while drum tanning provides efficiency with greater environmental management needs.
Aesthetic and Texture Variations
Vegetable pit-tanned leather exhibits a richer, more unique patina with subtle irregularities due to the slow tanning process in pits, enhancing its aesthetic appeal and depth of character. Drum vegetable-tanned leather typically presents a more uniform texture and consistent coloration, resulting from the mechanical tumbling in drums that smooths and softens the hide. These differences in tanning methods significantly impact the tactile experience, where pit-tanned leather feels firmer and more rugged, while drum-tanned leather tends to be more supple and pliable.
Common Applications and Uses
Vegetable pit-tanned leather is commonly used for crafting durable goods like belts, saddles, and high-quality shoes due to its slow tanning process, which results in thicker, firmer leather with a rich patina. Drum vegetable-tanned leather, processed faster in rotating drums, is favored for lighter, more flexible products such as wallets, handbags, and garments that require a softer feel and uniform texture. Understanding these differences helps you select the right type of vegetable-tanned leather for your projects based on durability and flexibility needs.
Cost and Production Time Considerations
Vegetable pit-tanned leather typically involves a longer production time and higher labor costs due to its traditional, manual tanning process in earthen pits, resulting in a more artisanal finish. Drum vegetable-tanned leather, produced using mechanized drums, reduces production time significantly and generally lowers costs, making it more affordable for mass manufacturing. Your choice between the two may depend on whether you prioritize cost efficiency or the unique qualities achieved by slower, pit tanning methods.
Choosing the Right Vegetable-Tanned Leather
Choosing the right vegetable-tanned leather depends on your desired texture and durability, with pit-tanned leather offering a denser, more flexible feel due to its slow, natural tanning process. Drum vegetable-tanned leather tends to be softer and more uniform, as the faster, mechanical method allows for consistent dye absorption and a smoother finish. Understanding these differences helps you select leather that best suits your project's quality and aesthetic requirements.
Vegetable pit-tanned vs drum vegetable-tanned Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com