Cold seal packaging uses pressure-sensitive adhesives to bond materials without heat, making it ideal for heat-sensitive products and energy-efficient processes. Heat seal packaging relies on heat and pressure to create a strong, durable seal, providing superior barrier protection and extending the shelf life of your products.
Table of Comparison
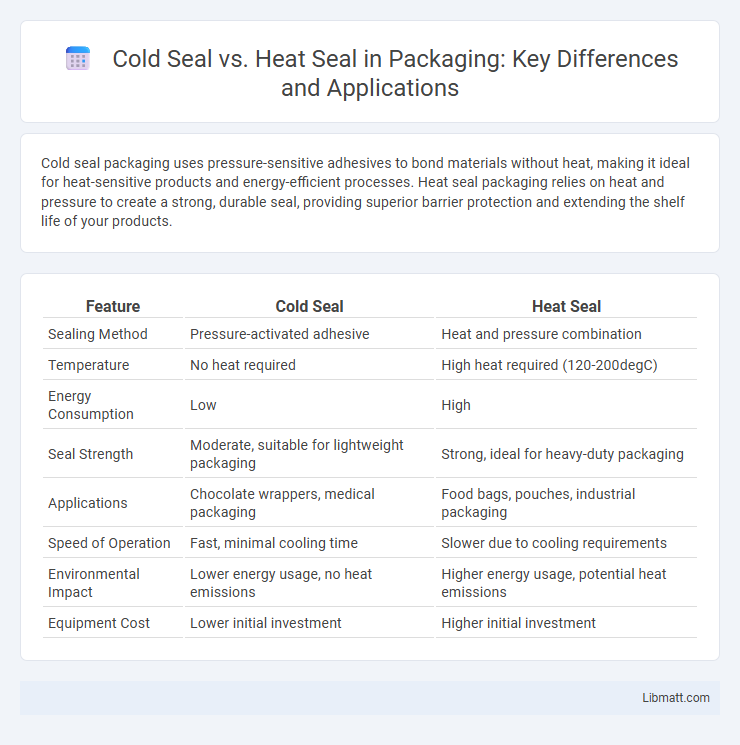
| Feature | Cold Seal | Heat Seal |
|---|---|---|
| Sealing Method | Pressure-activated adhesive | Heat and pressure combination |
| Temperature | No heat required | High heat required (120-200degC) |
| Energy Consumption | Low | High |
| Seal Strength | Moderate, suitable for lightweight packaging | Strong, ideal for heavy-duty packaging |
| Applications | Chocolate wrappers, medical packaging | Food bags, pouches, industrial packaging |
| Speed of Operation | Fast, minimal cooling time | Slower due to cooling requirements |
| Environmental Impact | Lower energy usage, no heat emissions | Higher energy usage, potential heat emissions |
| Equipment Cost | Lower initial investment | Higher initial investment |
Introduction to Cold Seal and Heat Seal Technologies
Cold seal technology uses pressure-sensitive adhesives activated by pressure without heat, making it ideal for temperature-sensitive products and fast packaging lines. Heat seal technology utilizes heat and pressure to bond materials, providing a strong, durable seal suitable for food, medical, and industrial applications. Understanding your packaging needs can help determine whether cold seal or heat seal offers the optimal combination of efficiency and product protection.
How Cold Seal Works: Principles and Applications
Cold seal technology uses pressure-sensitive adhesives that bond at room temperature without requiring heat, relying on the mechanical force to create a secure seal. This method is ideal for heat-sensitive products like chocolates and pharmaceuticals, preserving product integrity by avoiding thermal damage. Cold seal's rapid setting time and energy efficiency make it a preferred choice for flexible packaging applications in the food and medical industries.
The Heat Seal Process Explained
The heat seal process involves applying heat and pressure to fuse two thermoplastic materials, creating a durable and airtight bond used extensively in packaging industries. Precise temperature control, adequate dwell time, and uniform pressure are critical factors to ensure consistent weld strength and seal integrity. Unlike cold sealing, which relies on adhesives or cold-activated binders, heat sealing enhances product shelf life by providing superior barrier properties against moisture, oxygen, and contaminants.
Key Differences Between Cold Seal and Heat Seal
Cold seal uses pressure-sensitive adhesive activated by pressure at room temperature, while heat seal relies on heat and pressure to bond materials. Heat seal creates stronger, more durable seals ideal for plastic and foil packaging, whereas cold seal is ideal for heat-sensitive products like chocolate and delicate items. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the best sealing method for your packaging needs.
Material Compatibility: Cold Seal vs Heat Seal
Cold seal adhesives are specifically compatible with heat-sensitive materials such as polyethylene and polypropylene films, ensuring no damage during sealing processes. Heat seal technology requires materials like foil laminates and thermoplastics that can withstand elevated temperatures for effective bonding. Material choice influences seal integrity, with cold seal preferred for delicate packaging and heat seal favored for durable, high-barrier applications.
Advantages of Cold Seal Packaging
Cold seal packaging offers significant advantages including faster sealing times and reduced energy consumption since it does not require heat. It prevents product damage by avoiding exposure to high temperatures, making it ideal for heat-sensitive items like chocolates and pharmaceuticals. The process also enhances safety by eliminating the risk of burns and reduces the carbon footprint due to lower energy use compared to heat seal packaging.
Benefits of Heat Seal Packaging
Heat seal packaging offers superior airtight and moisture-resistant seals, enhancing product freshness and extending shelf life. The strong bonds created by heat sealing improve tamper evidence and packaging durability, crucial for food safety and pharmaceutical products. This method supports compatibility with various materials including plastics and laminates, providing versatility for different packaging needs.
Industry Use Cases: Cold Seal vs Heat Seal
Cold seal packaging is widely used in industries like food, confectionery, and pharmaceuticals where heat-sensitive products require secure, tamper-evident seals without exposure to high temperatures. Heat seal technology dominates in sectors such as medical devices, automotive components, and high-barrier packaging, providing strong, durable seals through thermal bonding in materials like polyethylene and polypropylene. Your choice between cold seal and heat seal depends on product sensitivity, packaging speed, and required seal strength within your industry application.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Sealing Methods
Choosing between cold seal and heat seal methods depends on factors such as material compatibility, production speed, and package integrity requirements. Cold seal is ideal for heat-sensitive materials and faster production lines, while heat seal provides stronger, tamper-evident seals suitable for a wider range of substrates. Cost-effectiveness, environmental impact, and equipment availability also influence the optimal sealing method selection.
Future Trends in Packaging Seal Technologies
Future trends in packaging seal technologies emphasize advancements in cold seal methods, driven by their energy efficiency and suitability for heat-sensitive products. Innovations in cold seal adhesives are enhancing seal strength and durability, providing sustainable alternatives to traditional heat seal processes. You can expect a shift toward hybrid sealing systems that combine the benefits of cold and heat seals to optimize performance and environmental impact.
Cold seal vs heat seal Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com