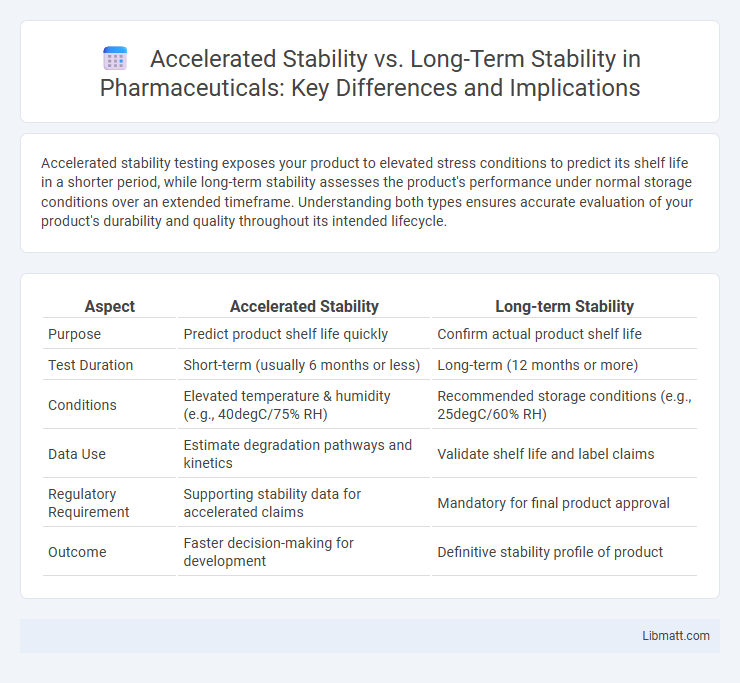
Accelerated stability testing exposes your product to elevated stress conditions to predict its shelf life in a shorter period, while long-term stability assesses the product's performance under normal storage conditions over an extended timeframe. Understanding both types ensures accurate evaluation of your product's durability and quality throughout its intended lifecycle.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Accelerated Stability | Long-term Stability |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Predict product shelf life quickly | Confirm actual product shelf life |
| Test Duration | Short-term (usually 6 months or less) | Long-term (12 months or more) |
| Conditions | Elevated temperature & humidity (e.g., 40degC/75% RH) | Recommended storage conditions (e.g., 25degC/60% RH) |
| Data Use | Estimate degradation pathways and kinetics | Validate shelf life and label claims |
| Regulatory Requirement | Supporting stability data for accelerated claims | Mandatory for final product approval |
| Outcome | Faster decision-making for development | Definitive stability profile of product |
Introduction to Stability Testing
Stability testing evaluates the shelf life and quality of pharmaceutical products under various environmental conditions, distinguishing between accelerated stability and long-term stability studies. Accelerated stability testing exposes products to elevated stress conditions such as higher temperature and humidity over a shorter period to predict long-term effects efficiently. Long-term stability testing monitors product integrity under recommended storage conditions for extended durations, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and confirming product safety and efficacy throughout its intended shelf life.
Definition of Accelerated Stability
Accelerated stability testing simulates long-term conditions by exposing products to elevated temperatures, humidity, or light to quickly assess their shelf life and potential degradation. This method helps predict how a product might perform over extended periods without waiting for real-time aging. Your understanding of accelerated stability is crucial for efficient product development and regulatory compliance.
Definition of Long-term Stability
Long-term stability refers to the ability of a pharmaceutical product to maintain its intended physical, chemical, microbiological, therapeutic, and toxicological properties throughout its shelf life under recommended storage conditions. This type of stability testing is conducted over an extended period, typically months to years, to ensure consistent product quality and efficacy. Regulatory guidelines, such as ICH Q1A(R2), provide frameworks for conducting long-term stability studies to guarantee drug safety and performance up to the expiration date.
Key Objectives of Stability Studies
Stability studies aim to assess the shelf life and quality of pharmaceutical products by evaluating their physical, chemical, and microbiological attributes under specific conditions. Accelerated stability testing simulates long-term storage by exposing products to elevated temperature and humidity, helping predict potential degradation and establish expiration dates more quickly. Your ability to ensure product safety and efficacy over time depends on integrating both accelerated and long-term stability data for comprehensive regulatory compliance.
Testing Conditions: Accelerated vs Long-term
Accelerated stability testing involves exposing products to elevated stress conditions such as higher temperatures, humidity, and light to quickly evaluate potential degradation within a short time frame. Long-term stability testing maintains products under recommended storage conditions, typically 25degC and 60% relative humidity, over an extended period to monitor genuine shelf life and performance. Your choice between these protocols impacts the reliability of stability data used for regulatory approval and shelf-life determination.
Regulatory Guidelines and Compliance
Regulatory guidelines from agencies like the FDA and ICH emphasize conducting both accelerated stability and long-term stability studies to ensure pharmaceutical product quality and shelf life. Accelerated stability testing uses increased stress conditions to predict product degradation quickly, complementing long-term stability data collected under recommended storage conditions over months or years. Compliance with these guidelines requires integrating results from both study types to establish robust expiration dating and storage instructions essential for regulatory approval.
Data Interpretation and Shelf-life Prediction
Accelerated stability testing provides rapid data on product degradation by exposing samples to elevated stress conditions, enabling early identification of potential stability issues and formulation weaknesses. Long-term stability testing offers comprehensive data under recommended storage conditions, yielding accurate shelf-life predictions based on real-time chemical, physical, and microbiological changes. Combining accelerated stability data with robust mathematical models enhances shelf-life estimation accuracy, supporting regulatory submissions and ensuring product efficacy throughout its intended market life.
Advantages of Accelerated Stability Testing
Accelerated stability testing offers significant time and cost savings by predicting product shelf life within a shortened timeframe through exposure to elevated stress conditions such as heat, humidity, and light. This method enables faster decision-making during formulation development and packaging selection, allowing for quicker market release and improved risk management. By simulating long-term degradation patterns rapidly, accelerated stability testing enhances the overall efficiency of stability assessment without compromising data reliability.
Limitations of Accelerated vs Long-term Data
Accelerated stability testing often fails to replicate the exact storage conditions, leading to potential inaccuracies in predicting product shelf life compared to long-term stability data. Chemical degradation pathways may differ under elevated stress conditions, causing discrepancies in stability profiles. Reliance solely on accelerated data can underestimate or overestimate product stability, emphasizing the need for corroborating long-term stability studies to ensure accurate shelf-life determination.
Choosing the Right Stability Testing Approach
Choosing the right stability testing approach depends on the product's shelf life and regulatory requirements, with accelerated stability tests providing rapid data by simulating long-term storage conditions in a shorter period. Long-term stability studies offer comprehensive information on product behavior under normal storage conditions, ensuring accurate shelf-life determination. Selecting between these methods involves balancing speed, cost, and the necessity for detailed degradation profiles to maintain product quality and compliance.
Accelerated stability vs Long-term stability Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com