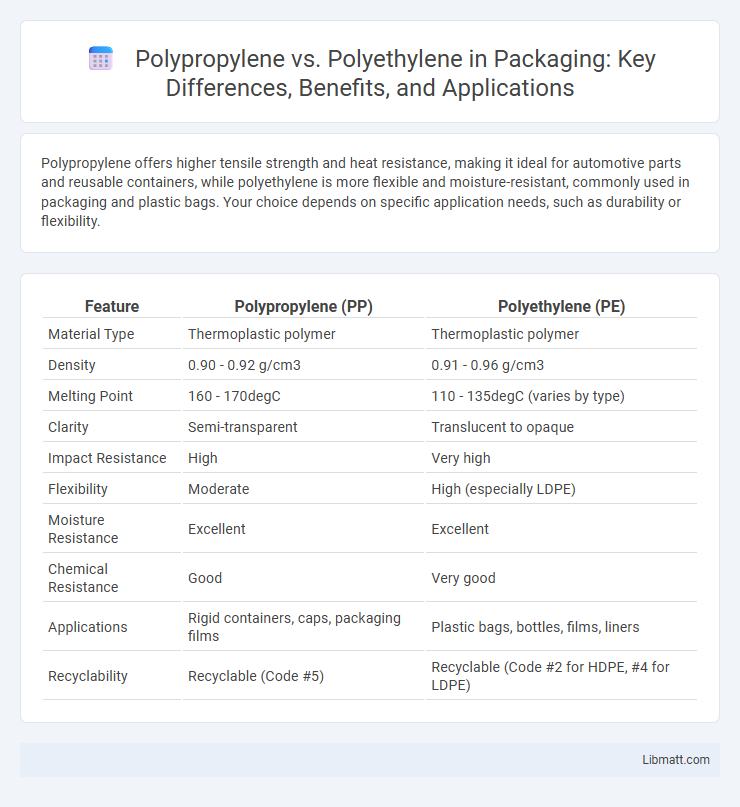
Polypropylene offers higher tensile strength and heat resistance, making it ideal for automotive parts and reusable containers, while polyethylene is more flexible and moisture-resistant, commonly used in packaging and plastic bags. Your choice depends on specific application needs, such as durability or flexibility.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polypropylene (PP) | Polyethylene (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Density | 0.90 - 0.92 g/cm3 | 0.91 - 0.96 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 160 - 170degC | 110 - 135degC (varies by type) |
| Clarity | Semi-transparent | Translucent to opaque |
| Impact Resistance | High | Very high |
| Flexibility | Moderate | High (especially LDPE) |
| Moisture Resistance | Excellent | Excellent |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Very good |
| Applications | Rigid containers, caps, packaging films | Plastic bags, bottles, films, liners |
| Recyclability | Recyclable (Code #5) | Recyclable (Code #2 for HDPE, #4 for LDPE) |
Introduction to Polypropylene and Polyethylene
Polypropylene and polyethylene are two of the most widely used thermoplastics in the world, each with unique chemical structures and properties. Polypropylene is characterized by its rigidity, higher melting point, and resistance to chemicals, making it ideal for automotive parts, packaging, and textiles. Polyethylene, available in various densities like LDPE and HDPE, offers excellent flexibility, impact resistance, and moisture barrier properties, perfect for applications such as plastic bags, containers, and piping.
Chemical Structure Differences
Polypropylene features a methyl group (CH3) attached to every other carbon atom in its polymer chain, giving it a more asymmetric structure compared to polyethylene, which consists of a simple repeating ethylene unit (CH2-CH2) without side groups. This difference in chemical structure results in polypropylene having higher crystallinity and greater thermal resistance than polyethylene. The presence of the methyl group in polypropylene also affects its density and mechanical properties, making it stiffer but less flexible than polyethylene.
Physical Properties Comparison
Polypropylene (PP) and polyethylene (PE) differ significantly in physical properties, with PP offering higher tensile strength and a greater melting point around 160degC, compared to PE's lower melting range of 115-135degC, depending on the type. PP is more rigid and resistant to stress cracking, whereas PE exhibits superior flexibility and impact resistance, especially in low-density varieties. Your choice between these polymers should consider the required durability, temperature tolerance, and flexibility for the intended application.
Common Applications of Polypropylene
Polypropylene is widely used in packaging, automotive components, textiles, and consumer goods due to its high chemical resistance and versatility. Its ability to withstand high temperatures makes it ideal for microwave-safe containers and reusable food packaging. Unlike polyethylene, polypropylene's rigidity and fatigue resistance enable applications such as living hinges and durable plastic parts.
Common Uses of Polyethylene
Polyethylene is widely used in packaging materials such as plastic bags, film wraps, and containers due to its excellent moisture resistance and flexibility. It also serves as a key material in the production of household goods, toys, and pipes because of its durability and chemical resistance. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) is frequently chosen for heavy-duty applications like milk jugs and industrial containers, while low-density polyethylene (LDPE) is preferred for applications requiring softer and more pliable plastic.
Durability and Strength
Polypropylene offers higher tensile strength and greater resistance to fatigue, making it ideal for applications requiring durability under repeated stress. Polyethylene provides excellent impact resistance and flexibility, especially in low-density forms, but generally has lower tensile strength compared to polypropylene. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize toughness and repeated use or flexibility and impact absorption in the material.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polypropylene (PP) and polyethylene (PE) differ significantly in environmental impact and recyclability, with both being widely recyclable but often processed through separate recycling streams due to their distinct polymer structures. Polyethylene, especially high-density polyethylene (HDPE), is more commonly recycled and has a well-established infrastructure, contributing to a lower environmental footprint compared to polypropylene, which requires more energy-intensive recycling processes. Both materials are derived from non-renewable fossil fuels, but advances in chemical recycling and biopolymer alternatives aim to reduce environmental impact and enhance the sustainability of polypropylene and polyethylene products.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Polypropylene (PP) typically offers greater cost efficiency than polyethylene (PE) due to its lower raw material and production costs, making it a preferred choice for high-volume manufacturing. Availability of polyethylene is higher globally, with vast supply chains supporting its widespread use in packaging, containers, and household goods. Your decision between polypropylene and polyethylene should consider the balance between PP's cost advantages and PE's broader availability to optimize budget and supply reliability.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Polypropylene and Polyethylene
When choosing between polypropylene and polyethylene, consider factors such as chemical resistance, temperature tolerance, and mechanical strength. Polypropylene offers higher heat resistance and rigidity, making it suitable for applications requiring durability and thermal stability. Polyethylene provides superior impact resistance and flexibility, ideal for low-temperature environments and flexible packaging solutions.
Conclusion: Which Material is Better for Your Needs?
Polyethylene excels in flexibility, chemical resistance, and low cost, making it ideal for packaging, containers, and plastic bags. Polypropylene offers higher temperature resistance, stiffness, and durability, better suited for automotive parts, reusable containers, and medical applications. Choosing between polypropylene and polyethylene depends on specific requirements like temperature tolerance, mechanical strength, and cost efficiency.
Polypropylene vs polyethylene Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com